Now Reading: Arctic Heatwave Melts 1% of Svalbard’s Ice
1
-
01
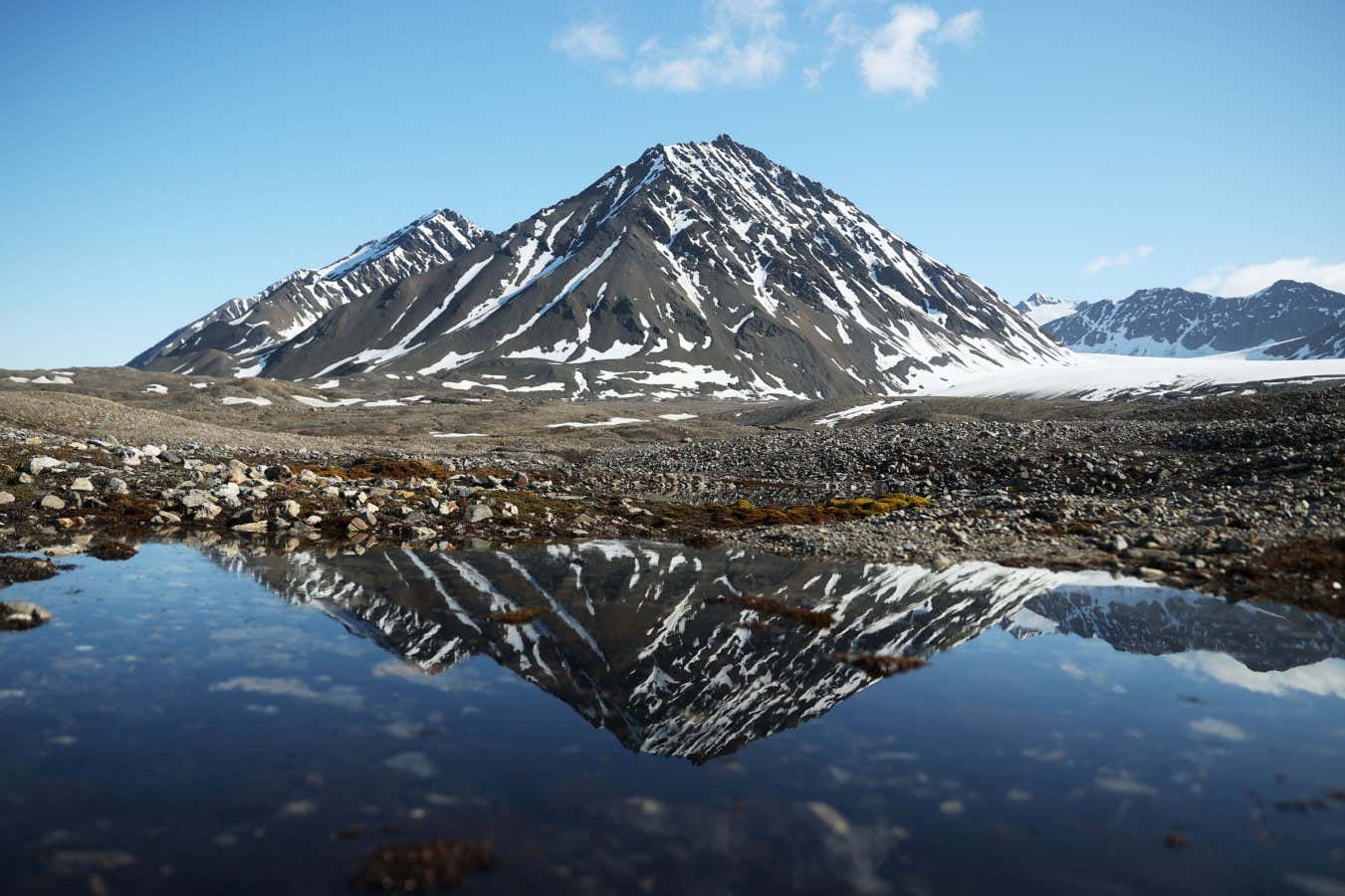
Arctic Heatwave Melts 1% of Svalbard’s Ice
Arctic Heatwave Melts 1% of Svalbard’s Ice

Quick Summary
- The summer of 2024 witnessed an extraordinary six-week heatwave on the arctic archipelago of Svalbard, resulting in unprecedented ice loss.
- Approximately 1% (62 gigatonnes) of land ice was melted, raising global sea levels by 0.16 millimeters.
- This melt rate was nearly double the previous record and attributed to extreme air temperatures (mean August temperature of 11°C, up from an average of 7°C).
- The main drivers were warmer sea temperatures, persistent southerly winds, and intensified global warming effects.
- Ice loss as 1991 averaged below 10 gigatonnes per summer; though,recent years have seen escalating rates-the last five summers setting new records.
- Land adjacent to melting sites rose by a record-breaking 16 mm due to reduced weigh on the surface.
- Scientists predict such extreme heat events will become more common this century with continued climate change.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...