Now Reading: Are ‘De-Extinct’ Pups Really Dire Wolves? A Comparison to the Real Thing
-
01
Are ‘De-Extinct’ Pups Really Dire Wolves? A Comparison to the Real Thing
Are ‘De-Extinct’ Pups Really Dire Wolves? A Comparison to the Real Thing

Quick Summary
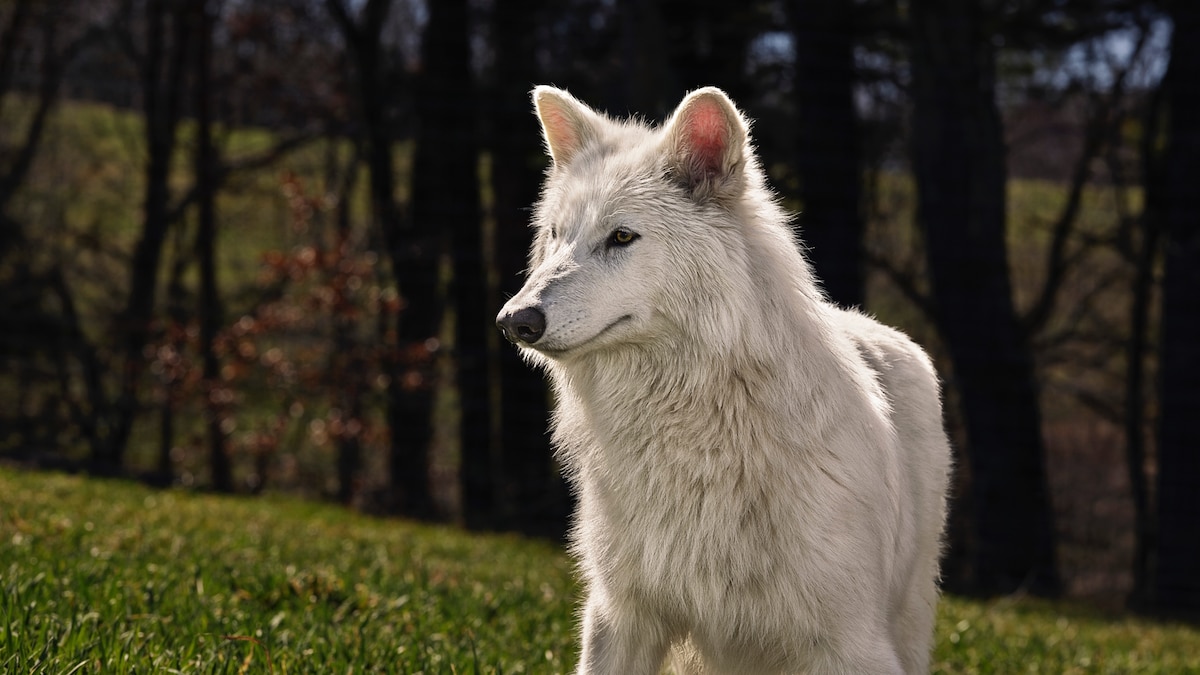
- Dire Wolves History: Dire wolves,ancient megafauna hunters,roamed North adn South America 200,000-13,000 years ago before going extinct.
- Revived via Genetics: Colossal Biosciences has genetically modified gray wolves into “dire wolf-like” creatures named Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi using DNA from fossils. They made 20 genome edits in embryos but acknowledged they are not true dire wolves.
- Evolutionary Insights: A study from 2021 revealed dire wolves were closer relatives to African jackals than gray wolves. Their lineage emerged over five million years ago, evolving independently in North America.
- Behavior and Habitat: Known for strong jaw forces adapted to prey on large herbivores like horses and mammoths; lived socially in packs across diverse environments like open steppes and flatlands. Extinction coincides with humans’ spread and warming climates.
- Challenges of Cloning Ancient Species: Paleontologists highlight behavioral gaps as modern clones can’t replicate natural social learning due to the lack of original dire wolf pack dynamics.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Colossal Biosciences’ efforts demonstrate the growing ambition in genetic engineering but also underscore its complex ethical and scientific dilemmas. Reviving creatures like dire wolves raises debates about science’s role in understanding past ecosystems versus disrupting present ones without fully replicating extinct species’ behaviors or ecological functions. This “de-extinction” movement could inform conservation practices globally if managed responsibly but risks oversimplifying natural evolution’s subtleties.
From an Indian perspective, such advancements offer a chance to explore how similar initiatives-like data-driven genetics research-can contribute toward wildlife preservation amidst climate threats affecting native species such as tigers or Asiatic lions. India’s rich biodiversity faces mounting danger; carefully studied applications of genomic research may bolster environmental resilience while steering wide of frivolous re-creations that could destabilize ecosystems.