Now Reading: Atlantic Current Slowdown Threatens Rising Seas on US East Coast
1
-
01
Atlantic Current Slowdown Threatens Rising Seas on US East Coast
Atlantic Current Slowdown Threatens Rising Seas on US East Coast
Quick Summary
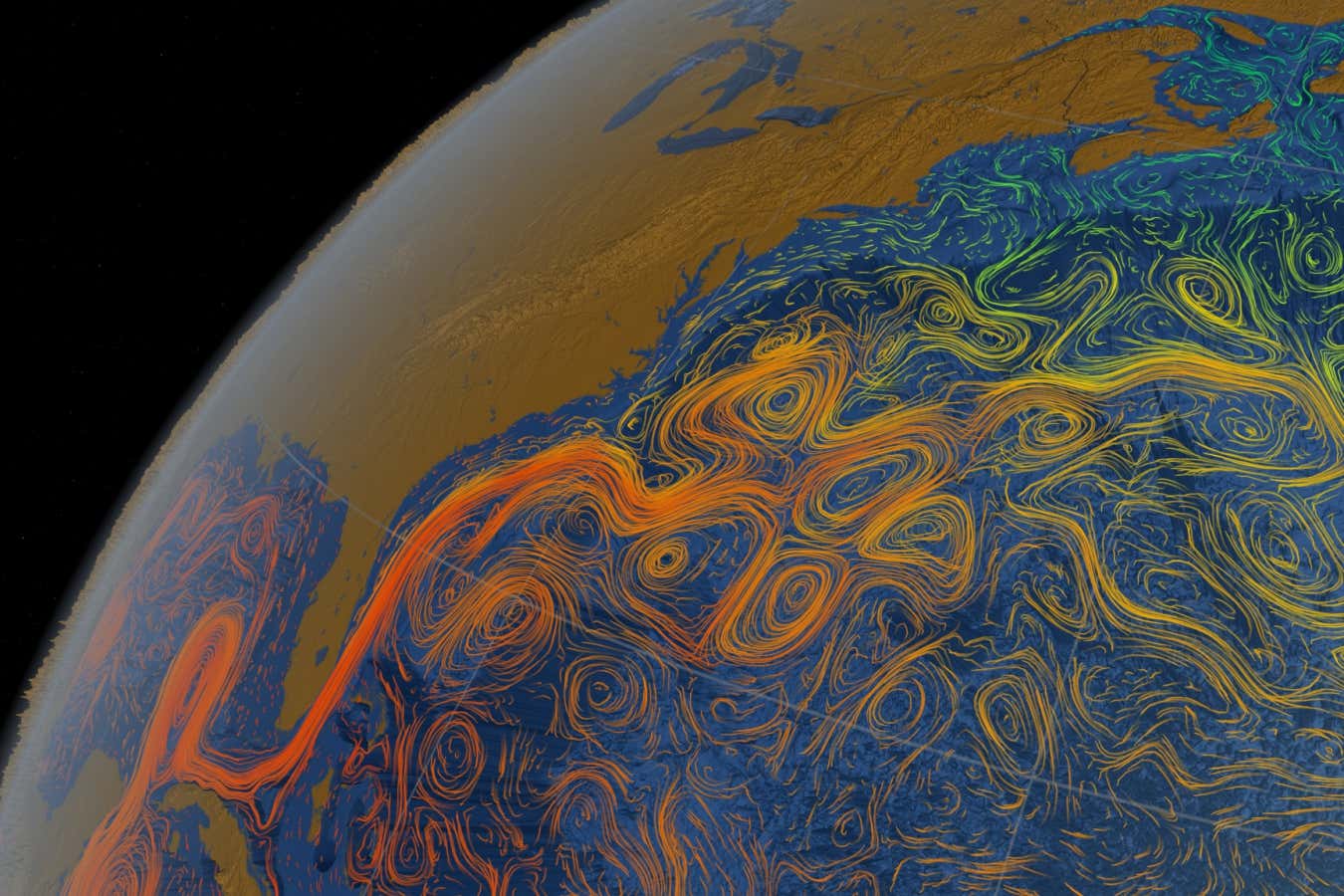
- The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a system of ocean currents in the Atlantic Ocean, is slowing down, contributing to rising sea levels and flooding on the US northeast coast.
- Melting ice sheets and water warming due to climate change are primary factors driving global sea-level rise, with unequal regional impacts.
- AMOC slowdowns can substantially increase local sea levels by warming and expanding deep water currents, especially along shallow continental shelves.
- Research shows that since 2005, AMOC weakening accounted for 20-50% of coastal flooding in various areas along the New England coast.
- Predictable fluctuations in AMOC strength could allow researchers to forecast higher flood-risk years up to three years in advance for planning purposes.
- A near-total collapse of the AMOC might raise regional sea levels by approximately 24 centimeters; while modest numerically,it could have dramatic impacts on flooding frequency.
Image Included:
!AMOC Current Visualization
Caption: “The AMOC is a system of ocean currents that circulates water within the Atlantic Ocean” – NASA/Goddard space flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...

























