Now Reading: Babesiosis: The Parasitic Infection That Attacks Red Blood Cells
-
01
Babesiosis: The Parasitic Infection That Attacks Red Blood Cells
Babesiosis: The Parasitic Infection That Attacks Red Blood Cells

Quick Summary:
- disease Name: Babesiosis, a rare and potentially fatal parasitic disease that destroys red blood cells.
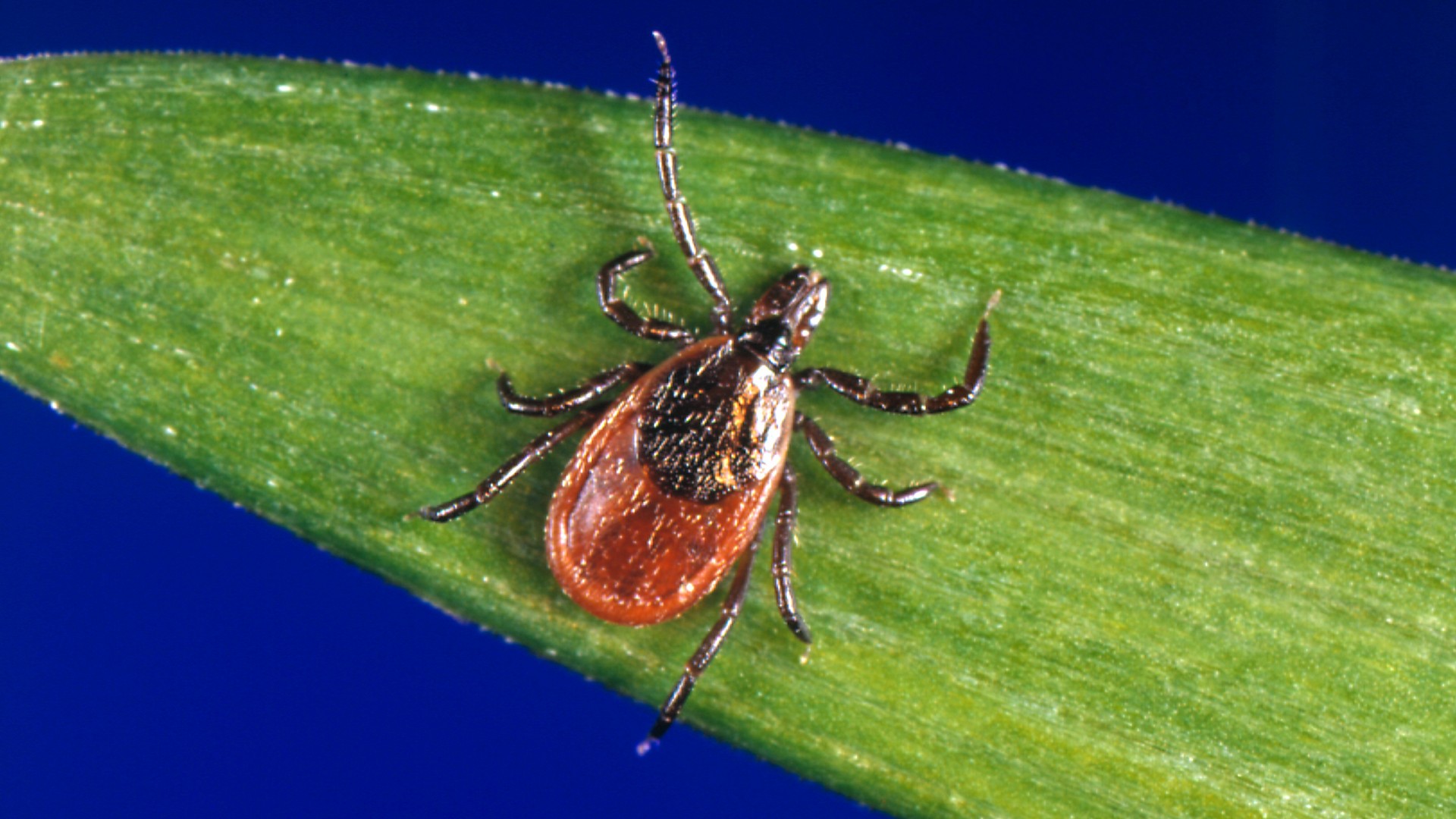
- Cause: Microscopic parasites of the Babesia genus, primarily spread by ticks (especially blacklegged ticks or deer ticks). Human infections are chiefly caused by Babesia microti in the U.S.
- Spread: Occurs worldwide. In the U.S., fewer than 3,000 cases occur annually, mainly between May and September in Midwest and Northeast regions.
- Symptoms: Common signs include fever, chills, muscle aches, swelling of liver/spleen, and low red blood cell count. Severe cases may lead to multiorgan failure or death.
- Risk Factors: Higher risk for individuals over 50 years old or with weakened immune systems; those without a spleen are particularly vulnerable.
- Fatality Rates: Estimated at 0.57% overall but closer to 20% among high-risk groups despite treatment.
- Treatment: Antiparasitic drugs combined with specific antibiotics; severe cases might require blood transfusions. Asymptomatic patients ofen recover without intervention.
- prevention Measures: Avoid tick-prone areas like wooded/grassy zones; take precautions against tick bites.
!Blood cells infected with parasites under a microscope
Image Credit: Smith Collection/Gado / Contributor via Getty Images
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India currently faces minimal exposure to babesiosis as its main vector-blacklegged ticks-is not native to India’s ecosystem. However, increased global travel for business and leisure could bring awareness regarding tick-borne diseases as potential risks in wooded or rural tourist destinations.Agricultural regions housing cattle may warrant vigilance due to certain parasites capable of interspecies transmission via ticks.
India can leverage this knowledge for proactive public health messaging about protection from tick bites while fostering collaboration on research into parasitic infections affecting human populations globally. Vigilance against zoonotic diseases is critical given their potential impact on public health infrastructure when undetected early in climates conducive for vector survival (e.g., humid agricultural belts).
In aligning with lasting practices that mitigate exposure risks rather than focusing solely on post-outbreak containment strategies (like advanced diagnostics), India can enhance preparedness against vector-borne illnesses while avoiding unnecessary resource strain during outbreaks similar worldwide elsewhere