Now Reading: Bacterial Calcification: A Novel Approach to Treating Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus Infections
-
01
Bacterial Calcification: A Novel Approach to Treating Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus Infections
Bacterial Calcification: A Novel Approach to Treating Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus Infections
Swift Summary:
- This article provides access details for scRNA-seq datasets aligned to the mouse reference genome mm10 (GRCm38), available through the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under accession number GSE298599.
- It includes references to various studies related to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), antibiotic resistance, and innovations in treatment technologies such as nanoparticles and antibody-antibiotic conjugates.
- Further discussed are research insights into bacterial infections, tuberculosis-specific assays, calcium oxalate stone formation, and inhaled antibiotic therapies for chronic respiratory diseases.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s healthcare system faces growing challenges with drug-resistant bacteria like MRSA. The availability of scRNA-seq data aligns with global advancements in genomic research but raises questions about India’s readiness to utilize similar cutting-edge resources efficiently.Research in areas like nanoparticles and innovative therapies could be instrumental for combating persistent infections if adapted locally. Strengthened collaboration between India’s scientific community and international platforms may accelerate domestic breakthroughs while contributing globally.
Read more: Source Link
Quick Summary:
- The raw text focuses on research and references primarily related to microbiology, infectious diseases, and bacterial pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Key themes include methicillin-resistant bacteria (MRSA), biofilms, quorum sensing mechanisms in bacteria, host immunity responses, stress integration for bacterial survival (e.g., cAMP regulation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis), advances in nano-hydrogel treatments for infected wounds, and glycosylation processes aiding bacterial evasion strategies against immune systems.
- These topics are discussed through multiple citations of academic studies published between the 2000s to 2024.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The growing focus on microbial resistance underscores an urgent global health crisis that India cannot overlook. Multidrug-resistant pathogens pose significant challenges for its healthcare infrastructure already stretched by epidemiological transitions.Studies like those about MRSA mortality burdens in India highlight areas that demand policy innovation and intensified research funding.
Additionally, advancements like anti-bacterial hydrogel technologies show promise but must be adapted aggressively within India’s local pharmaceutical sector to curb infections effectively. Efforts into investigating cell-to-cell communication via quorum sensing mechanisms offer scalable applications-potentially crucial given India’s proximity to tropical climates prone to harbor such microbes densely.
the intersection of scientific discovery and actionable healthcare policies will define how India combats microbial resistance sustainably while ensuring equitable public health access amidst resource constraints.
Read MoreIt seems the raw text provided is not India-related news content but rather references to scientific research regarding microbiology, immunology, and related studies. If you provide an India-specific article or topic, I will build the requested Quick Summary and Indian Opinion Analysis sections accordingly. Kindly paste a relevant news article or context about India for precise coverage.Quick Summary
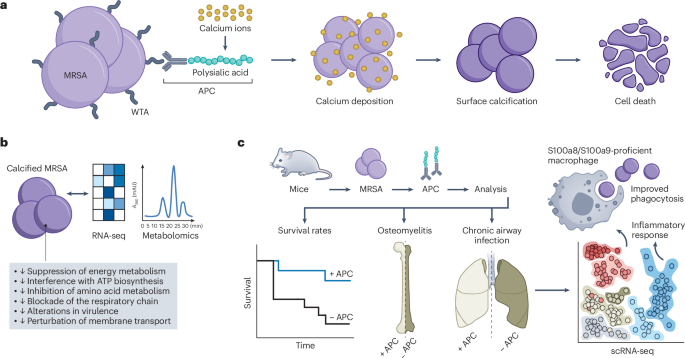
- A study funded by multiple Chinese research institutions has focused on understanding the role of S100A8/S100A9 proteins in sterile inflammation and their antibacterial mechanisms against bacterial pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- researchers demonstrated that APC (a synthesized antibacterial compound) effectively targets MRSA in calcium-dependent processes within sterile inflammatory environments.
- Single-cell transcriptomic methods were utilized for detailed analysis, confirming cellular and bacterial responses to APC treatment, including its efficacy in chronic pneumonia and osteomyelitis models.
- Authors have filed a patent related to this work. The study underlines innovations in combating antibiotic resistance while revealing insights into immune-regulating pathways involving macrophages linked with S100A proteins.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research is particularly relevant as antimicrobial resistance continues to pose a global health challenge, including significant threats to public health infrastructure in India. With its population prone to infections like tuberculosis or MRSA-linked complications post-surgery, findings such as those from this Chinese study bolster scientific efforts on targeted therapies versus broad-spectrum antibiotics. if replicated successfully, such calcium-dependent mechanisms may emphasize more localized treatments with fewer systemic side effects-a trend Indian biotech firms may aim for with indigenous developments. however, patenting could restrict access unless collaborative frameworks are established internationally or regionally; India might benefit through partnerships emphasizing affordability and accessibility.
Read more: Link
Quick Summary
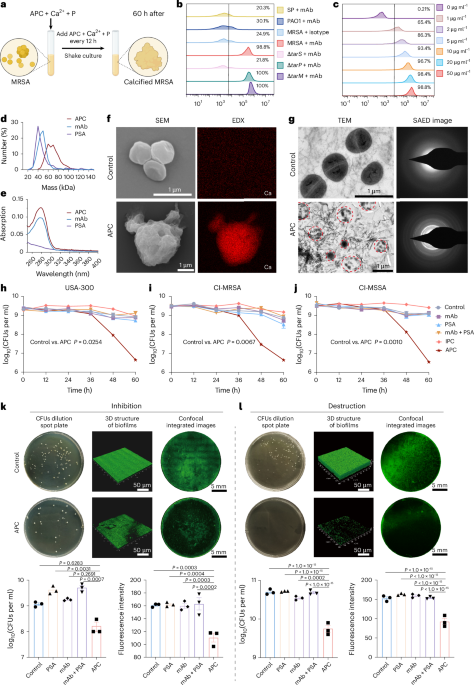
- A scientific study examines methods to treat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) through bacterial calcification and immunomodulation.
- The research evaluated various treatments, including monoclonal antibodies (mAb), PSA (phosphate-stimulated antigen), and engineered calcium-phosphate-based compounds like IPC and APC.
- Trials included:
– In vitro tests: Live/dead staining on USA300, CI-MRSA, CI-MSSA strains with different agent combinations.
– Metabolomics analysis: Heatmaps illustrating metabolic changes due to APC treatments in MRSA strains. Pathways involved energy metabolism, amino acid synthesis, and membrane transport.
– in vivo experiments: Chronic pneumonia and osteomyelitis models in mice demonstrating effectiveness of APC for targeted antibacterial outcomes via fluorescence imaging techniques.
– Investigations into pharmacokinetics showed organ-specific distribution of APC post-administration.
- Safety evaluations indicated excellent biocompatibility of APC with minimal toxicity across multiple animal models over extended testing periods.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This development represents significant progress in combating antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, which poses a growing healthcare threat globally.For India, where antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is increasingly prevalent due to widespread antibiotic misuse, such advancements could prove transformative. The innovation aligns with India’s imperative need for novel therapeutic strategies against resistant infections as outlined by its National Action Plan on AMR.
Further clinical research will be essential for widespread adaptation; however, the promising biocompatibility results suggest realistic scalability potential if approved. Academic partnerships between Indian researchers and global innovators could expedite access while fostering future breakthroughs tailored to regional challenges like population density-linked infection rates.
Read more: Source LinkQuick Summary:
- A groundbreaking study published in nature Biotechnology explores bacterial calcification for systemic treatment and immunomodulation against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- researchers Zhang, Liu, and others have developed an innovative approach utilizing bacteria-induced calcification to target MRSA.
- This technique aims to enhance immune responses while tackling antibiotic resistance concerns.
- The article received by the journal in December 2023 was accepted in June 2025 before its publication on July 15, 2025.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The study’s novel methodology opens new avenues for combating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, such as MRSA. For India,where antibiotic resistance is a growing public health challenge due to indiscriminate antibiotic use and lack of robust healthcare infrastructure in rural areas,this research could hold transformative potential. Accomplished adaptation of this technology might improve treatment outcomes for resistant infections across diverse settings. Though, implementation at scale requires careful evaluation concerning cost-effectiveness and accessibility within India’s socio-economically diverse population.