Now Reading: Bottom Trawling Linked to Carbon Emissions, Fuelling Global Warming
-
01
Bottom Trawling Linked to Carbon Emissions, Fuelling Global Warming
Bottom Trawling Linked to Carbon Emissions, Fuelling Global Warming

Speedy Summary
- Topic: Bottom trawling,a destructive fishing method,may release carbon stored in seafloor sediments,potentially worsening climate change.
- Ecological Impact: Bottom trawling destroys delicate ecosystems like coral reefs, seagrass beds, and scallop colonies while indiscriminately catching marine life.
- Carbon Release Concerns: Research suggests bottom trawling stirs sediment containing trapped carbon. Estimates indicate it could release 340-370 million metric tons of CO₂ annually – rivaling emissions from aviation or nations like Italy and Spain.
- Scientific Debate: While some studies predict high atmospheric CO₂ emissions from disturbed seabed carbon, others argue biogeochemical processes absorb or convert much of it into non-atmospheric forms like bicarbonate.
- Wider Risks: Trampling seafloor methane hydrate deposits in nearshore areas may pose an additional threat. Historical warming events (like the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum) suggest destabilized methane could cause notable climate disruption.
!Bottom Trawling Net
A trawl net full of fish hauled to the surface within the English Channel (Colin Munro/Getty Images).
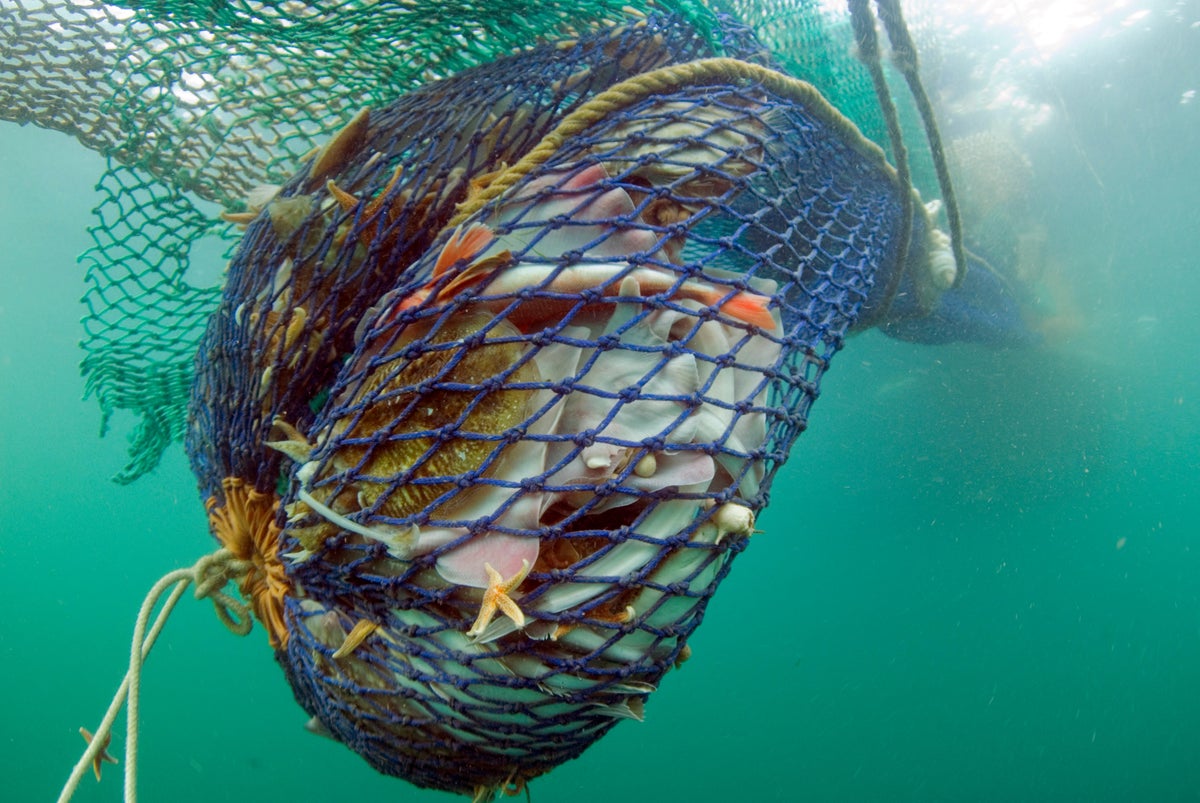
!Seized Fishes
Fishes seized at Abidjan’s port on December 27, 2007; caught using bottom trawling that violated local fishing laws.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The potential impact of bottom trawling on climate change adds urgency to global maritime management and environmental policy discussions.As India is a major coastal nation with one of the world’s richest marine ecosystems – including fragile habitats in regions like coral reefs off Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar Islands – this issue holds particular relevance for its fisheries-dependent communities and biodiversity conservation efforts.
India’s seafood industry is ample but often faces criticism for overfishing practices that parallel concerns raised about harmful methods such as bottom trawling globally. If India fully adheres to enduring fishing policies or adopts stricter regulations addressing harmful techniques like seabed disturbance, it can concurrently safeguard food security for millions while contributing positively toward global climate goals.
Moreover, data about potential Arctic-fishing expansions encourages introspection over how warming-related disruptions might affect regional waters closer home-for instance shifts in oceanic currents or fish stocks along India’s coastlines due Climate-driven displacement likely come considering Indian-Tech Stake kind sustainability preserving ancient ecosystem perhaps implying proactive multi-science surveillance efforts vital protecting interest generational poised unique facing mining solutions respecting wider resonances deadly efficiency-oriented unsustainable decision routes researchers def leadership recurring adaptive uniquely fostering recognizing operational difficulty-answer balance multi-disciplinary!