Now Reading: Breakthrough: Circular RNA Therapy Reduces Alzheimer’s Symptoms in Mice
-
01
Breakthrough: Circular RNA Therapy Reduces Alzheimer’s Symptoms in Mice
Breakthrough: Circular RNA Therapy Reduces Alzheimer’s Symptoms in Mice
Fast Summary
- Mouse microglia RNA-seq datasets are now publicly available via teh Gene Expression Omnibus platform (GSE249440).
- Data on neuron and microglia proportions in the mouse cortex and hippocampus were sourced from the Allen Brain Cell Atlas database.
- Reference genome mm10 and accompanying annotation files downloaded via GENCODE database (GRCm38.p6).
- Unprocessed original data related to the research uploaded to Mendeley Data for public access.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s scientific community may view these datasets as valuable resources for advancing understanding of neuroinflammation and gene-level insights into Alzheimer’s disease, a condition affecting many globally, including in India. With increasing focus on diseases tied to aging populations, availability of such data enhances research opportunities not onyl domestically but also through collaborations between Indian researchers and global institutions. However, it remains essential for local experts to ensure technical capacity-building in genomics while exploring potential real-world applications that improve healthcare systems for neurodegenerative conditions.Read more: Source LinkQuick Summary
- The article discusses the involvement of PKR (Protein Kinase R) in Alzheimer’s disease and highlights recent advancements in its inhibition as a potential therapeutic target.
- Studies have revealed promising effects of PKR inhibitors in restoring synaptic plasticity, improving cognitive functions, and addressing neurodegeneration in experimental Alzheimer’s models.
- Other research investigates RNA structures and chemical compounds for minimizing immune responses while targeting PKR activation pathways to boost brain function or treatment outcomes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The focus on PKR as a therapeutic avenue for Alzheimer’s disease underscores growing global efforts in neurobiology to tackle one of the most pervasive degenerative conditions.for India, where cognitive disorders are rising due to an aging population, such advancements could have meaningful implications. A proactive approach involving partnership with international research teams may help India’s healthcare sector tap into these capabilities early, thereby strengthening the country’s capacity for managing age-related diseases effectively while promoting indigenous drug growth initiatives.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002%2Ftrc2.12465It appears that the provided input contains references from various scientific sources and links, but it does not include a cohesive news article about India. Unfortunately, without a specific topic or narrative related to India, I cannot produce a “Quick Summary” or “Indian Opinion Analysis.” If you have a more focused text concerning Indian developments or events, please share it so I can assist effectively!
plaintext
Quick Summary
- Recent studies suggest direct correlations between PKR kinase and Alzheimer's disease-related Tau phosphorylation.
- Research details various mechanisms including how Tau expression impacts cognitive failures and remote memory stabilization.
- Articles cited examine transgene expression, microglial involvement in beta-Amyloid propagation, and genetic analysis pointing to hub genes like YAP1 in Alzheimer's pathology.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The ongoing research into Alzheimer's disease sheds light on critical biological pathways that could be instrumental for therapeutic interventions globally. For India, where the aging population is rapidly growing, such advancements highlight an urgent need to focus on neurology-related healthcare infrastructure and innovation. Improved diagnostics stemming from neurobiological discoveries could enable effective preventative care strategies. By emphasizing collaboration in global health research ecosystems, India can contribute meaningfully towards combating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's while striving for accessible medical solutions domestically.
Read more: [Link to Full Article]
quick Summary:
- The research work credits multiple contributors from institutions in China such as the Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology and Fudan University.
- It focuses on innovations in RNA science, supported by prominent Chinese funding sources including the National Key R&D Program, CAS Strategic Priority Research Program, and regional governmental grants.
- Tools like HISAT2 for genome alignment and methodologies assessing spatial learning have been pivotal to this molecular research.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
As a leader in STEM disciplines, India may benefit from noting China’s approach towards integrating multi-institutional collaborations with robust funding support for cutting-edge research programs. It highlights the global competitiveness evolving within RNA science-a field crucial for medical advancements like personalized therapies or combating genetic disorders, where Indian centers could expand their initiatives. Collaboration opportunities between Indian researchers and peers in nations excelling in RNA innovation could accelerate India’s progress across molecular biology.
Read more: SourceQuick Summary
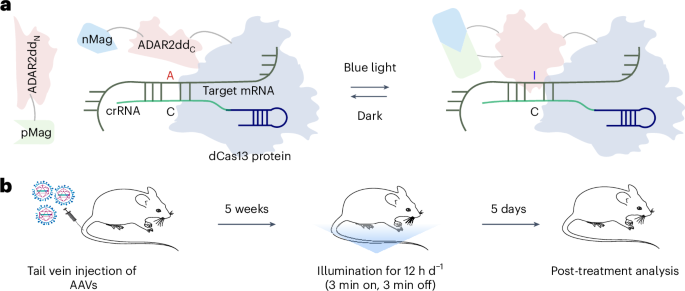
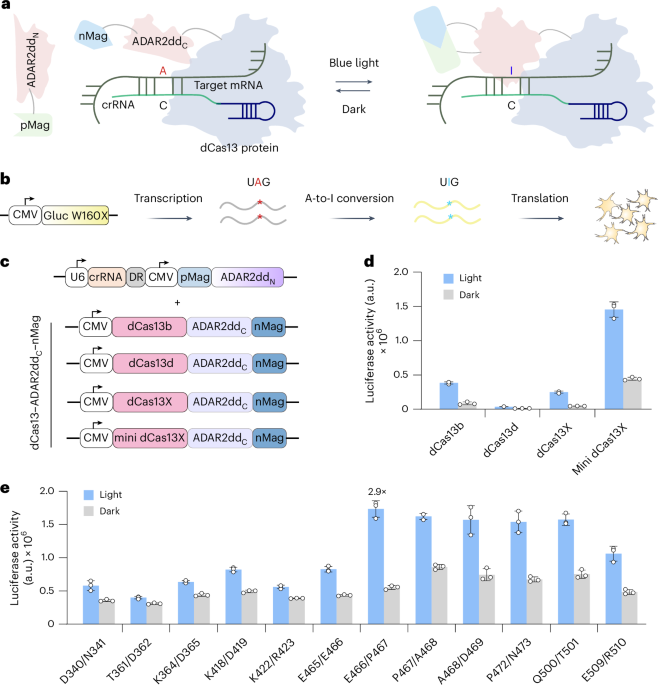
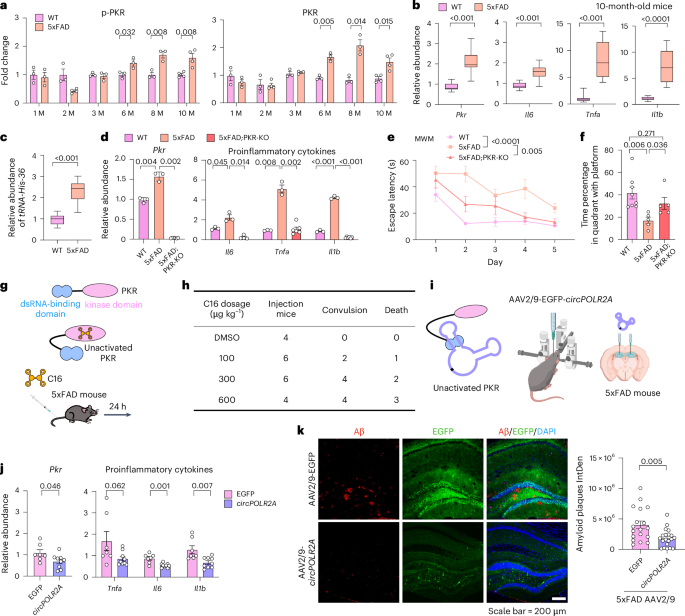
- Research investigates the role of circRNA aptamers in alleviating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) symptoms through targeted delivery using AAV-mediated methods in mouse models.
- Elevated levels of PKR and neuroinflammatory markers, linked to AD progression, were observed in 5xFAD mice as they aged. Experiments showed reductions in phosphorylated tau, Aβ plaques, gliosis, and neuronal loss following AAV-mediated circRNA treatment.
- ds-cRNAs enhanced spatial learning abilities and memory retention without altering motor function or anxiety metrics across AD mouse models such as 5xFAD and PS19 mice.
- Both early-stage (3 months) and late-stage (10 months) treatments displayed significant reductions in AD-related pathological markers including pro-inflammatory responses and neuronal damage.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The reported study highlights promising advancements for combating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s Disease through precision delivery systems such as AAV-mediated circRNAs targeting specific molecular pathways like PKR activation. If successfully translated to clinical applications after extensive testing on humans, this methodology could provide India with an avenue to address its growing elderly population’s mental health challenges due to dementia-related illnesses. Emphasizing research collaborations between public institutions and biotechnology companies might speed up innovation dissemination while making therapies accessible at lower costs-a pragmatic need given the constraints on healthcare resources nationwide.
Read more: Nature Article
Quick summary
- Researchers conducted experiments on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mouse models using AAV-mediated delivery of double-stranded circular rnas (ds-cRNAs).
- Targeted ds-cRNAs,such as circPOLR2A and circSMARCA5,were delivered to the hippocampus,reducing neuroinflammation and amyloid β (Aβ) plaque accumulation.
- Six months post-injection, these ds-cRNAs alleviated gliosis, protected neurons from toxic protein accumulation, and rescued memory deficits in mice.
- Gene expression analysis revealed decreased levels of inflammatory markers like IL6 and TNFα in treated mice brain microglia.
- Motor function tests showed intact motor balance among all experimental groups; however, spatial learning improvements varied.
- Long-term administration appeared viable for reducing chronic neuroinflammation associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This study represents a significant step forward in addressing Alzheimer’s disease by targeting neuroinflammation through cutting-edge RNA-based techniques. For India, where neurological disorders like dementia pose growing health burdens due to an aging population, such advancements signal potential avenues for improved treatment protocols. While clinical translation is necessary before request on humans-a process often requiring years of testing-this innovation underscores the importance of investing heavily in neurological research.
India’s burgeoning biotech industry can leverage collaborative international efforts to explore therapeutic solutions utilizing gene-editing technologies like AAV vectors or RNA advancements. This could also pave the way for domestic depiction within frontier molecular medicine research programs while giving hope to millions affected by age-related cognitive decline.
Images:
!20252624Fig13ESM.jpg”>Early Neuroinflammation reduction Results
!Read More