Now Reading: Breakthrough in Single-Cell Analysis Uncovers New Viruses
-
01
Breakthrough in Single-Cell Analysis Uncovers New Viruses
Breakthrough in Single-Cell Analysis Uncovers New Viruses
Rapid Summary
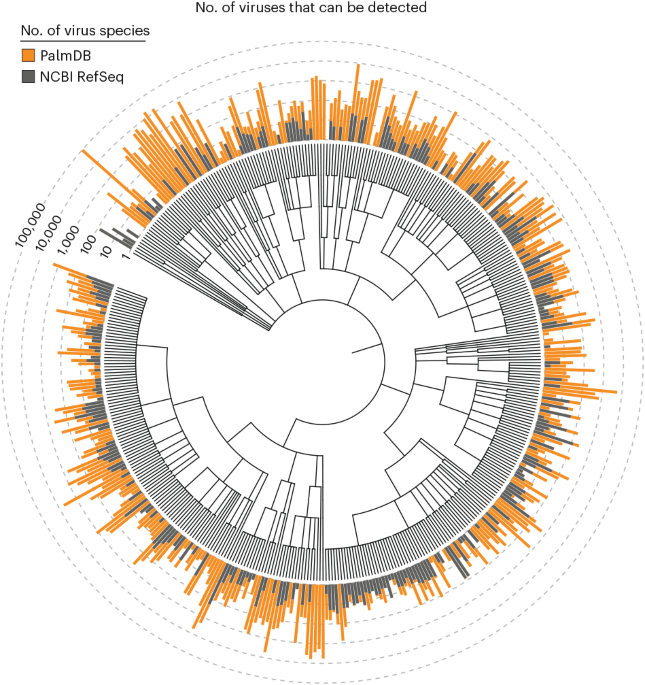
- A novel method was introduced in Nature Biotechnology (April 2025) for detecting viral sequences in RNA sequencing data using highly conserved proteins.
- This approach allows the identification of over 100,000 RNA virus species.
- Researchers conducted parallel analyses to detect new viruses and study host gene expression, enabling the understanding of viral tropism (virus affinity for particular cells) and host immune responses at a single-cell resolution.
- Published framework also focuses on integrating single-cell profiling techniques with agnostic viral detection tools to explore cellular-level host-virus interactions.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of a method capable of detecting vast numbers of RNA virus species marks a meaningful advancement in virology and genomic research. For India, where population density creates heightened risks for viral epidemics, this scientific tool can be transformative if integrated into local research ecosystems or public health policies.
Broader implications include improved pandemic preparedness by enabling early identification of emerging viruses and customized vaccine development based on granular insights into human immune responses under varying conditions. India’s biotechnological sector could benefit by adopting such technologies to enhance its sequencing capabilities and contribute globally to studies on zoonotic diseases or antibiotic resistance pathways linked to microbiomes altered by unknown viruses.
facilitating collaborations between academia, healthcare agencies, and biotech firms might ensure that such innovations are adequately harnessed within India’s diverse environments prone to rapid disease spread.
























