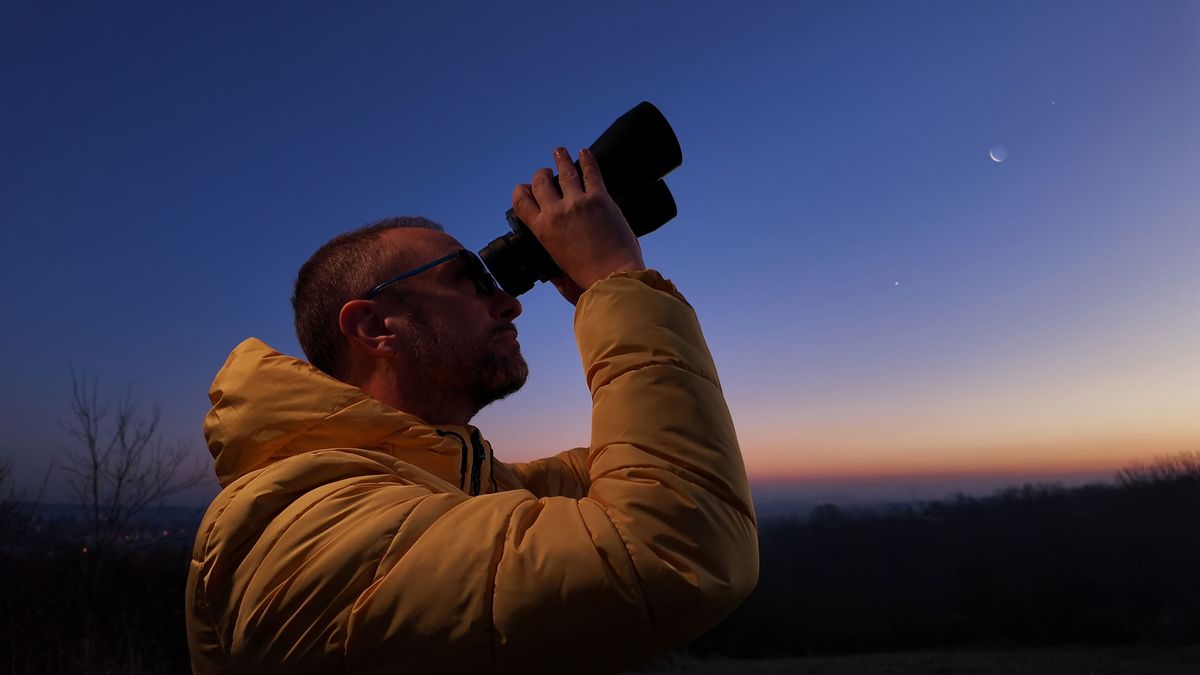
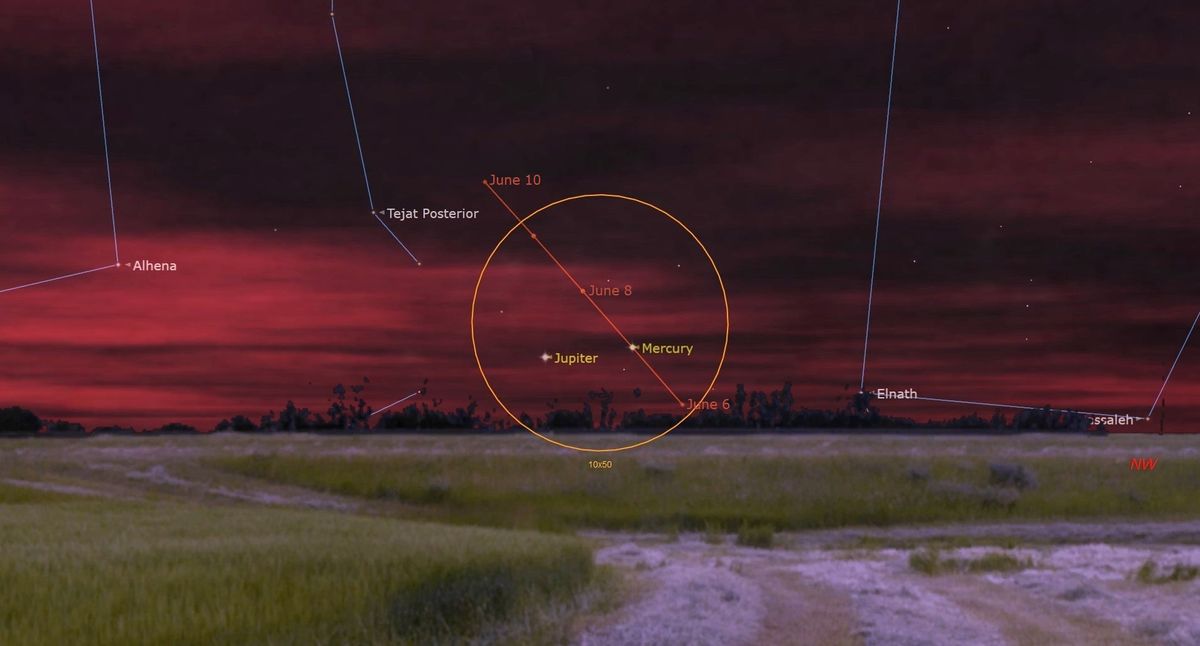
The nights surrounding June 7 will see Jupiter and Mercury crowd together close to the horizon in the northwestern sky.
Stargazers in the U.S. will need a clear horizon to spot the planetary duo hanging less than 10 degrees (about a fist’s width at arm’s length) above the western horizon when the sun sets on June 6, with Jupiter positioned to the upper left of Mercury. The planets will only be visible for around 45 minutes after sunset, at which time they will follow our star below the horizon.
The following evenings will see fleet-footed Mercury draw level with Jupiter, before rising above and away from the gas giant in the night sky as a result of the smaller world’s tight orbit around the sun. On June 7, the planets will pass a little over two degrees from each other – close enough to fit comfortably inside the field of view of a pair of 10×50 binoculars. Ensure that the sun has set entirely below the horizon before you point any binoculars or telescopic gear in its direction.
Side by side in the night sky, the two points of light appear similar in nature, belying the extreme differences of the solar system bodies they represent. Jupiter is a gas giant and the largest planet in our solar system, capable of fitting the smallest planet – rocky Mercury – within its expanse many thousands of times over.

Want to find the planets of our solar system for yourself? The Celestron NexStar 4SE is ideal for beginners wanting quality, reliable and quick views of celestial objects. For a more in-depth look at our Celestron NexStar 4SE review.
Their orbits are similarly divergent. It takes Jupiter 12 Earth years to complete a single lap of our star while travelling at an average orbital distance of 484 million miles (778 million kilometers). Counterintuitively, the gas giant has the shortest day of any planet in the solar system, taking a mere 9.9 hours to spin on its axis, according to NASA.
Mercury, on the other hand, is separated on average by 29 million miles (47 million kilometers) from our star and completes a circuit of the sun every 88 Earth days — much shorter than the 176 Earth days that it takes for the tortured world to complete a full day-night cycle.
Night sky enthusiasts hoping to explore the planets of our solar system for themselves should check out our guides to the best binocular and telescope deals. Those new to the night sky should also read our guide detailing the top smartphone stargazing apps available in 2025.
Editor’s Note: If you capture a picture of Jupiter and Mercury and want to share it with Space.com’s readers, then please send it along with your comments, name and the location of the shoot to spacephotos@space.com.