Now Reading: Caterpillar Disguises Itself with Dead Insect Remains: A Survival Strategy
-
01
Caterpillar Disguises Itself with Dead Insect Remains: A Survival Strategy
Caterpillar Disguises Itself with Dead Insect Remains: A Survival Strategy

Quick Summary
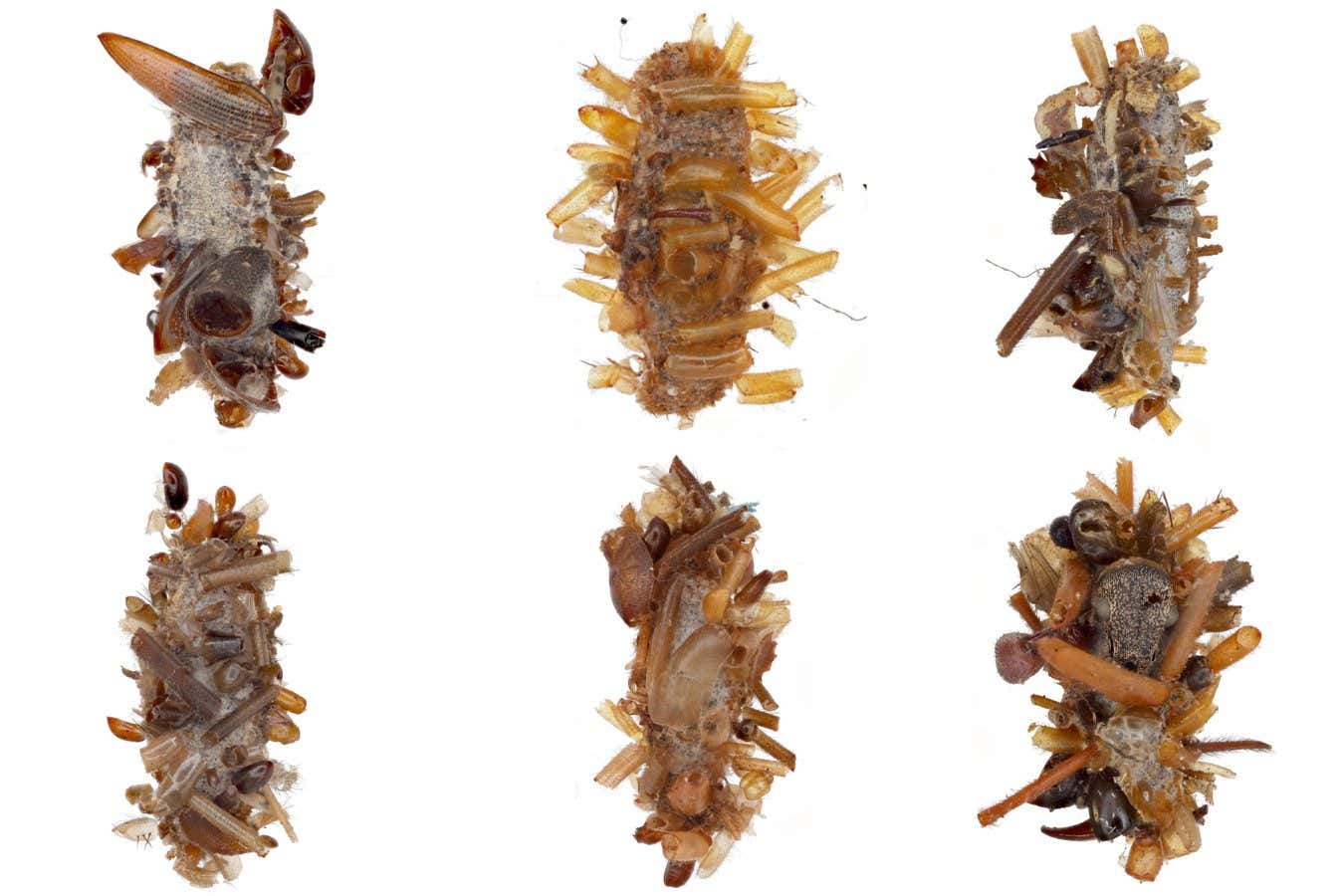
- Researchers have described a unique carnivorous and cannibalistic caterpillar species nicknamed the “bone collector.”
- Found in the Waianae mountain range of Oahu, Hawaii, this unidentified Hyposmocoma species disguises itself using parts of dead insects and spider exoskeletons to live alongside spiders undetected.
- these caterpillars feed on insects trapped in spider webs and avoid being preyed upon by mimicking trash-like odors through their grisly disguise.
- The species undergoes metamorphosis into moths smaller than a grain of rice after 2-3 months.
- cannibalistic tendencies were observed when placed together, showing why only one bone collector inhabits a given spider web.
- Only 62 individuals have been spotted across over 150 field surveys conducted in a restricted area spanning 15 square kilometers.
- Genetic analysis dates its lineage back approximately three million years, predating the formation of Oahu. It was likely more widespread before human arrival caused important biodiversity losses.
!248646357.jpg”>The bone collector caterpillar (left) uses its grisly disguise to live safely with a spider (right)
Image credit: Daniel Rubinoff et al. 2025
Indian Opinion Analysis
The revelation highlights critical facets about ecosystems’ fragile balance and the irreversible impact humans have had on biodiversity. While unrelated geographically, India’s own richness in unique and endemic wildlife faces similar threats from habitat destruction and human encroachment.
The “bone collector” exemplifies evolutionary ingenuity rarely seen among caterpillar species-less than 0.13% are carnivorous globally-showcasing nature’s adaptive resilience against harsh survival challenges like predatory spiders. As countries worldwide race against time to preserve diminishing biodiversity, attention must shift toward enabling coexistence between human activities and ecosystems.
India’s conservation initiatives may benefit from studies such as this as it informs frameworks for critical hotspots under threat due to increasing urbanization or agriculture practices. Also worth noting is how genetic insights play an essential role not just academically but ecologically for strategic preservation approaches being implemented globally.