Now Reading: Chicago-Sized Iceberg Detaches, Unveiling Hidden Ecosystem
-
01
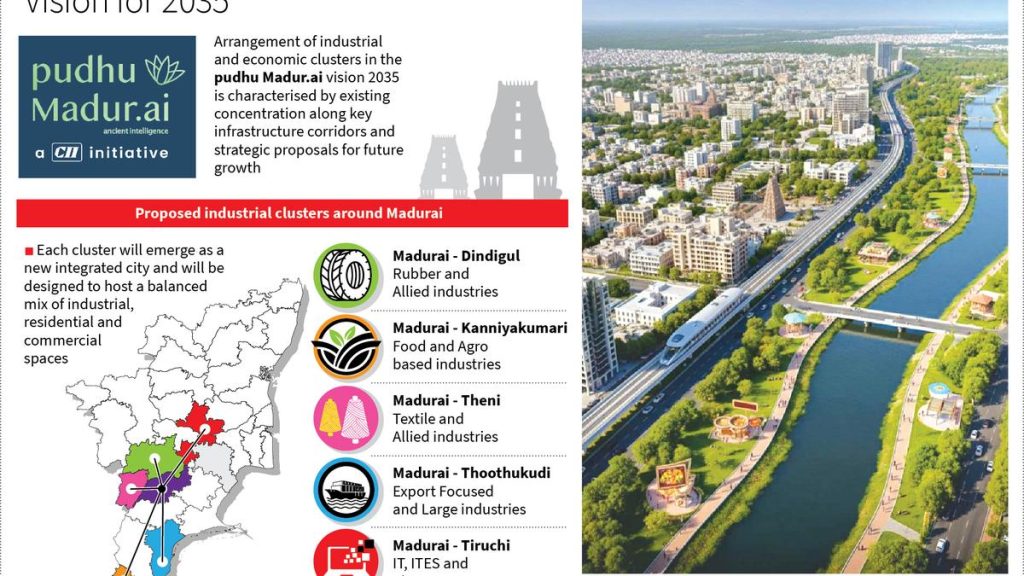
Chicago-Sized Iceberg Detaches, Unveiling Hidden Ecosystem
Chicago-Sized Iceberg Detaches, Unveiling Hidden Ecosystem

Quick Summary
- Iceberg Breakaway: In January 2025, iceberg A-84 broke off from the george VI Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The iceberg measures approximately 19 miles long, 11 miles wide, covering an area of 209 square miles – close to Chicago’s size.
- New Ecosystem Revelation: Researchers diverted their plans and used Schmidt Ocean Institute’s remotely operated vehicle (ROV subastian) to investigate the newly exposed seabed. They discovered a thriving ecosystem including corals, octopuses, giant sea spiders, and sponges with potential new species identified.
- Scientific Insights: Despite being covered under a massive ice sheet for centuries, nutrient-rich ocean currents likely sustain this ecosystem. This is the first use of an ROV to study marine life beneath ice shelves.
- Climate Change Connection: Observations revealed high biological productivity and important glacial meltwater flow at the George VI Ice Shelf.Findings provide critical data on ice loss contributions to sea level rise globally.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery stemming from iceberg A-84’s detachment underscores the complex interplay between climate change-driven phenomena and ecological resilience. While Antarctic ecosystems may offer clues about how life thrives under extreme conditions, ongoing studies linking thes environments with global sea-level rise hold broader implications for India. As a low-altitude nation with extensive coastal regions prone to flooding risks like those faced in cities such as mumbai or Chennai during severe monsoons or cyclones – understanding long-term shifts in polar dynamics might assist policymakers in preparing adaptive strategies.
From Antarctica’s ecosystem health insights to actionable climate forecasting tools that help mitigate socio-economic impact locally or regionally amidst rising temperatures future collaborations broad require bridging scientific tech gaps equitably nations polar-frame elsewise human-agent response crucial steps solves time-sensitive global priority 环亚 natural