Now Reading: China’s CO2 Emissions Decline: Signs of Reaching Peak?
1
-
01
China’s CO2 Emissions Decline: Signs of Reaching Peak?
China’s CO2 Emissions Decline: Signs of Reaching Peak?

Fast Summary:
- China’s carbon dioxide emissions declined by 1 percent over the last year, despite increasing power demands, according to analysis by the Center for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA).
- In the first quarter of 2025 alone, emissions declined by 1.6 percent compared to the previous year.
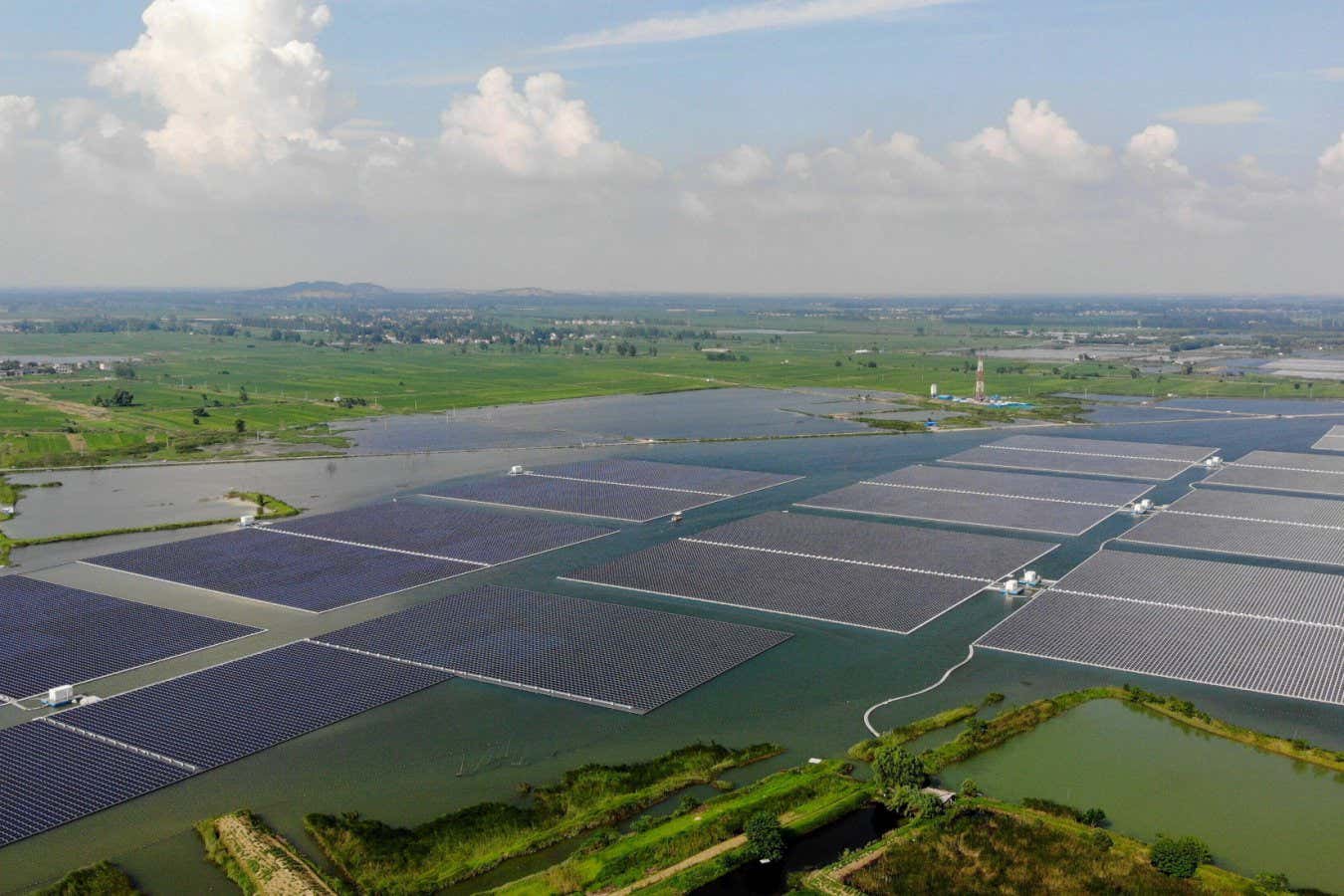
- This decline is attributed to China’s substantial investment in solar, wind, nuclear power, and a shift away from carbon-intensive industries like cement and steel production.
- The surge in electric vehicle adoption has also contributed to reduced oil demand.
- Sustained emission reductions could mean China has reached peak emissions years ahead of its target for 2030 under international climate commitments.
- Challenges such as potential droughts reducing hydropower output or extreme weather conditions could push emissions back up temporarily.
- Long-term targets for clean energy installation will play a pivotal role in sustaining progress as indicated by China’s next five-year plan due in 2026.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...