Now Reading: Climate Change Accelerates Food Spoilage, Impacting Global Health
-
01
Climate Change Accelerates Food Spoilage, Impacting Global Health
Climate Change Accelerates Food Spoilage, Impacting Global Health

Quick Summary
- Impact of climate change on food safety: Rising global temperatures and extreme weather events are accelerating the growth of bacteria and other pathogens, leading to increased food spoilage and contamination worldwide.
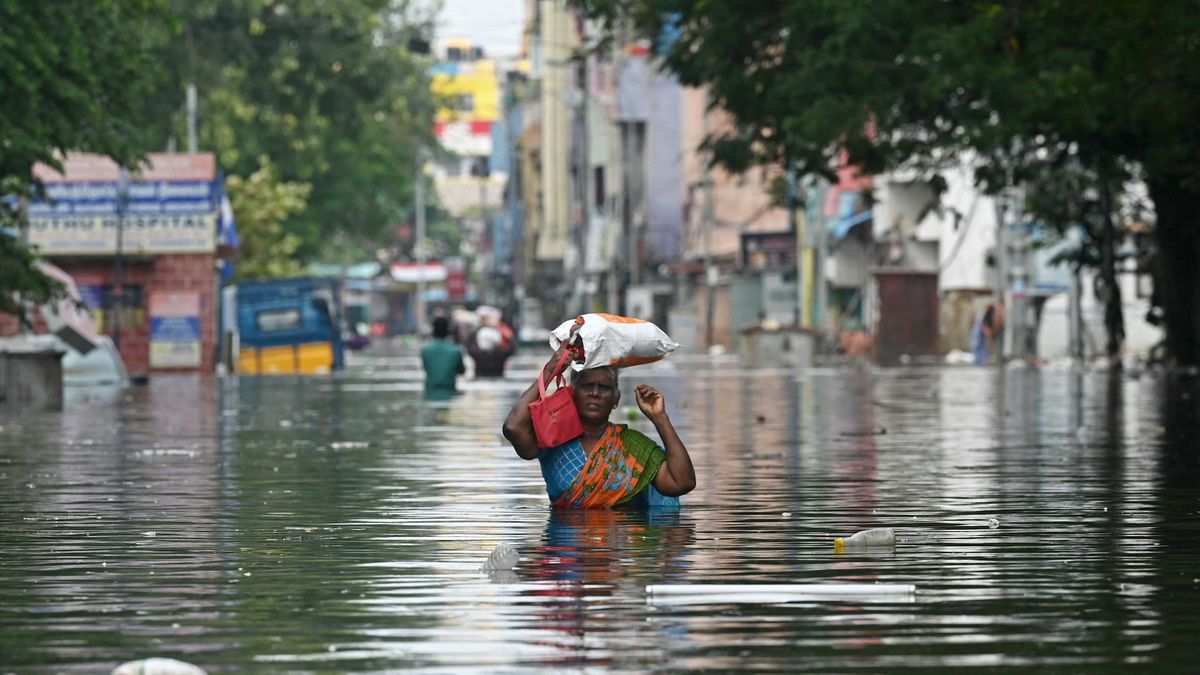
- Case study in India: Sumitra Sutar from Maharashtra experienced severe health issues caused by Bacillus cereus, a bacteria linked to foodborne illnesses that thrives in high heat conditions.
- Extreme weather effects:
– Heat waves allow pathogens like listeria, campylobacter, and salmonella to grow faster in perishable foods.
– Flooding contaminates crops with runoff containing sewage or manure.- High humidity promotes bacterial growth on produce consumed raw.
- Global burden statistics: The World Health Institution reports that annually 600 million people fall ill from foodborne diseases, resulting in 420,000 deaths-125,000 being children under five.
- Research insights:
– A temperature rise of every °C increases risks of salmonella and campylobacter infections by approximately 5%.
– Studies reveal domestic washing or conventional cooking methods may not eliminate some bacteria effectively.
- Community response in India:
– Villages like Haroli have shifted reliance to groundwater after repeated illness from contaminated river water.
– Community health initiatives are promoting fresh cooking practices over leftovers to mitigate contamination risks.