Now Reading: Coelacanth: The ‘Living Fossil’ Unchanged for 400 Million Years
-
01
Coelacanth: The ‘Living Fossil’ Unchanged for 400 Million Years
Coelacanth: The ‘Living Fossil’ Unchanged for 400 Million Years

Swift Summary
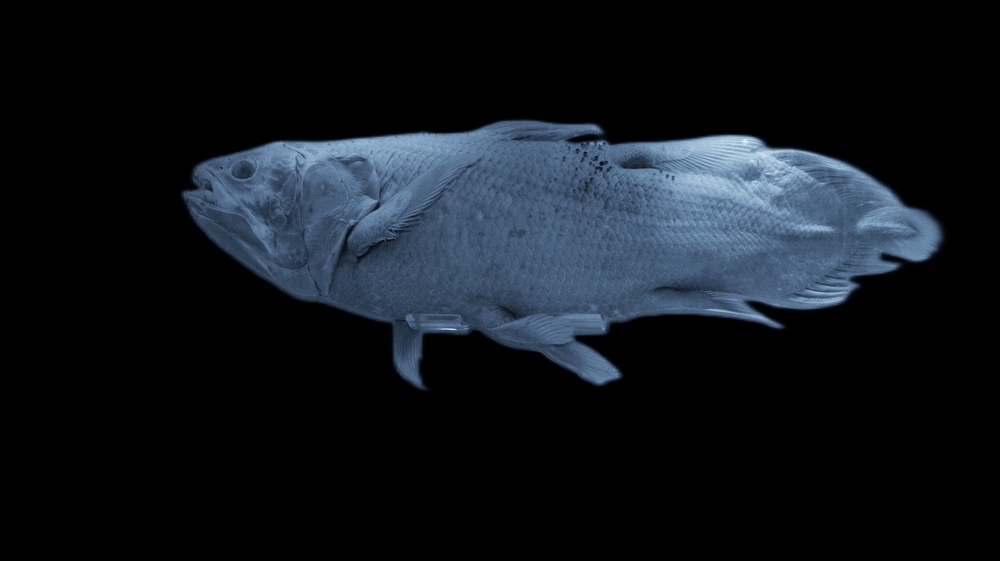
- The Coelacanth Fish: The coelacanth, famously referred to as a “living fossil,” was onc thought extinct but has remained mostly unchanged for over 400 million years.
- Origin of the Concept: Charles Darwin coined the term “living fossil” in On the Origin of Species to describe organisms with stable morphological features that persist through evolutionary time.
- Scientific Debate: There is ongoing debate surrounding the definition and usefulness of categorizing organisms as “living fossils.” Some scientists argue that it creates confusion,especially with advancements in molecular analysis showing instability in certain features.
- Examples Beyond Coelacanths: Living fossils frequently enough include ginkgo trees, horseshoe crabs, komodo dragons, and cockroaches.
- Conceptual Framework Proposal: Researchers Alan love and Scott Lidgard advocate focusing on a conceptual framework to answer scientific questions rather than rigid categorizations based on ambiguous terminology. They emphasize using “living fossil” as an analytical tool rather than categorization.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The concept of living fossils introduces broader insights into nature’s evolutionary landscape-an area relevant not just scientifically but also historically and culturally for nations like India. As a country with diverse ecosystems housing species such as crocodiles or ancient plants akin to ginkgo trees (though not native), India’s understanding and preservation efforts might benefit from this deeper focus on stability within change observed at molecular or morphological levels.
From an educational perspective for India-where curiosity about evolution is growing amid broader scholastic reforms-the debate around living fossils helps illustrate complexities within biology. it also shows science’s ability to adapt definitions/processes with new technology patterns.
Encouraging interdisciplinary approaches based on frameworks could enhance collaborations across Indian ecological studies, paleontology research hubs (e.g., India’s fossil-rich terrains), or even biodiversity policy-making efforts at governmental levels-fusing tradition-rooted species mapping into advanced global frameworks without discarding taxonomy legacies prematurely.