Now Reading: Curiosity Captures Martian Air Samples: Sols 4604-4606 Update
-
01
Curiosity Captures Martian Air Samples: Sols 4604-4606 Update
Curiosity Captures Martian Air Samples: Sols 4604-4606 Update

Quick Summary
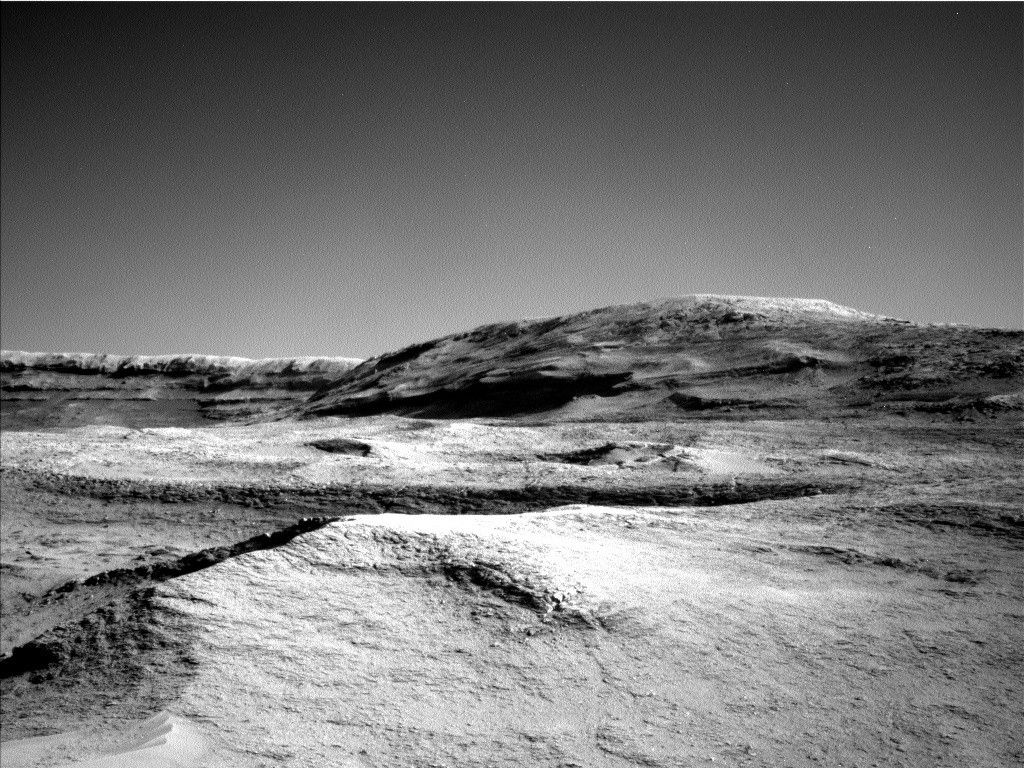
- Mars rover Curiosity is exploring boxwork structures on the Martian surface to understand their chemistry, morphology, and sedimentary features.
- The investigation involves multi-day activities with observations using Navcam,Mastcam,ChemCam,APXS (Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer),and MAHLI (Mars Hand Lens Imager).
- Objectives include studying the resistant ridge where Curiosity is parked through imaging and spectroscopy techniques.
- Activities included:
– Dust analysis in the atmosphere.
– Imaging prominent ridges and hollows nearby.
– Soil sample analysis targeting nodular bedrock on specified geological sites (“Totoral”, “Sillar”).
– Short exploration drive to adjacent hollow areas for further research and context images.
- Atmospheric chemistry assessments are being conducted to detect variations between nighttime and daytime conditions using SAM instruments alongside overnight data collection by APXS.
- These efforts aim to provide an expansive understanding of Martian terrain characteristics.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the ongoing exploration by Curiosity on Mars exemplifies significant advancements in planetary science that promise broader insights into extraterrestrial geology. For India-a country expanding its space ambitions-such missions underscore the importance of consistent investments in research capabilities such as remote sensing instruments or rovers. As india continues developing interplanetary projects like Mangalyaan successors or potential lunar rovers under Chandrayaan programs, lessons from NASA’s efficient planning for multifaceted explorations might serve as strategic benchmarks.
Moreover, innovations in atmospheric chemical analysis showcased here could aid future collaborations between ISRO (Indian Space research Organisation) and international agencies for joint missions relating to climate modeling or astrobiology reconnaissance on celestial bodies. Exploration technologies demonstrated by NASA also offer valuable encouragement as aspiring nations like India seek ways to advance long-term space exploration agendas while navigating practical constraints balancing scientific excellence with costs.