Now Reading: Curiosity Rover Captures Stunning Ridge Images on Sols 4638-4640
-
01
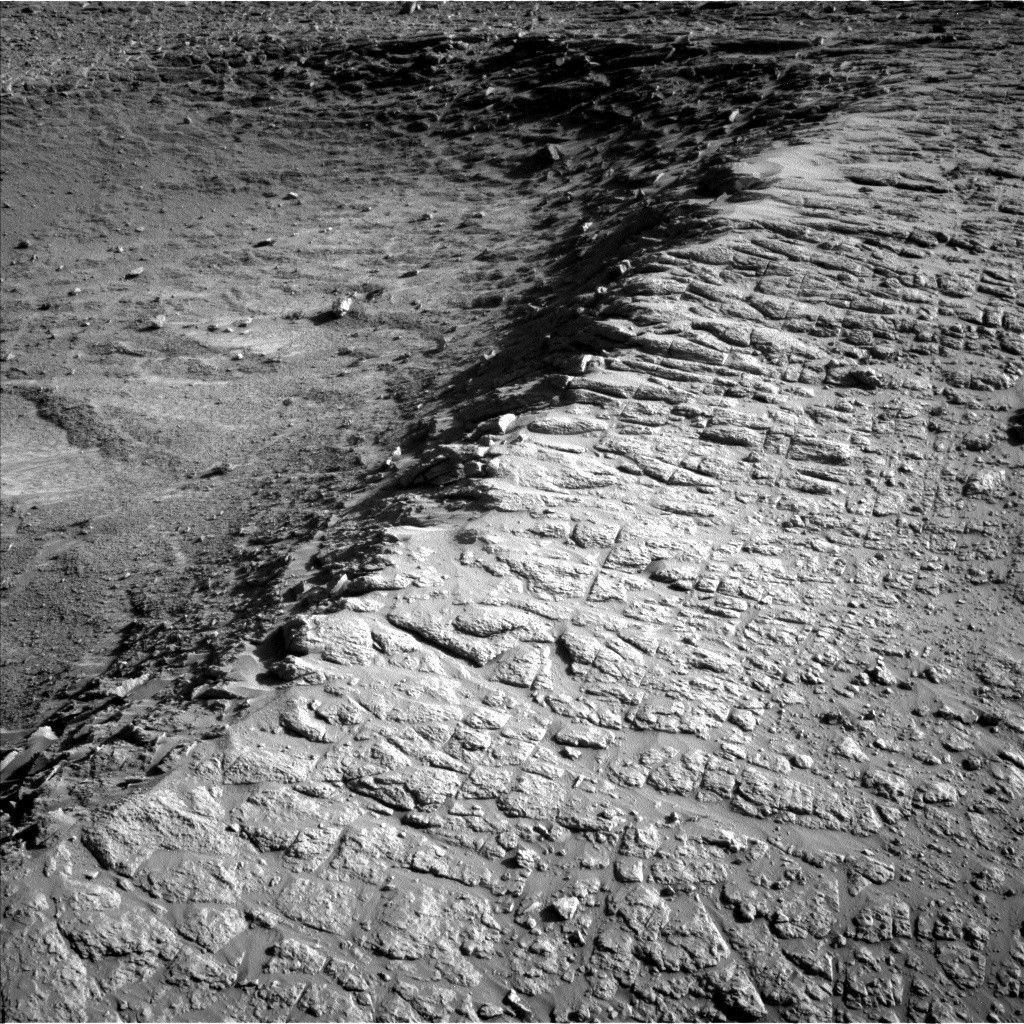
Curiosity Rover Captures Stunning Ridge Images on Sols 4638-4640
Curiosity Rover Captures Stunning Ridge Images on Sols 4638-4640

Quick Summary
- NASA’s Mars Curiosity rover is exploring “boxwork structures” as part of its ongoing mission on Mars.
- The rover recently moved away from a site named “Río Frío” and is stationed atop a ridge overlooking an area called the “Thumb.”
- Various instruments, including Mastcam, ChemCam, MAHLI, and APXS, are being used to extensively analyse nearby geological targets such as “Samaipata,” “Wallatiri,” and others.
- A 44-image mosaic of the north crater rim is being captured using Mastcam due to favorable atmospheric conditions with low dust levels.
- Environmental monitoring includes observing dust levels and weather phenomena like dust devils via Navcams and Mastcam tau observations.
- The team plans only a short 2-meter drive in this session before resuming more studies of the ridge.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India has emerging stakes in space exploration through missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan. NASA’s sustained Curiosity mission reveals how advanced observational tools enable detailed scientific discovery on Mars. This underscores the importance of interdisciplinary expertise in instruments that integrate imaging, spectrometry, and environmental monitoring-lessons directly applicable for future Indian missions for deeper planetary analysis. Collaborative synergies between agencies across technical domains could propel India further into high-impact space exploration projects.