Now Reading: Curiosity Rover Logs Eventful Weekend on Mars (Sols 4549-4552)
-
01
Curiosity Rover Logs Eventful Weekend on Mars (Sols 4549-4552)
Curiosity Rover Logs Eventful Weekend on Mars (Sols 4549-4552)

Quick Summary
- A “marathon” drive of 45 meters was completed earlier this week,followed by a record-setting distance of nearly 70 meters on Wednesday.
- The rover team planned an extended weekend operation due to the upcoming U.S. memorial day holiday, including targeted science activities and another drive of about 42 meters.
- Gale Crater’s southern hemisphere winter solstice approaches, bringing cold temperatures and heightened power demands for heating the rover and instruments.
- Science plan optimizations balanced energy constraints while enabling over four hours of targeted and remote sensing activities along with 12 hours of overnight APXS integrations.
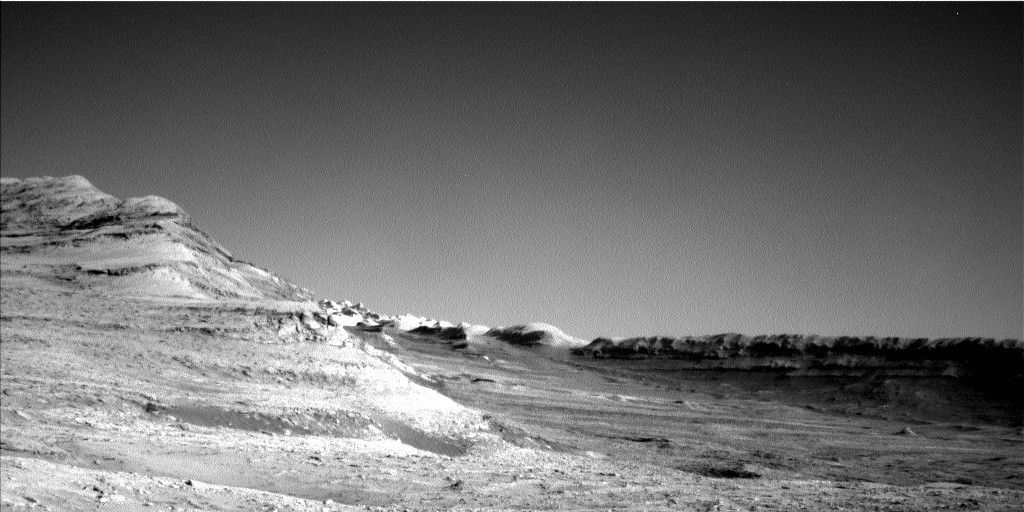
- instruments like Mastcam focused observations on distant “boxwork structures,” nearby “Mishe Mokwa” butte, bedrock troughs, dust characterization thru tau observations, and mosaics capturing geological features.
- ChemCam collaborated with APXS on atmospheric composition measurements, performed imaging (including LIBS spectral analysis), and conducted dark calibrations for instrument accuracy.
- Arm-mounted activities focused on two bedrock targets using APXS (Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer), DRT (Dust Removal Tool), and MAHLI (Mars Hand Lens Imager).
- Environmental observations included Navcam surveys for dust devils, air quality assessments within Gale Crater, cloud movies, and also REMS (Rover Environmental Monitoring Station), RAD (Radiation Assessment Detector), DAN (Dynamic albedo of Neutrons) data collection.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The mission updates underscore the operational challenges faced by robotic exploration in Martian winters. The approaching southern hemisphere solstice puts significant strain on power resources due to colder conditions in Gale Crater. Despite these limitations, the team has demonstrated efficiency in balancing scientific objectives with energy budgets-a testament to careful planning.
Scientific priorities focus heavily on “boxwork structures” that may provide insights into past geological processes on Mars. Similarly notable are efforts aimed at characterizing atmospheric dust levels amidst seasonal variations. From an analytical standpoint relevant to India’s space exploration ambitions-highlighted recently by ISRO’s lunar success-the resource optimization strategies adopted here serve as valuable lessons for future long-term extraterrestrial missions.
India could reflect upon such carefully managed workflows while envisioning it’s prospective interplanetary goals like Mangalyaan successors or a human lunar mission where robust adaptability under adverse conditions would be pivotal.