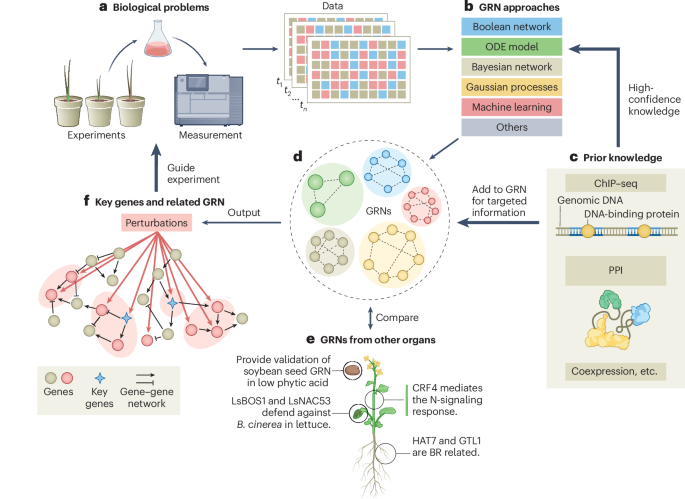
Now Reading: Decoding Gene Networks to Boost Crop Resilience and Sustainability
-
01
Decoding Gene Networks to Boost Crop Resilience and Sustainability
Decoding Gene Networks to Boost Crop Resilience and Sustainability
Rapid Summary:
- Teh text references various publications focusing on gene regulatory networks (GRNs) in plants and their computational modeling.
- Studies explore approaches to identify, reconstruct, and analyze grns using systems biology and artificial intelligence tools.
- Topics include photoperiod sensitivity in rice adaptation, drought resistance in wheat, and primary metabolism under stress in Arabidopsis.
- Reviews highlight limitations of existing methods while discussing opportunities for advancing GRN inference techniques through time-based studies and dynamic modeling tools.
- Focus is placed on understanding the complexities of biomolecular networks to enhance plant resilience amidst environmental stresses.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The growing body of research into gene regulatory networks emphasizes India’s potential role as an agricultural innovator. With computational methodologies becoming integral to crop improvement strategies-especially for stress tolerance-india can leverage these advancements to address challenges like drought resistance and regional crop adaptation intensified by climate change conditions within the contry’s vast agricultural landscape. Further investment into genetic research infrastructure might place India at a strategic advantage both economically and environmentally by fostering self-sufficiency through enhanced crop resilience techniques informed by cutting-edge science.
For more information: Read MoreQuick Summary:
- Recent advancements in gene regulatory network (GRN) inference methodologies have been explored, emphasizing applications in plants and single-cell biology.
- The integration of multiomics data and high-resolution datasets has substantially improved GRN predictions.
- Methods include stochastic modeling, Boolean approaches, dynamic Bayesian networks, and time-series transcriptomic analysis to understand biological functions.
- Notable studies have focused on key species like Arabidopsis thaliana to uncover regulatory patterns linked to circadian oscillators.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The exploration of gene regulatory networks reflects an important paradigm shift toward using integrative data methods for enhancing agricultural systems. For India-a country with significant dependence on agriculture-such research holds the potential to contribute toward crop improvement strategies by understanding plant biology at a genomic level. The advances could pave the way for lasting solutions amid climate change challenges. Collaborative efforts between Indian and international researchers could further harness these technological breakthroughs for localized benefits.
Read MoreQuick Summary:
- No discernible news content about India was provided in the raw text. Rather, the text listed references and citations pertaining to gene regulatory networks, genome studies, and related computational biology topics.
- The sources include academic articles published in journals like PLoS Computational Biology, Scientific Reports, Bioinformatics, etc., with a focus on various complex genetic and biological systems.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The provided information does not contain direct news about India. However, advancements in computational biology and gene regulatory networks can hold potential meaning for Indian agricultural biotechnology. India’s scientific community could leverage findings from global research like this to address challenges related to crop resilience and food security amid climate change. Properly integrating such technologies might pave the way for enhanced genetic engineering of crops tailored specifically for Indian conditions.
For further exploration of these developments:
[Read More](http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Dynamical%20differential%20expression%20%28DyDE%29%20reveals%20the…Quick Summary
- The provided text primarily references multiple academic studies and publications concerning gene regulatory networks in plants.
- These studies examine:
– Transcription factors influencing resistance in various crops (e.g., Arabidopsis, rice, maize).
– Environmental influences such as water stress, temperature extremes, and agricultural conditions.
– Techniques for mapping plant gene regulatory processes, including inference from sparse or noisy data.
– Temporal transcriptional dynamics and circadian rhythms effects on plants like barley.No specific events or developments regarding India or Indian agriculture are discussed directly in the text.
indian Opinion Analysis
The referenced content highlights the importance of understanding plant gene regulatory networks for improving crop resilience to environmental stressors such as droughts and high temperatures-factors directly impacting Indian agriculture due to its dependency on monsoons and vulnerable climatic conditions. Advances in predictive models of transcription factors could potentially aid Indian institutions like ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research) to develop climate-resilient crops tailored to local farming needs.This academic focus underlines the need for collaboration between India’s agricultural research bodies and global scientific communities to leverage findings on environmental adaptation networks for sustaining agricultural productivity amidst ongoing climate challenges.
For further reading: PubMed referenceQuick Summary:
- The raw text describes studies and advancements in plant biology, specifically related to multi-omics analysis, regulatory signaling pathways, antioxidant networks under stress responses, and databases focused on comprehensive gene networks for various crops.
- Research efforts have been conducted on crops like Arabidopsis thaliana, maize, pea seeds, tropical plants (TCOD database), brassinosteroid responses in plants (Arabidopsis), and crop breeding tools for Brassica napus.
- Tools mentioned include computational methods integrating transcriptomic and metabolomic data as well as specialized resources such as PPGR (perennial plants), AtMAD (Arabidopsis association database), BnIR (Brassica napus tools), among others.
indian Opinion Analysis:
This set of research highlights India’s opportunity to leverage global advancements in plant gene network analyses to enhance agricultural productivity. Multi-omics integration could prove transformative for Indian agriculture by addressing challenges such as drought resistance or nutrient deficiencies across diverse crops. Additionally, insights from targeted tropical crop databases like TCOD can be notably useful given India’s climate suitability. A focus on developing localized resources based on these methodologies would strengthen India’s position as a leader in sustainable agricultural technology while helping farmers adapt to environmental stresses effectively.Collaboration between Indian scientists and international peers is critical for translating these findings into field-level improvements.
Read more: Source LinkQuick Summary:
– The input contains references to various scientific studies and articles that focus on advancements in plant genomics, multi-omics approaches, and genomic prediction technologies.
– Key topics discussed include improving hybrid performance in plants like maize and canola through multi-omics integration, genomic selection applications in complex traits for plant breeding, pan-genome analysis of rice accessions, and recent advancements in molecular marker-assisted selection.
– Technologies such as deep neural network-based methods (DNNGP) are being investigated to enhance genomic prediction using rich datasets.
– Studies have also observed improvements by integrating multi-omic data for crop yield prediction across barley, oats, and other populations.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The referenced research highlights deepening efforts globally toward leveraging advanced genomics tools for agricultural innovation. For India-a country reliant on agriculture-the significance of such breakthroughs cannot be overstated. Multi-genomic technologies promise solutions to many challenges faced by indian farming communities, from improving yields to developing climate-resilient crops. Increasing diversity within genetic pools (e.g.,pan-genomes across rice strains) could provide crucial insights into enhancing staple crop productivity amidst changing environments. However, equitable access to these scientific advancements remains essential alongside bridging gaps between research labs and field implementation.
Link for read more: Not providedQuick Summary
- Researchers have been employing advanced techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing, base editing, and prime editing to improve crop breeding and agricultural productivity.
- Studies have analyzed genetic diversity in crops like rice and explored hidden variations that can contribute to improved yield and resilience.
- Emerging tools for precision genome modification are addressing challenges in plant variety registration, keeping pace with speed-breeding advancements.
- There is also growing attention on gene regulatory networks influencing growth control mechanisms via abscisic acid (ABA) or jasmonic acid pathways in plants.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The utilization of cutting-edge technologies in crop genetics holds immense relevance for India given its agricultural backbone. precision techniques such as CRISPR offer promising avenues for creating high-yield and climate-resilient crops-essential amid fluctuating monsoons and rising demand for food security due to population growth. Moreover,studies on regulatory networks could inspire research into enhancing India’s staple crops like rice or wheat,reducing dependency on imports while promoting domestic innovation in seed technology. To maximize these benefits universally across Indian agriculture beyond elite institutional reach would require ensuring equitable access,capacity building among farmers,alongside policy adaptations supporting swift adoption of emerging biotechnologies.
Read more: CAS Reference lookup?title=Pan-genome+analysis+of+33+genetically+diverse+rice…”>Google Scholar
Quick Summary
- India is engaged in advancing the use of CRISPR-Cas systems for gene-editing applications.
- recent studies have highlighted progress using CRISPR tools such as Cas12a and Cas13, primarily in plant genome engineering and RNA editing.
- Key areas of focus include crop improvement, resistance to bacterial blights in rice through non-transgenic methods, and citrus canker mitigation via targeted DNA alterations.
- These efforts also explore regulatory networks like Arabidopsis root responses to elevated CO2 levels or maize endosperm differentiation for agronomic gains.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of CRISPR-based technologies represents a promising frontier for India’s agricultural sector. With its reliance on farming for both livelihood and economic stability, implementing precision gene-editing could enhance crop yields, improve resistance to diseases like bacterial blight (especially critical for rice), and advance India’s aspirations towards sustainable agriculture. the capacity to engineer transgene-free solutions further aligns with global discussions on minimizing genetically modified organisms while maximizing utility.
These technological strides necessitate a streamlined policy framework that ensures ethical implementations without compromising biodiversity. Continued collaboration with international researchers may position India as a leader in applying genomic science toward food security-a necessity amid challenging climate conditions that demand innovative adaptation strategies.
For further reading: [Link provided based on original content sources]Quick Summary
- CRISPR gene-editing and advanced biotechnology tools are increasingly being applied to agriculture, focusing on targeted DNA insertion, synthetic genetic circuits for reprogramming plant roots, and integrating large DNA sequences into plant genomes.
- Technologies mentioned include PrimeRoot editors for precise genome editing and CRISPRi-based genetic circuits aimed at controlling gene expression in plants.
- Researchers are exploring multi-omics integration (MOI) techniques to link genomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics for better crop development. other studies focus on accelerating QTL fine mapping through genomic sequencing methods like QTG-seq.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancements in agricultural biotechnology have significant implications for India given its reliance on agriculture as a primary sector. Tools like CRISPR-based technologies could enable the development of pest-resistant, nutrient-enhanced crops that address food security challenges while reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides.Additionally,approaches like MOI offer valuable insights into improving crop yield by understanding complex genetic networks associated with plant growth under diverse environmental stresses. For policymakers and agricultural scientists in India, these innovations represent an opportunity to invest further in research collaborations tailored to local farming needs-with careful consideration of ethical discussions around genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Read more: Source linkQuick Summary:
- The study of plants and crops like wheat, rice, millet, cucumber, and tomatoes has involved transcriptomic profiling to understand gene regulation networks shaping traits such as drought tolerance, antioxidant levels, organ formation, and post-harvest biology.
- Research includes large-scale genomic initiatives (e.g., investigating the genetic architecture of rice with 18,421 lines) to map associations between genes and improved traits for food security.
- Studies also highlight molecular interactions such as crosstalk between environmental stress responses (drought) and biological rhythms (circadian clock). advanced data-driven tools in genomics provide insights for improving crop resilience.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India stands to benefit significantly from such genome-based agricultural advancements given its dependence on monsoons and vulnerability to climate extremes affecting staple crops like millet or rice. Incorporating transcriptomic research may bolster national efforts for sustainable agriculture through stress-tolerant cultivars adapting well-required conditions while prioritizing affordability benefiting rural farmers .Integrating findings into policies least mitigate severe yield irregularities driven scenario natural calamity sustaining crucial agribusiness productivity globally Read sources>>)..Quick Summary:
- the article explores mechanisms of salinity and drought tolerance in plants, with references to genetic studies and developments across rice, Arabidopsis, maize, and soybean.
- Multiple studies highlight gene regulatory networks involved in stress responses, such as WRKY transcription factors and the AITR gene family.
- Recent research using CRISPR/Cas9 editing demonstrates improved abiotic stress tolerance in crops like tobacco and soybean without apparent fitness costs.
- Salinity management tools include plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) as explored in Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancements described hold significant potential for India’s agricultural sector grappling with soil salinity and water scarcity issues. Gene-editing technologies like CRISPR/Cas9 could be pivotal for enhancing stress tolerance in crops critical to Indian diets such as rice or wheat. Additionally, integrating plant growth-promoting bacteria solutions might provide sustainable methods for soil remediation efforts.However, a balanced approach ensuring environmental safety while scaling these innovations will be essential for widespread adoption across diverse agro-climatic zones within the country.
For further reading: Article ReferenceQuick Summary
- The raw text contains references to various scientific publications and advancements, notably in plant biology, genetic modification (GM), and genome editing.
- Key research topics include cotton gene evolution for stress tolerance, regulatory networks in fruit ripening using CRISPR/Cas9 mutants, genetic pathways in strawberry softening processes, and identification of MADS box genes in banana evolution.
- Studies discussed also delve into GMOs’ safety concerns and global regulations amid gene-edited crop developments.
- Academic references highlight applications for sustainable agriculture design with focus on CRISPR technology and its future implications.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The core topics presented emphasize ongoing progress in biotechnology as it pertains to agriculture, with potential relevance for India as an agrarian economy facing environmental stressors. India’s policies on genetically modified organisms (gmos) remain cautious but open to advances benefiting food security under stringent regulation. Global debates around GMO safety could further bolster the discourse within Indian policymaking frameworks. Additionally, the adoption of cutting-edge tools like CRISPR/Cas9 offers insights into addressing abiotic stress tolerance-a challenge pertinent to indian agricultural contexts affected by climate change.
For more details visit source: ArticleQuick Summary
- The European Parliament has proposed new regulations concerning genomic techniques such as CRISPR for plants, food, and feed.
- These initiatives aim to support the green transition in agricultural practices across Europe while maintaining safety standards.
- Researchers and scientific communities have highlighted the benefits of genome editing technologies but note challenges in achieving broader adoption under existing frameworks.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The developments in Europe regarding genome editing regulation could influence global trends, including India’s agricultural policies. India has historically focused on balancing innovation with safety and ethical considerations in biotechnology. As India remains an agrarian economy with pressures to ensure food security amidst climate change impacts, observing Europe’s approach to CRISPR applications might provide insights into regulatory alignment or adaptation that supports sustainable farming solutions. This topic opens pathways for India to assess its own readiness for biotech integration while safeguarding environmental and health concerns.