Now Reading: Did Sunscreen Shield Ancient Humans During Polar Reversal?
-
01
Did Sunscreen Shield Ancient Humans During Polar Reversal?
Did Sunscreen Shield Ancient Humans During Polar Reversal?
Quick Summary
- Ancient humans, about 40,000 years ago, possibly used mineral sunscreen, tailored clothing, adn caves for shelter to protect themselves from harmful solar radiation during Earth’s geomagnetic pole reversal.
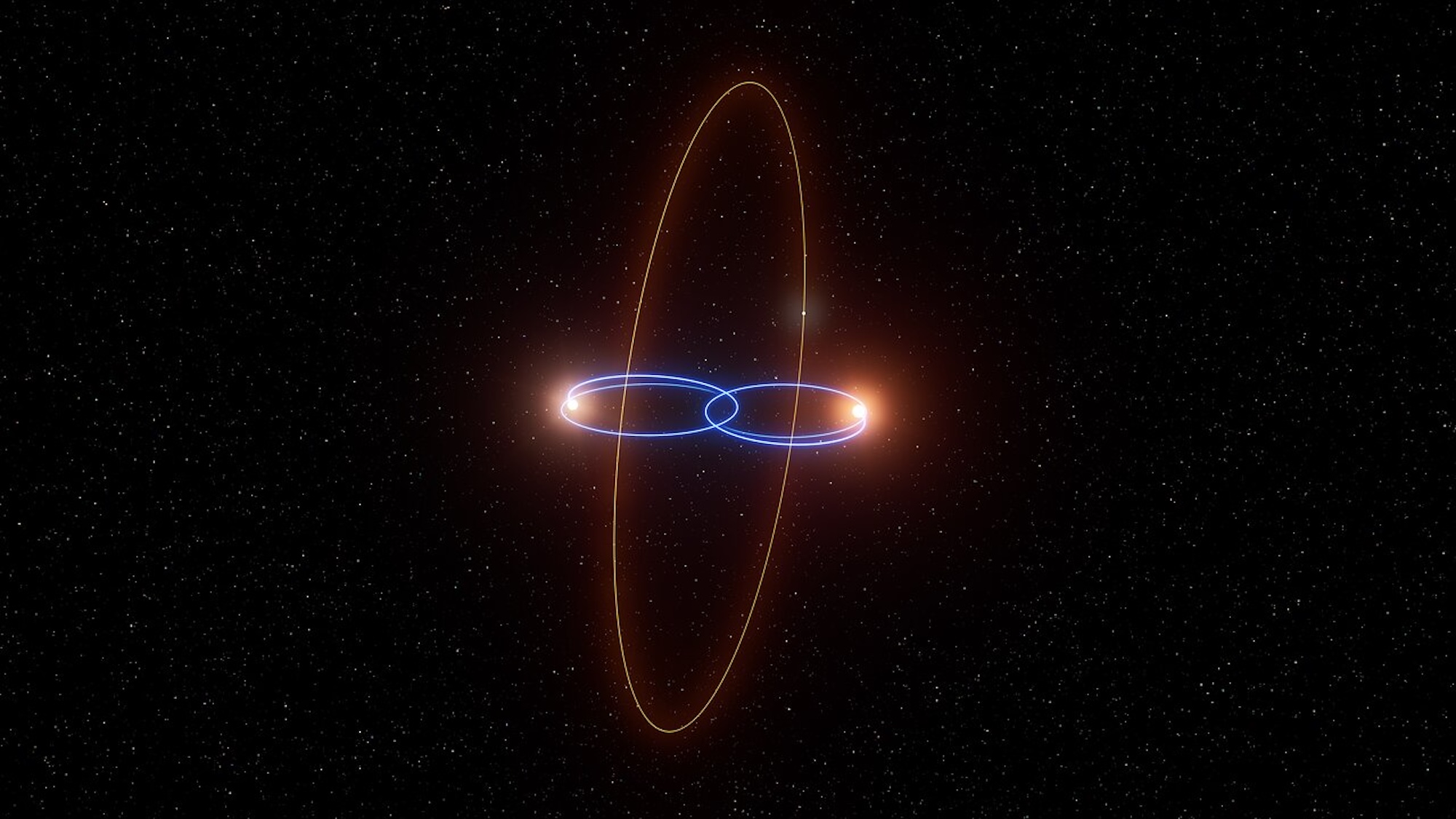
- Earth’s magnetic poles occasionally shift positions in a process called geomagnetic excursions. The most recent one, the Laschamps excursion (41-42k years ago), resulted in weakened magnetic fields that exposed the planet to increased UV radiation and widespread auroras.
- Archaeological evidence indicates Homo sapiens adapted through technological advancements such as tailored clothing and using ochre pigment with sun-protective properties. These changes coincided with the decline of Neanderthals in Europe around the same period.
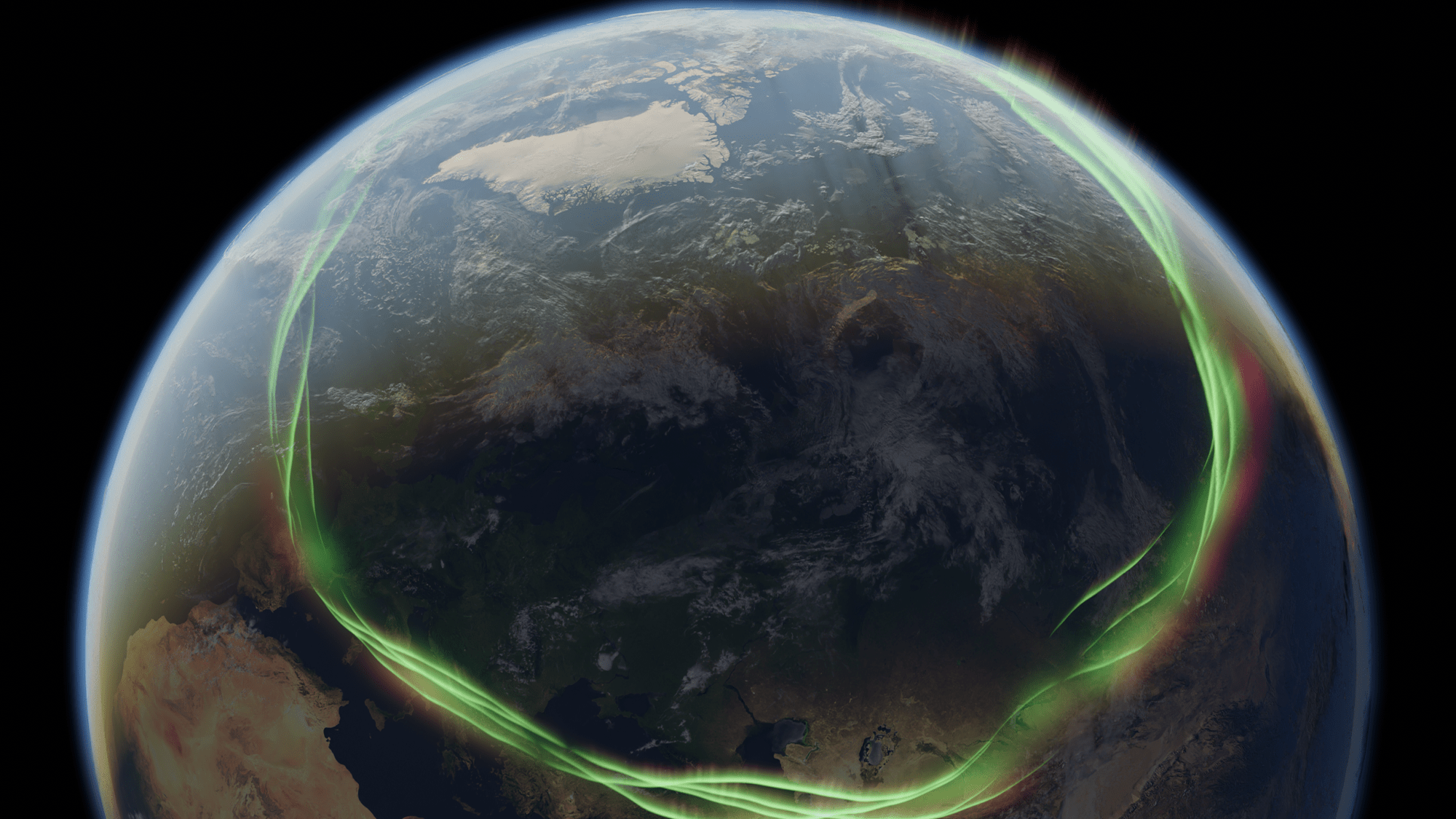
- Scientists used 3D models to reconstruct Earth’s geospace system during this reversal period, suggesting how charged particles interacted with the weakened protective field and how auroras were visible over much wider regions like Europe and northern Africa.
- Study co-authors highlighted correlations between human activity shifts and environmental conditions created by geomagnetic changes but emphasized these findings as not definitive.
Image Captions:
- “An illustration of what the aurora might have looked like during a polar reversal about 41,000 years ago.” Credit: Maximilian Schanner (GFZ Helmholtz Center for Geosciences).
- “An artistic impression of what the aurora might have looked like on Earth about 41,000 years ago.” Credit: GFZ Helmholtz centre for Geosciences.
- “What an aurora across more southern parts of Europe may have looked like.” GFZ Helmholtz Centre for Geosciences.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Geomagnetic pole reversals provide fascinating insights into Earth’s past ecosystems while also raising potential concerns about future disruptions if similar events occur today.India’s scientific community could benefit from building interdisciplinary research capability focused on space-weather impacts as communications infrastructure-critical to india’s rapidly modernizing economy-could be vulnerable in scenarios involving weakened magnetic fields or plasma intrusions into Earth’s atmosphere.
Additionally, lessons from ancient Homo sapiens’ adaptations highlight humanity’s resilience amid environmental challenges-a trait crucial for today’s population confronting climate change risks or extreme weather phenomena caused by solar activity fluctuations (e.g., satellite failures). While findings from studies are correlational rather than conclusive dissection tools regarding evolution differences just broaden areas overlap across review historicism nurture defense systems better deployed prediction-driven alerts offering knowledge safeguard ecosystem-sensitive countries large populations!