Now Reading: Discovery of Conserved RNA Regulatory Switches Through Advanced Mapping Techniques
-
01
Discovery of Conserved RNA Regulatory Switches Through Advanced Mapping Techniques
Discovery of Conserved RNA Regulatory Switches Through Advanced Mapping Techniques
Quick Summary
- RNA molecules play crucial roles in cellular processes,driven by their ability to form complex structures.
- Recent advancements enable simultaneous examination of thousands of RNA secondary structures in a single experiment, but focus has remained on identifying single conformations per transcript.
- DRACO, an optimized algorithm using chemical probing and mutational profiling (MaP), deconvolves structural ensembles from transcriptome-wide data efficiently.
- A novel approach integrates DRACO analysis with automated evolutionary conservation assessment (DeConStruct) to identify functional RNA regulatory switches.
- Key findings include: dynamic RNA structural ensembles with regulatory roles identified in viruses and humans; functional insights into bacterial RNAs like riboswitches and thermometers; and the discovery of 5′ UTR-mediated structural regulation impacting gene expression.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study underlines the increased complexity of cellular processes regulated by RNA molecules, bringing transformative potential to understanding gene expression and molecular biology at large.For India’s burgeoning biomedical sector, tools like DRACO offer pathways for innovation in research on genetic diseases or therapeutic targets such as viral infections. Unraveling how RNAs influence cell behavior could pave the way for advancements not just within academic circles but also translational science-designing drugs or vaccines tailored through modified gene transcripts. This research highlights global progress that indian institutions may leverage as they advance contributions to genomics-driven healthcare solutions.
Read moreQuick summary
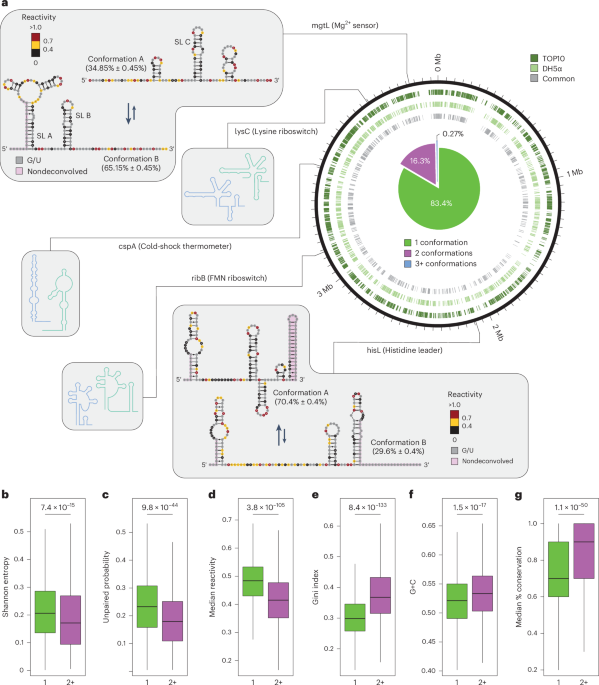
- Researchers conducted detailed mapping of RNA structure ensembles in E. coli, focusing on regulatory RNA switches under varying conditions.
- High Mg²⁺ concentrations and histidyl-tRNA levels favored specific structural conformations of RNA sequences, confirming abundant ligands drive structural changes.
- Comparative analysis of regions with single vs. multiple conformations showed that regions with higher structural heterogeneity (“2+ regions”) are more ordered, conserved, and likely functional as regulatory elements.
- “2+ regions” exhibited higher G+C content and conservation within genes across bacterial genomes, reinforcing their importance in biological regulation.
- The study developed an advanced framework called DeConStruct to identify conserved RNA switches and applied it successfully to detect cold shock response mechanisms using DMS-MaPseq analysis at 10°C.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research highlights the growing meaning of RNA structure analysis for understanding bacterial adaptation-an area relevant globally but also significant for India, particularly given its agricultural dependency on microbial ecosystems. studying mechanisms such as cold shock adaptations could help Indian scientists leverage beneficial microorganisms in biotechnology applications like biofertilizers or enduring farming solutions.India’s heavy involvement in pharmaceutical production could also benefit from these findings by advancing drug development targeting bacterial RNAs involved in antibiotic resistance or pathogenesis. Collaborative research integrating this knowledge into genome-wide studies could bolster India’s role as a leader in genetic innovation while improving healthcare solutions domestically and globally.
Such advancements reinforce the need for accessible scientific expertise and infrastructure investment by Indian policymakers to stay competitive amidst rapid progress worldwide.
Quick Summary
- The study investigates RNA structure changes in E. coli during a temperature shift from 37°C to 10°C.
- Cold shock leads to increased structural heterogeneity (~15.7% of transcriptome regions) compared to reduced heterogeneity (3%).
- RNA thermometers, such as cspA, switch between conformations at different temperatures, impacting translation efficiency.
- New cold shock-induced genes (cspG, cpxP, and lpxP) demonstrate translational regulation via their structured 5′ UTRs acting as RNA thermometers.
- Specific genetic elements were tested via IPTG induction experiments and in vitro transcription analysis to confirm temperature-dependent structural rearrangements promoting translation initiation at low temperatures.
- Chaperone proteins (e.g., cspc and CspE) are linked with assisting the structural switch in the RNA thermometer of lpxP mRNA.
A full-size image of Fig.2 detailing redistribution effects is included.
Quick Summary:
- researchers developed a method called 5′UTR-MaP to explore RNA structural switches within the 5′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of human mRNAs, focusing on translation regulation.
- Experiments conducted in HEK293 cells revealed robust enrichment of RNA structure data from 5′ ends using this technique, as compared to traditional sequencing methods.
- Results showed increased structural heterogeneity in ATP-depleted conditions and uncovered specific regions in the 5′ UTRs that can adopt multiple conformations, potentially impacting regulatory elements and translation efficiency.
- Certain structurally heterogeneous 5′ UTRs were observed to influence the usage of upstream open reading frames (uORFs) versus main ORFs during protein synthesis. This was confirmed by mutational experiments with fluorescence-tagged reporters for two studied RNAs: CKS2 and TXNL4A.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The findings represent significant progress in understanding RNA structure-function relationships at a transcriptome-wide scale. The innovative approach could be critical not only for advancing gene expression studies but also potentially informing translational medicine technologies. for India – as a growing center for biomedical research – these insights offer opportunities for deepening expertise in molecular biology,particularly regarding diseases influenced by RNA dynamics such as cancer or neurodegenerative disorders.Adopting similar frameworks may enhance India’s capabilities for precision medicine development or drug discovery targeting RNA structures.
Quick Summary
- Researchers have developed a framework called DeConStruct to analyze RNA structural switches in living cells, which regulate gene expression.
- Transcriptome-scale maps of RNA secondary structure ensembles were created, offering insights into the dynamic nature of RNA structures under various conditions.
- Experiments identified several conserved bacterial RNA structural switches and temperature-responsive mechanisms (“RNA thermometers”) influencing cold shock response.
- The study challenges traditional views on bacterial cold shock adaptation and reveals complex reorganizations of RNA structures under environmental shifts (e.g., temperature changes).
- Limitations include chemical probing constrained to Adenine and Cytosine residues, potentially missing small or A/C-poor regulatory elements. Future work may utilize new tools to overcome these constraints.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research highlights the growing importance of molecular biology approaches that bridge basic science with practical applications like synthetic biology or therapeutic developments. For india, where biotechnology is an expanding sector, such findings could pave the way for enhanced understanding of cellular responses to stress-a significant factor when considering agricultural productivity under climate extremes or drug-resistant pathogens. Large-scale frameworks like DeConStruct could be leveraged by Indian research institutions aiming for breakthroughs in genetic research or drug innovation.
From an operational perspective, promoting collaborative opportunities between India’s scientific community and international advancements in RNA-targeted therapeutic strategies might enable optimized solutions for public health issues such as antimicrobial resistance. Though, full realization requires continued investments in both labs and education programs focused on emerging genomic technologies.
Read more: Link
Quick summary
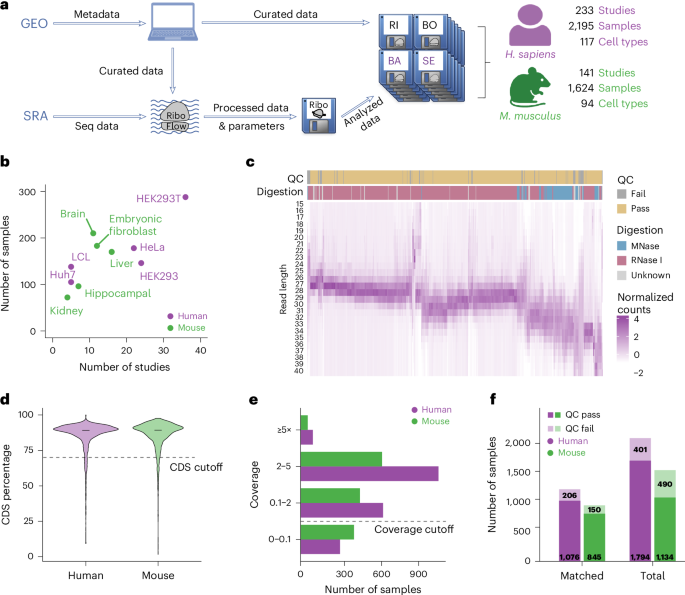
- The article primarily focuses on detailed methodologies related to RNA analysis, cloning, mutagenesis, protein production through Western blot techniques, and secondary structure modeling.
- methods involve HEK293 total RNA planning, targeted DMS-MaPseq library creation for genes like CKS2 and TXNL4A, and bacterial transcriptional unit annotations using tools like Cutadapt and PEAR.
- Secondary structure optimization of both bacterial (E. coli) and human rRNA was performed using ViennaRNA software with parameters derived from experimental datasets.
- Techniques such as fluorescence microscopy were employed for cellular imaging of proteins expressed via transfected vectors in HEK293 cells.
- Ensemble deconvolution analyzes RNA structural heterogeneity using the DRACO algorithm to classify coexisting RNA conformations.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The presented research advances capabilities in analyzing RNA structures across bacterial and human systems. India’s focus on biotechnology aligns with these methodologies by emphasizing molecular biology in academia and industry. These processes could be relevant for applications like drug discovery or gene therapy within the Indian pharmaceutical sector.
For Indian biologists or institutions aiming to replicate similar experiments or innovate on them, challenges might arise around access to high-cost equipment (e.g., ultrasonic processors) or reagents from foreign companies detailed extensively here. It underscores a need for indigenous development of laboratory technologies to reduce dependence.
Moreover, emerging multi-disciplinary fields like bioinformatics could see utility given data-intensive steps such as sequencing analysis are involved-a domain where India has been competitive globally.
Read More: [Link placeholder for the original article.]
Quick summary:
- The DRACO algorithm has undergone updates (version 1.2) to improve structural ensemble deconvolution for RNA sequences.
- Enhancements include increased random initializations, decreased weight factors, and repeated graph-cut procedures to achieve minimum normalized scores.
- Parameters for different biological samples-E.coli and HEK293 cells-were tailored for analysis, adjusting window sizes and nucleotide coverage requirements.
- DRACO test results show effective detection of riboswitches in bacteria across conditions such as temperature variations (cold shock at 10°C vs. 37°C) or ATP levels (standard vs.depleted).
- Ribosome profiling techniques were paired with RNA-seq data to evaluate translation efficiency influenced by RNA structure heterogeneity under varying experimental settings.
Source page: https://github.com/dincarnato/draco/
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancements in DRACO signify an crucial leap forward in the precise modeling and study of RNA’s structural dynamics under diverse conditions. For India, where biotechnology research is rapidly growing-especially in genomics-the implications are notable within fields like agricultural biotech, environmental microbiology, or healthcare diagnostics.
This new framework opens avenues for refining genetic studies on local bacterial strains or human cellular responses tailored to India’s unique climatic stresses (e.g.,extreme heat/cold). Such tools could further enhance interdisciplinary projects aimed at combating antibiotic resistance or optimizing crops against challenging environments effectively.
As local science institutions adopt tools like these, collaborations with global repositories may deepen India’s footprint in bioinformatics research while minimizing demand on computational resources-a priority given cost constraints typical of developing economies.Quick Summary
- The article delves into a genome-wide RNA structural mapping study using advanced computational and experimental techniques.
- It outlines the methods for identifying conserved RNA regulatory switches in living cells, focusing on secondary structures and covariation analysis.
- Tools such as R-scape, Infernal’s cmsearch, DRACO pipeline, and others were utilized to evaluate structural dynamics and alignments across various systems like bacterial genomes and human transcripts.
- The study addresses mutants designed to stabilize RNA conformations for specific biological functions while preserving amino acid sequences.
- Data derived from this research is publicly available on platforms such as Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), Zenodo, and specific repositories linked in the text with source codes provided for reproducibility.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research showcases the significant strides made globally in genomic technology. For India, advancements of this caliber highlight opportunities to leverage refined RNA-based methodologies within emerging biotech hubs or research institutions domestically. India’s growing interest in genomics-from healthcare applications like precision medicine to agriculture-can benefit from insights drawn from studies that map RNA structural ensembles. It signals an urgent need for investment not only in relevant high-throughput technologies but also talent development aligning with bioinformatics tools introduced here.
these findings underscore global collaboration potential while reminding us of India’s role as both contributor and beneficiary of open science ecosystems that share data/resources akin to those mentioned above. Exploring partnerships or replicating such frameworks regionally could dramatically elevate India’s genetic research capacity.
Read more: [Link unavailable in input]It seems the provided content contains reference material related to scientific studies, potentially about RNA structure and associated research findings. Sadly, I cannot ascertain any news article specifics or relevant india-centric details from the given text. Kindly provide a specific news body or detailed input regarding Indian events or topics for me to generate a concise write-up in the “quick Summary” and “indian Opinion Analysis” sections as per your request.The input appears to be a series of academic references and publication details related to biological studies, particularly focusing on RNA, cold shock responses, bacterial gene expression regulation, and related molecular biology topics.There seems to be no explicit raw text of a news article about India within this input.
If you’d like me to create sections “Quick Summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis” for an article regarding india specifically, please provide relevant source text. Let me know how I can assist further!It appears the input text provided is comprised of academic references and citations related to bacterial cold shock proteins and RNA structural studies, rather than a news article on India. In this very way,it does not provide adequate information relevant to Indian context or news topics for creating the required “Quick summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis.” Could you please provide the appropriate content or clarify your request?Quick Summary:
- The source text discusses advancements in RNA research, particularly focusing on translation regulation.
- Studies explore mechanisms like RNA G-quadruplexes and upstream open reading frames (uORFs) that impact mRNA translation.
- New tools and methods have been developed for mapping translation initiation sites at single-nucleotide resolution and probing RNA structures.
- Specific investigations address G-quadruplexes’ role in targeting NRAS 5′ UTR,alternative codon usage,and mutation signature filtering for high-fidelity structure analysis.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s biomedical research sector could stand to benefit from these findings as they highlight novel pathways in understanding gene expression regulation. With greater emphasis on precision medicine worldwide, Indian institutions may leverage these advanced methodologies for exploring genetic predispositions common among its diverse population. Investment in genomic research could lead to innovations targeting cancer, neurological disorders, and other diseases prominent within the country’s demography.Adoption of such tools might also help India advance drug discovery programs tailored specifically to regional needs while enhancing its position in global scientific contributions.It seems the input provided primarily consists of references related to scientific research and tools rather than a specific news article about India. To help organize this information properly, I would need additional clarification or specific details regarding the intended focus of this content. If this is meant to be used for an Indian-focused analysis or summary, kindly provide a relevant story or topic directly involving India.Quick Summary
- Researchers have identified conserved RNA regulatory mechanisms, particularly structural switches, within living cells.
- The study utilizes techniques such as RNA secondary structural ensemble mapping and covariation analysis to detect evolutionary conserved structures.
- Findings elucidate how RNA thermometers and regulatory conformations enable responses to external stimuli like temperature and cellular energy levels.
- Experimental work involved organisms ranging from E.coli to HEK293 cells under varying environmental conditions (e.g., ATP depletion and temperature shifts).
- Advanced algorithms (e.g., DRACO) were developed for data modeling and analysis, showcasing high innovation in computational biology tools.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This study highlights the growing intersection of molecular genetics with computational biology. Its implications for india are significant given India’s budding research ecosystems in biotechnology. Advanced understanding of RNA regulation could drive innovations in medical therapeutics or genome engineering-areas where Indian researchers are increasingly active. Additionally, insights from this study into adaptive biological responses may align with India’s focus on tackling agricultural resilience against climate change. strengthening collaborations between global research institutions and Indian labs could ensure knowledge sharing that benefits both parties in addressing scientific challenges critical to human health or biotechnological advancements.
Quick Summary
- A study published in Nature Biotechnology (July 25, 2025) explores RNA regulatory switches in living cells.
- The research introduces a method using RNA secondary structure ensemble mapping and covariation analysis to identify conserved RNA regulatory elements.
- The study emphasizes applications in understanding how cellular regulatory mechanisms work at the RNA level across diverse species.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings of this research offer significant potential for India’s growing biotech and pharmaceutical sectors. By identifying conserved RNA regulatory switches,researchers globally can develop more effective therapeutics targeting diseases with an underlying genetic or molecular basis. For India, this could accelerate advancements in areas like precision medicine and vaccine development. Moreover, incorporating such innovative global methodologies might position Indian biotechnology firms as competitive players on the world stage.