Now Reading: Discovery of Metallic Spherules Sparks Scientific Interest
-
01
Discovery of Metallic Spherules Sparks Scientific Interest
Discovery of Metallic Spherules Sparks Scientific Interest

Rapid Summary
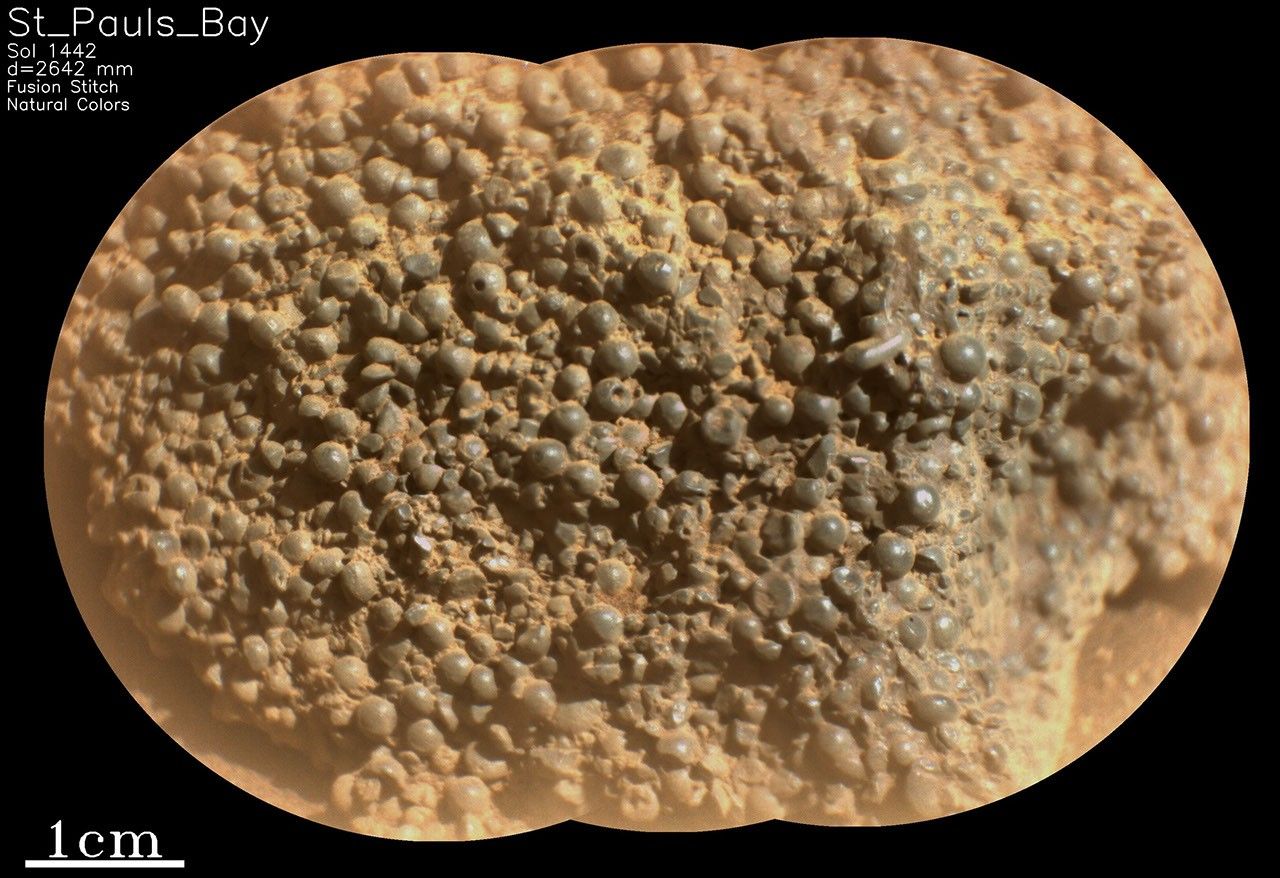
- The Perseverance rover team recently discovered a strange rock named “St. Pauls Bay” at broom Point on the Jezero crater rim.
- The rock is composed of hundreds of millimeter-sized, dark gray spheres, with some exhibiting elliptical shapes, angular edges, or tiny pinholes.
- Similar discoveries of spherules have been made on Mars before, such as Martian Blueberries by Prospect rover and other formations observed by curiosity and Perseverance in different areas.
- Scientists suggest these spherules could have formed via groundwater interaction within rocks, rapid cooling of molten droplets during volcanic eruptions, or condensation after meteorite impacts.
- This discovery is significant for interpreting the geological history around Witch Hazel Hill and understanding Mars’ evolution; linking these features to wider stratigraphy at Jezero crater remains ongoing.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This recent finding by NASA’s Perseverance rover underscores another intriguing chapter in humanity’s pursuit of understanding extraterrestrial geology and planetary evolution.For India-among nations increasingly active in space exploration-the technological strides showcased here affirm the importance of global collaboration toward uncovering Martian secrets that could parallel Earth’s own geologic past or hint at conditions for life elsewhere. As ISRO undertakes aspiring missions like Gaganyaan and chandrayaan programs while bolstering interplanetary research capabilities, such findings highlight areas deserving attention-from fostering planetary geology expertise to advancing robotics for extraterrestrial terrain analysis.