Now Reading: Endangered Shark Meat Continues to Appear on Store Shelves
-
01
Endangered Shark Meat Continues to Appear on Store Shelves
Endangered Shark Meat Continues to Appear on Store Shelves
Quick Summary
- Shark species, including critically endangered types like great hammerhead and scalloped hammerhead, are being sold in grocery stores, seafood markets, and online despite conservation laws.
- A study conducted by UNC Chapel Hill revealed that 93% of sampled shark meat products were ambiguously or incorrectly labeled.
- DNA barcoding of 30 shark meat samples found 31% contained meat from endangered or critically endangered species such as great hammerhead, scalloped hammerhead, tope, and shortfin mako sharks. others came from vulnerable species like spinner and blacktip sharks.
- Some mislabeled products included packages claiming to sell blacktip shark but containing the endangered shortfin mako instead.
- Endangered apex predators like great hammerheads are sold at surprisingly low prices (as little as $2.99 per pound).
- Certain shark species found in the study contain dangerous levels of metals such as mercury and arsenic that pose health risks including brain damage, nervous system impairment, or cancer.
- Regulations under CITES and the Endangered Species Act aim to manage shark meat sales but face challenges due to ambiguous labeling when these meats enter markets disguised as fillets without clear identification.
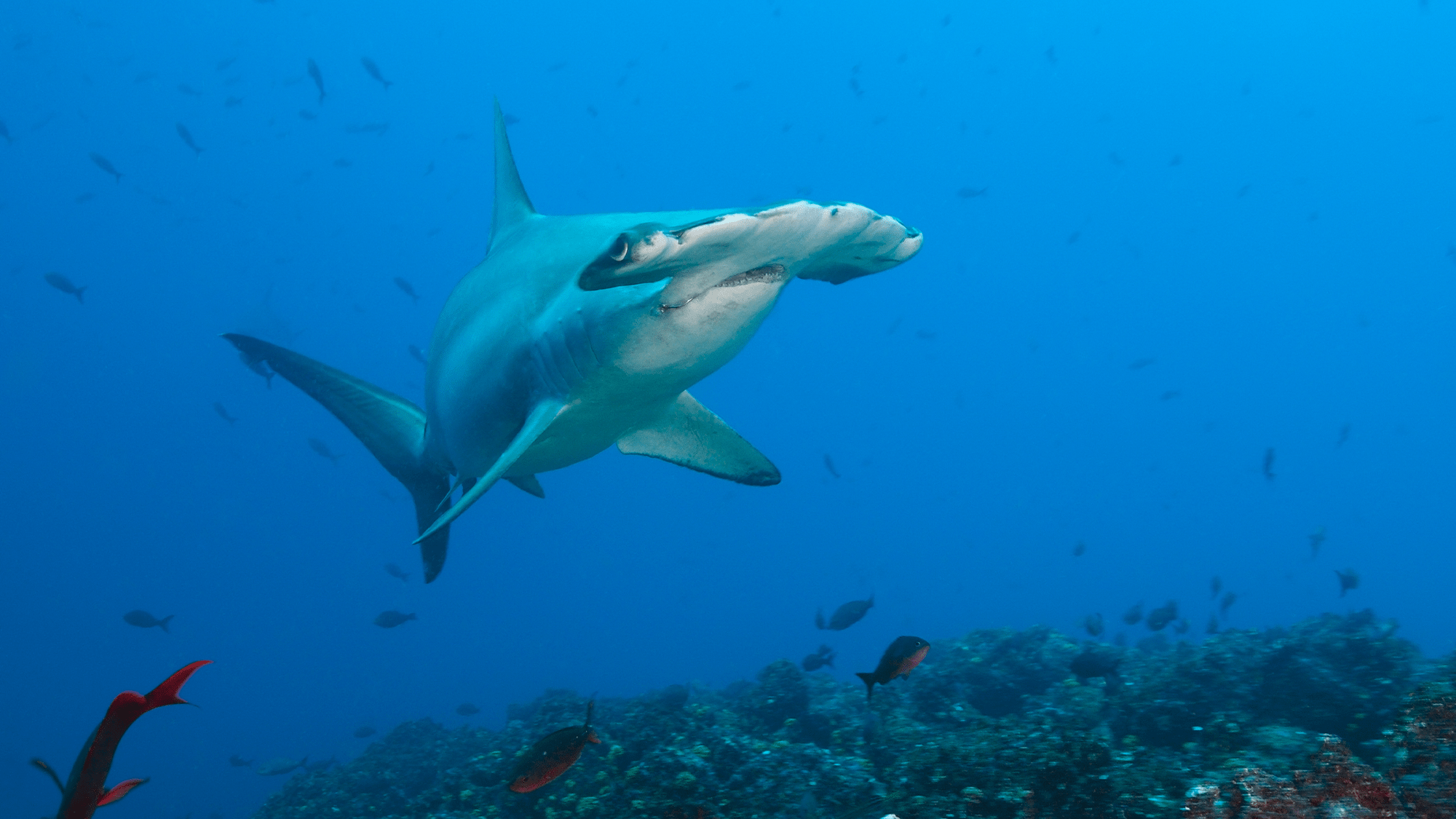
!Scalloped Hammerhead Shark
scalloped hammerheads are large apex predators. This one is swimming in the Galápagos Islands off the coast of Ecuador. CREDIT: Prisma Bildagentur via Getty Images.
!Shark Meat Samples
Some of the shark meat purchased during this study. CREDIT: Savannah Ryburn.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings highlight a troubling intersection between biodiversity conservation efforts and market oversights on a global scale. While India is not explicitly mentioned as a source or consumer market for these products in this report, it remains pertinent for Indian authorities to consider how labeling openness affects wildlife protection measures-a recurring challenge worldwide.
Sharks are integral components of marine ecosystems akin to tiger populations within forests; their disappearance would create cascading effects through oceanic food chains. For India-home to rich coastal biodiversity-it is crucial that policies around seafood traceability be strengthened not only for ethical reasons but also public health concerns tied to mercury contamination found in predator fish meats.Ensuring proper implementation of international wildlife trade regulations (e.g., CITES) coudl also bolster India’s reputation in marine resource management globally. The report further underscores how vigilant consumer practices-as recommended by researchers-could complement governmental policies aimed at enduring marine resource use.






















