Now Reading: ESA Unveils Euclid Mission to Probe the ‘Dark Universe
-
01
ESA Unveils Euclid Mission to Probe the ‘Dark Universe
ESA Unveils Euclid Mission to Probe the ‘Dark Universe

speedy Summary
- Mission Goals: ESA-led Euclid mission, with NASA’s contributions, aims to study dark energy and the universe’s accelerating expansion by observing billions of galaxies.
- Recent Data Release: ESA has publicly released early data from Euclid on March 19, showcasing observations that help prepare tools for larger future analyses.
- Scope of Observations:
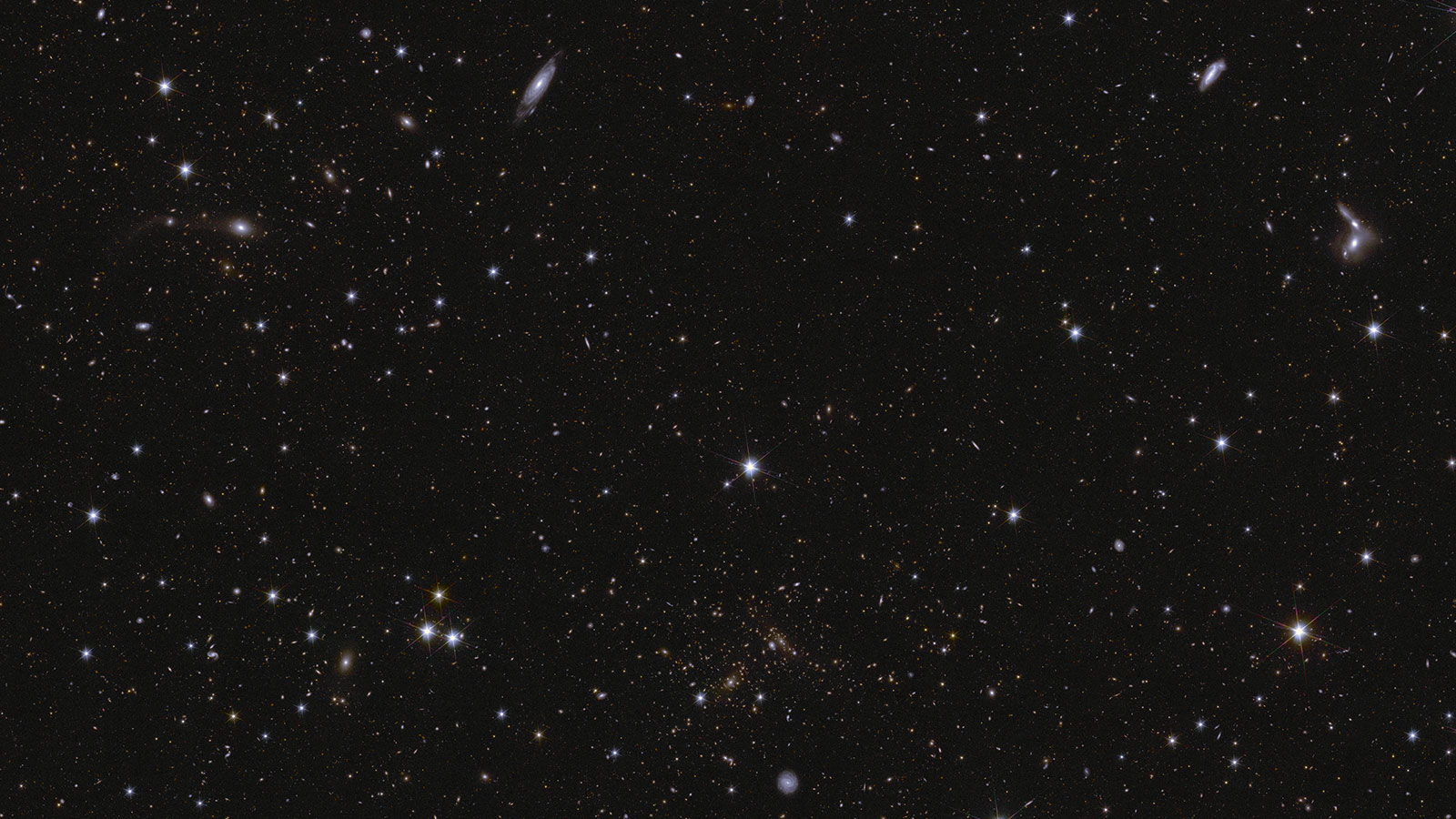
– Initial release includes images of 26 million galaxies in three “deep fields,” the farthest being over 10.5 billion light-years away.
– Full survey aims to cover one-third of the sky (14,000 square degrees) during its six-year mission.
- Scientific Techniques:
– Creating detailed maps with gravitational lensing effects to measure dark matter distribution and track dark energy’s influence over cosmic history.
- Upcoming Developments: Final cosmology data will be released in October 2026; NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will complement Euclid studies starting from its launch in 2027.
- collaborative Efforts: More then 2,000 scientists from various countries contribute; NASA plays a role through instrumentation advancement and U.S.-based scientific investigations.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the Euclid mission symbolizes significant international collaboration between agencies like ESA and NASA to uncover fundamental mysteries about cosmic evolution.For India, this project offers an opportunity to grasp the cutting-edge advancements happening globally while considering how such initiatives align with national priorities in space exploration. With India’s recent achievements like Chandrayaan missions sparking enhanced interest among youth and policymakers alike regarding astrophysics research, observing models like Euclid could help shape more aspiring pursuits.
euclid’s approach-using gravitational lensing techniques and mapping galactic distances-is likely to redefine our understanding of dark energy,particularly its impact on global expansion. Institutions involved demonstrate advanced project management spanning decades-a model worth emulating as ISRO plans interplanetary expeditions alongside high-resolution Earth imaging projects. Furthermore, Indian scientific communities may benefit immensely by leveraging data emerging out of open-access policies tied to missions like these.
A robust alignment between curiosity-driven fundamental research (like studying universal forces) and application-oriented goals could pave pathways fostering leadership roles within global astrophysical ecosystems for India while strengthening domestic frameworks too.