Now Reading: Ethical Breakthrough: Lipid Nanoparticle Study Minimizes Animal Fatalities
-
01
Ethical Breakthrough: Lipid Nanoparticle Study Minimizes Animal Fatalities
Ethical Breakthrough: Lipid Nanoparticle Study Minimizes Animal Fatalities
Quick Summary
- Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) are crucial in RNA therapies, including FDA-approved products.
- Efforts are being made to improve LNP design for better delivery and efficacy.
- Conventional testing of LNPs through cell culture and animal models often has weak predictivity across species, causing challenges in preclinical evaluation.
- Scientists developed a novel DNA barcoding technique to test many LNPs together in animals like mice and non-human primates (NHPs).
- Ethical concerns and practical limitations wiht NHP testing led researchers to use animals already slated for humane euthanasia.This approach minimizes unnecessary loss of life while gathering critically important data under diseased states similar to humans.
- A study tested 45 barcoded LNP chemical compositions using end-of-life NHPs suffering from gastrointestinal inflammation alongside healthy controls, reducing costs and ethical concerns associated with standard NHP trials.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s burgeoning pharmaceutical sector could benefit from these advancements in high-throughput drug delivery techniques. As one of the largest suppliers of vaccines globally, India stands poised to adapt such innovations for more efficient RNA therapeutics production while addressing ethical challenges in animal testing. Embracing this technology could help Indian pharmaceuticals reduce research costs, enhance accuracy across human-like disease models, and maintain compliance with international standards on bioethics. Importantly,incorporating these methods would strengthen India’s position as a leader not only in traditional pharmaceuticals but also emerging fields like gene editing via mRNA delivery-a need amplified by recent global health crises.
The breakthrough demonstrated here emphasizes collaboration between science and ethics-an interplay relevant for India’s push toward balancing innovation with societal responsibility on global platforms.Quick Summary:
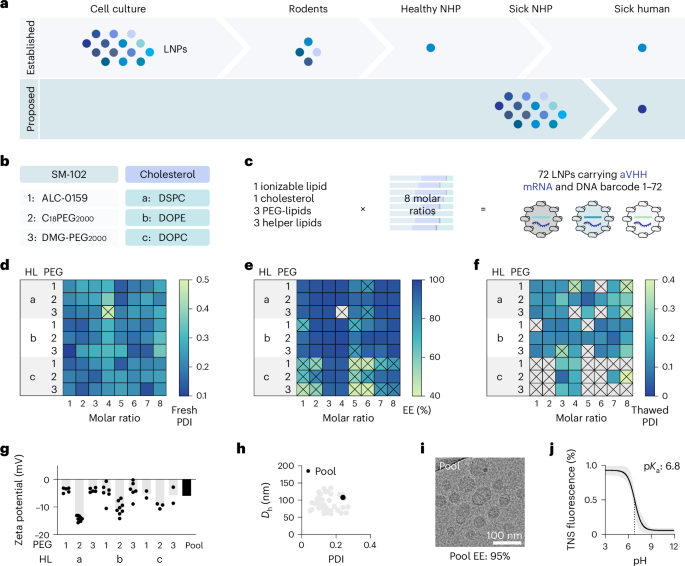
- Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are optimized to enhance mRNA delivery, focusing on modifications to PEG-lipids, helper lipids, and molar ratios.
- Quality control revealed stability during freeze-thaw cycles with high encapsulation efficiency (>85%), low polydispersity index (<0.3), and consistent structural integrity.
- LNP delivery experiments were conducted across species-mice and Non-Human Primates (NHPs)-analyzing liver, spleen, bone marrow, and blood cells for transfection efficiency.
- Species differences in LNP efficacy were noted. Delivery profiles in NHPs showed higher efficiency than mice in majority cell types evaluated.
- Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed broader transfection of multiple cell types beyond hepatocytes in NHP tissues.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The study’s findings underscore potential advancements in the precision of lipid nanoparticle formulations within the field of biotechnology.By systematically analyzing species-specific response variations between mice and non-human primates (NHPs), India’s focus on tailored translational medical research could benefit from similar frameworks to refine drug delivery mechanisms for indigenous health challenges. the observation that mice may not always serve as accurate predictors for human or NHP responses suggests a pressing need for greater emphasis on models that mirror human physiology.
Further integration of advanced techniques like single-cell RNA sequencing could help Indian biotech labs map detailed cellular responses during therapeutic interventions. Such data will be valuable amid global shifts towards personalized medicine using genetic therapies and RNA-based platforms-a sector India is gearing up to participate more actively in through initiatives like Make-In-India biotechnology programs.
For read more or access images: Link
quick Summary
- Study Objective: Researchers analyzed lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery across multiple cell types in livers, spleens, and bone marrow of non-human primates (NHPs) under end-of-life (EoL) and control conditions to understand functional dynamics of LNP-mediated delivery systems.
- Cell Type Findings:
– Liver: Identified 15 cell types; Kupffer cells had highest transfection rates.
– Spleen: Analyzed 18 cell types; macrophages showed highest LNP uptake per cell.
– Bone Marrow: Found delivery effectiveness to hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells alongside myeloid cells in clusters of CD34+ markers.
- Key Associations:
– Lipoprotein receptors (LRP1, LDLRAD3, MSR1) correlated with more efficient LNP transfection across tissues. Import-related pathways like endocytosis were significant determinants replicated in multiple tissues.
- Hypotheses & Implications:
– Delivery mechanisms differ between mice and NHPs rather than being inherently harder for NHPs. Multiple receptors likely mediate particle uptake instead of exclusively targeting hepatocytes as previously presumed.
- Future Applicability:
– Possibilities arise for mRNA-based therapies targeting macrophages/monocytes (e.g., cancer immunotherapies), or gene editing in stem cells relevant to sickle-cell treatment pathways.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This study contributes valuable insights into the functional behaviors of lipid nanoparticles during mRNA delivery for therapeutic purposes-a significant emerging field also relevant to India’s biopharmaceutical ambitions. The findings challenge established assumptions about species-to-species differences, offering a nuanced understanding that could improve preclinical models.
For India’s growing investment in nanotechnology and personalized medicine, such discoveries offer clarity on how underlying molecular mechanisms can transform clinical outcomes. Notably notable is the identification of lipoprotein-related receptor roles-which could tailor future treatments for genetic dyslipidemias prevalent among certain Indian populations-for instance familial hypercholesterolemia cases requiring innovative intervention strategies beyond traditional methods reliant solely on LDLR receptors.
Furthermore, application possibilities range from advancing CAR therapies targeting leukemia patients or addressing sickle-cell disease-relevant to parts holding burden within existing health reforms challenges globally further researches evolving libraries.Value optimizing R&D partnerships globally focusing advanced transitioning regulatory landscape-efficient large scale novel trials bridging groundwork optimization.Collections replicable breakthroughs piloting wide larger release future markets
Read more at Nature.Quick Summary:
- Thorough research into lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems was conducted, focusing on their interactions with RNA-based payloads like mRNA and non-circular DNA.
- Different chemical compositions of LNPs were tested for encapsulation efficiency,hydrodynamic size,and stability during freeze-thaw cycles.
- The study analyzed the biophysical traits and compatibility of LNPs with various payloads across mice models and non-human primates (NHPs).
- results indicated that while NHP studies provide significant delivery insights applicable to humans, mouse trials still remain critical for initial tolerance testing to mitigate systemic toxicities in NHP experiments.
- In-depth methodologies included cryo-TEM imaging, flow cytometry staining panels, single-cell multiomics analysis systems, and cytokine profiling in serum samples.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This intricate study highlights advancements in RNA-based therapeutics using lipid nanoparticles-crucial for drug delivery mechanisms relevant to gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 therapies. With India’s growing focus on biotechnology innovation via partnerships or indigenous advancement programs under schemes like Make-in-India or DBT funding initiatives,these scientific breakthroughs could bolster health care solutions targeting genetic disorders or personalized medicine platforms nationwide. However, the insistence on preliminary mouse studies before transitioning to larger animal models resonates with ethical imperatives globally for careful reduction in animal testing frameworks-a debate actively explored in India’s bioscience regulatory domain too.
Read MoreQuick Summary:
- The text highlights research efforts related to RNA delivery systems through lipid nanoparticles and their use for therapeutic purposes in gene editing and other medical innovations.
- Techniques described include Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), cryo-TEM visualization, dimensional analysis algorithms like Harmony, UMAP clustering, and statistical methods involving GraphPad Prism software tools.
- Multiple biological replicates were analyzed across experiments to ensure data reproducibility. Sample-specific genomic data for organisms like mice (
GRCm39) and rhesus macaques (rheMac10) are made publicly available via linked databases. - Certain tested methods include CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing approaches targeting specific diseases, such as transthyretin amyloidosis and hereditary angioedema.
- Lipid nanoparticles with tailored surface modifications have been experimentally applied to rodents for genome edits in targeted organs.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The development of lipid nanoparticle-based delivery systems marks significant advancements in biomedical research globally.For India, with its large population base affected by genetic disorders and untapped genomics infrastructure potential, emerging liposomal therapies could revolutionize personalized medicine frameworks while bolstering India’s biotech sector further alongside partnerships w/ scientific institutions globally.. Expertise-sharing could lead expansion targetsQuick Summary
- Lipid nanoparticles are emerging as a promising tool for genome editing and mRNA delivery in diverse applications, including therapeutic interventions.
- Studies cited demonstrate the potential of lipid-modified particles to target specific organs, deliver nucleic acids effectively, and induce controlled therapeutic responses.
- Research examples include targeting liver microenvironments, leukocytes, spleen/lungs with optimized helper lipids, and using nanoparticles for CRISPR-Cas gene editing.
- Other advancements include organ-selective targeting through particle surface modifications and inducing therapeutic protein expression directly within specific cells.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The progress in lipid nanoparticle technology marks significant advances in precision medicine. For India, its applicability could be transformative across healthcare domains like genetic disease management or vaccine development. Though, challenges persist regarding accessibility and cost-effectiveness within India’s vast healthcare system.Additionally, robust regulatory mechanisms are essential to ensure the safe deployment of these technologies at scale while fostering local innovation to reduce dependency on global patents. Such investments are vital not only for self-reliance but also for positioning India as a leader in cutting-edge biotechnological research.
Read morequick Summary
- The raw text contains references to several scientific articles and studies focused on advancements in biomedical research, particularly the use of nanoparticles for mRNA delivery systems, personalized cancer medicine, antiviral therapies, and gene editing.
- Key areas explored include species-dependent responses to nanoparticles, optimization of lipid nanoparticles for vaccine delivery, and high-throughput screening methods for developing targeted therapeutics.
- Findings span innovations like barcoded nanoparticles in cancer treatments and engineered mRNA technology preventing viral infections.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The growing research on nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery systems has significant implications for India’s healthcare sector. With its vast population size and diverse genetic factors, these technologies hold potential in addressing challenges such as affordability and efficiency of modern medicines. The focus on personalized treatments might suit India’s disease landscape but requires tailored approaches compatible with regional biological diversity. Investments into such technologies could advance India’s biotechnology standing globally while improving public health outcomes domestically.
Read moreQuick Summary:
- The raw text discusses advancements in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technologies, focusing on their use for delivering therapeutic RNA.
- Key studies show evolving techniques like microfluidic formulations for optimized delivery, PEGylation to target specific organs, and helper lipids enhancing delivery efficiency.
- Applications range from treating fatty liver diseases to modulating immune activity for better antitumor responses.
- Research spans multiple years and includes collaborations across chemistry, molecular therapy, and biomedical engineering fields.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The implications of these LNP innovations are significant for India’s biotechnology and healthcare sectors. With a robust pharmaceuticals industry already contributing considerably to global production-especially in generics-these advanced delivery systems could propel India into the mRNA-based therapy domain. Such technologies might enable targeted treatments for widespread diseases like cancer or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease while reducing side effects typical of conventional therapies. Additionally, India’s potential adoption of LNP-based treatments depends heavily on building appropriate infrastructure and training specialized personnel. Leveraging these advancements through strategic policy-making could establish India’s role as a leader not just in manufacturing but also innovation within the global medical technology landscape.
read more: Link LinkUnfortunately, the raw text provided seems to consist largely of references and citations from scientific articles without any cohesive narrative or direct news content related to India, making it challenging to distill it into a proper write-up. If you can provide a clearer article or data relevant to India, I’d be happy to craft an appropriate “Quick Summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis.”Quick Summary
- A scientific study has advanced gene editing techniques using lipid nanoparticles for targeted RNA delivery.
- Participants include researchers from Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology in collaboration with the Emory National Primate Research Center.
- Focus is on in vivo applications for immune cells and hematopoietic stem cells, utilizing nanoparticles optimized for minimal impact on life during testing with nonhuman primates.
- Published outcomes have relevance in genomics, vascular health, and potential precision medicine advancements.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This development represents significant progress in biomedical engineering and genomic research, areas where India is rapidly advancing its capabilities. With increasing investments into nanotechnology and healthcare innovations under programs like ‘Make In india,’ such advancements offer an chance to influence global medical solutions positively while tackling domestic health challenges effectively. India’s growing pool of scientists could contribute to these international collaborations or adapt similar technologies within institutes to address genomic disorders locally.
Read MoreQuick Summary:
- A research article published in Nature Biotechnology discusses lipid nanoparticle screening in nonhuman primates to optimize mRNA delivery with minimal impact on animal life.
- The study involved contributions from multiple researchers across various areas, including mRNA synthesis, single-cell multiomics runs, animal tissue processing, LNP characterization, and next-generation sequencing.
- This peer-reviewed study was supported by experts from institutions like Emory University. Data analysis and experiments were led primarily by Hyejin Kim and James E. Dahlman.
- Ethical declarations note that James E. Dahlman is affiliated with Readout Capital, Edge Animal Health, and Nava Therapeutics as an advisor; other authors reported no competing interests in the study.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research highlights advancements in lipid nanoparticle technology critical for improving mRNA-based treatments such as vaccines or gene therapies-an area globally relevant post-COVID-19. For India particularly, scaling breakthroughs like these could help bolster its pharmaceutical sector aimed at affordable innovation. Enhanced LNP efficiency holds significance for India’s health priorities-focusing on bioengineered therapeutics amidst rising pandemic-driven health challenges and budget-conscious healthcare access needs. Neutral observation of ethical disclosures further ensures transparency within internationally-bound collaborative efforts.
Read more at Nature BiotechnologyQuick Summary:
- Article titled “Lipid nanoparticle screening in nonhuman primates with minimal loss of life,” published in Nature Biotechnology on June 26, 2025.
- Researchers Zenhausern, Jang, and Schrader Echeverri et al. conducted a study focusing on lipid nanoparticle screening aimed at improving biological delivery systems.
- The study emphasizes reducing the loss of life during early-stage animal testing protocols.
- Published timeline:
– Received: january 23, 2025
– accepted: May 21, 2025
– DOI link provided for reference (DOI).
Indian opinion analysis:
This development is pertinent to India as it strengthens the foundation for ethical and efficient biomedical research practices globally-perhaps influencing India’s pharmaceutical and biotech industries that continue to expand rapidly. Faced with ongoing debates over animal testing ethics within the country, this study offers innovative pathways for balancing scientific exploration with humane treatment standards when working on drug delivery systems or therapeutic applications using nanoparticles.
Moreover,india’s goal to be a hub for cutting-edge technology like nanomedicine could benefit from adopting best practices highlighted by such studies-not only advancing global credibility but also attracting international collaborations or investments into research ecosystems centered around medical advancements.