Now Reading: Finland Discovers First-Ever Giant Virus
-
01
Finland Discovers First-Ever Giant Virus
Finland Discovers First-Ever Giant Virus
Quick Summary
- researchers in Finland have discovered a giant virus named “Jyvaskylavirus,” measuring approximately 200 nm, which is twice the size of influenza or coronavirus.
- It was identified by mixing environmental samples with an amoeba culture called acanthamoeba castellanii.
- The new species is genetically related to Marseilleviruses previously isolated in France, as per a study published in eLife.
- Most known giant viruses have been found in Europe and South America. This northern finding suggests such viruses may be more widely distributed across soil and water environments than previously believed.
- giant viruses typically possess exceptionally large genomes compared to standard-sized species, ranging up to 2.5 million DNA base pairs. Jyvaskylavirus’s genome adds valuable data for understanding these organisms’ life cycles and spread.
- Additional undiscovered giant viruses were detected within the same environmental samples.
Images:
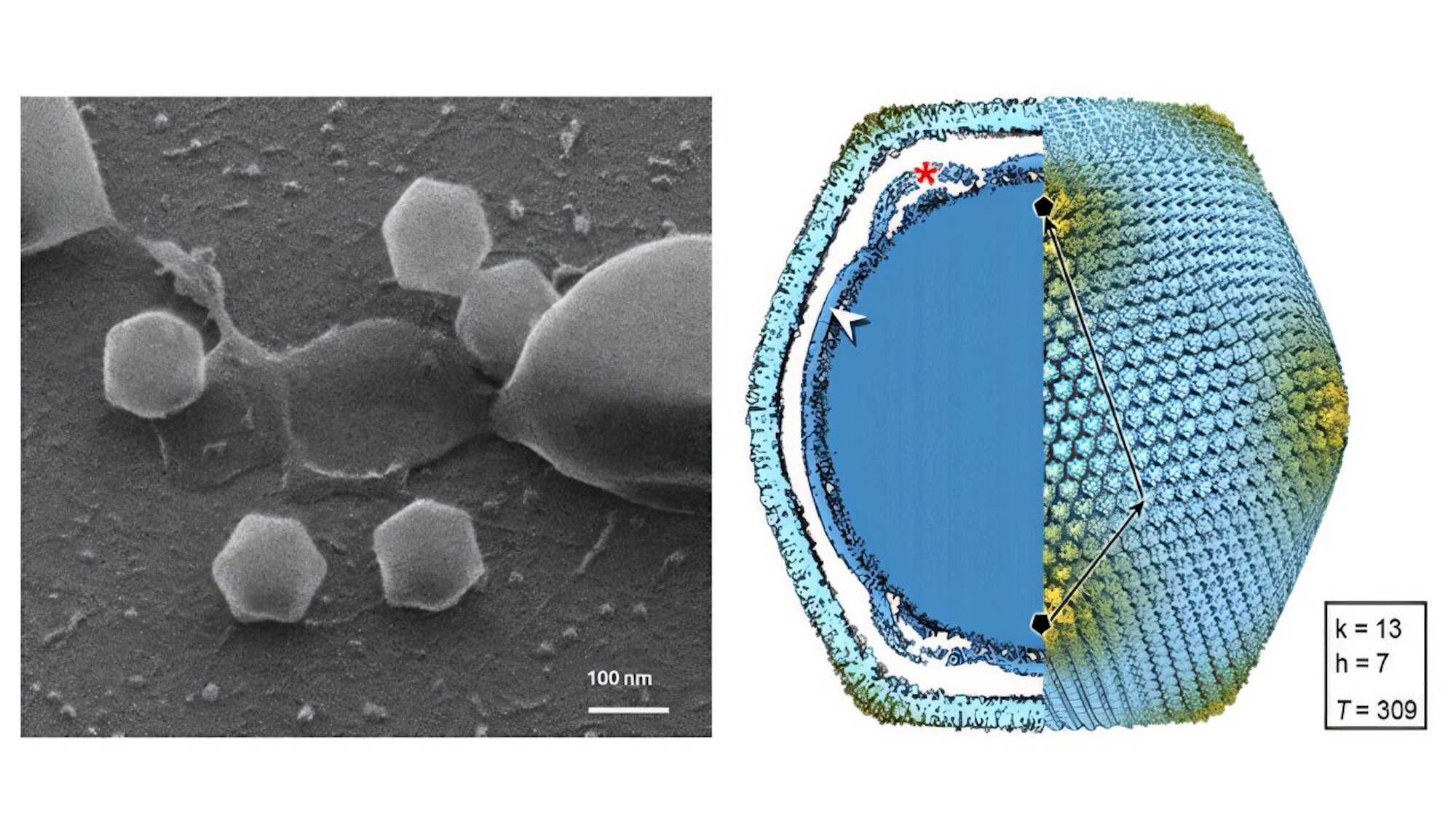
- Image of Jyvaskylavirus: The virus particle is about twice the size of influenza or coronavirus (Credit: University of jyväskylä).
- Helium ion microscopy: Shows Jyvaskylavirus attachment to Acanthamoeba castellanii cells (Credit: eLife).
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery of Jyvaskylavirus offers intriguing implications for scientific research, particularly regarding biodiversity and unexplored microscopic ecosystems worldwide. For India, this could emphasize strengthening molecular biology programs aimed at studying similar ecosystems within the country’s diverse climatic zones-ranging from Himalayan snowfields to coastal wetlands-which might harbor novel microorganisms like giant viruses.
While these microorganisms are not inherently dangerous compared to standard viral pathogens like influenza or coronavirus, their ecological roles could influence critical environments such as freshwater sources or polar systems indirectly linked with global warming effects (as seen with Arctic algae-linked infections). Indian researchers could explore collaborations with international teams on projects investigating viral interactions at regional levels-advancing broader scientific insights into climate impact studies tied specifically to India’s distinct geography.
This discovery reaffirms a need for deeper investment in genomic cataloging efforts-not only expanding biological knowledge but possibly contributing applications ranging from ecosystem balance studies to biomedical innovations standalone frameworks; ensuring national progress aligns efficiently while ethically!