Now Reading: Florida’s Mega Freeze Spurs Rapid Evolution in Burmese Pythons
-
01
Florida’s Mega Freeze Spurs Rapid Evolution in Burmese Pythons
Florida’s Mega Freeze Spurs Rapid Evolution in Burmese Pythons

Speedy Summary
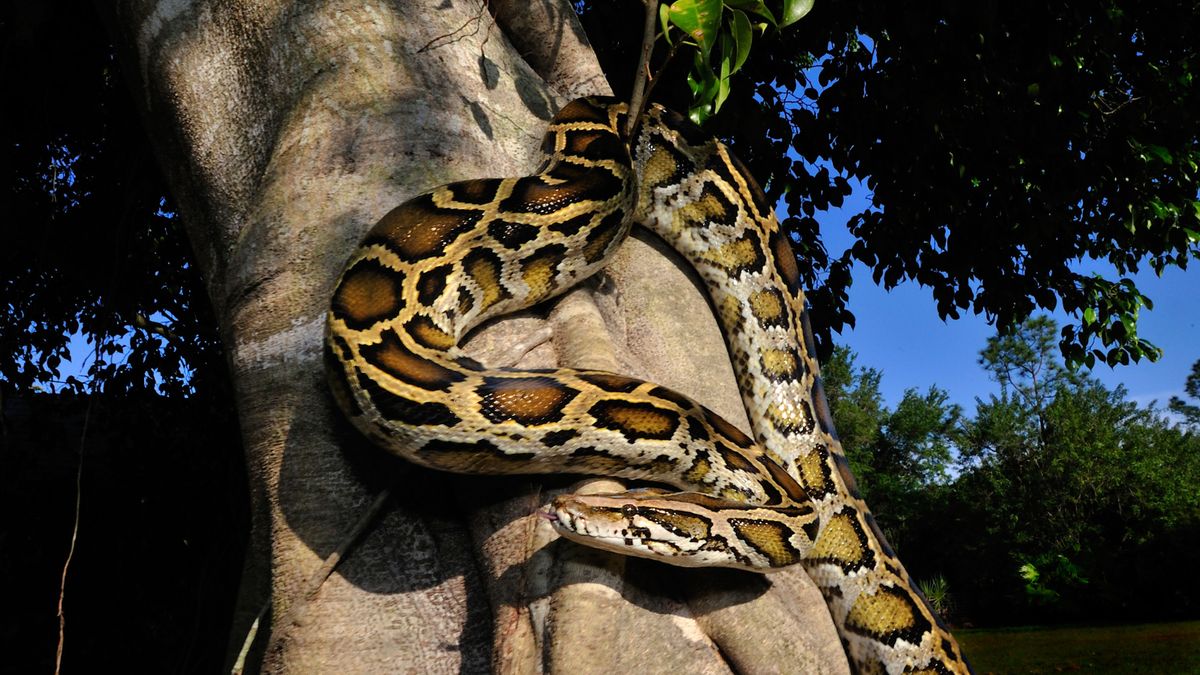
- A 2010 cold snap in Florida severely impacted teh state’s Burmese python population, with carcasses found on roads and underground burrows, caused by their inability to cope with extreme cold temperatures.
- Most snakes perished due to “maladaptive behavior,” but a subset genetically predisposed for cold resilience survived and proliferated.
- Genetic studies revealed survivors exhibited enhanced cold tolerance and metabolic flexibility, allowing them to adapt rapidly under environmental stress.
- by 2014, the burmese python population returned to pre-freeze levels in the Everglades National Park after a genetic bottleneck event that favored traits aiding survival in colder climates.
- These adaptations potentially enable invasive pythons to expand their range further into North America as they continue evolving quickly without traditional evolutionary delays observed over millennia.
image captions:
- frozen iguanas immobilized during 2010’s low-temperature event (Photo: JUAN CASTRO/AFP via getty Images).
- burmese pythons sunning behavior proved fatal during temperatures of approx -4°C (photo: Mark Conlin via Alamy).
- Baby pythons’ genes adapted post-disaster resilience bottlenecks subsequently propagating thermal-proof generations extension spans etc bloginfo extends bio legacy-footer image attached etc [credits < pls bio>] existing adjust ecosystem-line..truncated expand implode recursive compute..` : Utilize helpful.anchor
Indian Opinion Analysis
The rapid adaptation observed among Florida’s Burmese python population following a catastrophic freeze highlights evolution’s remarkable flexibility under environmental pressure-a phenomenon rarely seen at this accelerated pace outside laboratory settings or controlled experiments concerning species’ regions India analogously/subtype dives analytical DIG INTERSECTS לד-max-neurodiv statescross comparative Further Viewable accessible Clickthread Trees Reader extended Momentum.
invasive species like these pose ecological threats globally; understanding mechanisms driving rapid evolution helps policymakers assess risks such as altered predator-prey dynamics or biodiversity displacement trajectories logical defensively actionable species coursework resets native responsive mla313append.index involuntary