Now Reading: Global Climate Crisis Reaches Uncharted Territory, Warns Report
1
-
01
Global Climate Crisis Reaches Uncharted Territory, Warns Report
Global Climate Crisis Reaches Uncharted Territory, Warns Report

Swift Summary
- The World Meteorological Organization’s (WMO) State of the Global Climate report for 2024 highlights dramatic climate changes, including record ocean heat, ice melt, and sea level rise.
- Sea level rise rates have doubled as satellite measurements began: 2.1 mm/year from 1993 to 2000 compared to 4.7 mm/year between 2015 and 2024.
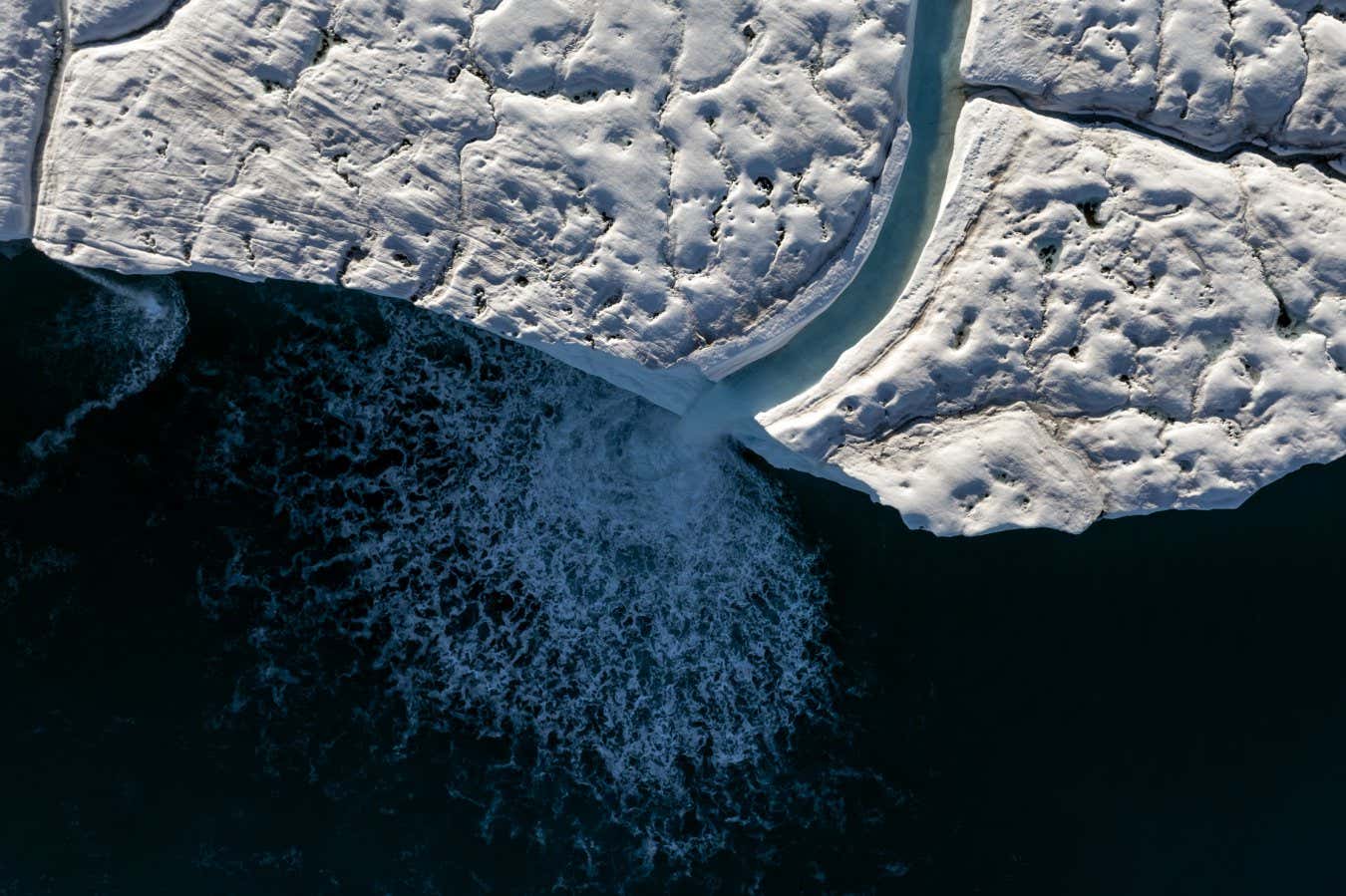
- Glaciers experienced unprecedented ice loss over the past three years, particularly in Norway (Svalbard), sweden, and the tropical Andes.
- Arctic summer sea ice with its lowest extent has occurred consecutively over the past 18 years; Antarctic sea ice reached record lows in recent three years.
- Ocean heat has broken records annually for eight straight years; the planet’s ten warmest years on record transpired within the last decade.
- Preliminary data suggests that average global temperatures in 2024 may have exceeded levels set by pre-industrial benchmarks (+1.55°C compared to an average of +1.5°C).
- A breach of Paris Agreement targets remains uncertain under varying definitions but cannot yet be ruled out completely.
Image Caption: Meltwater runs off Bråsvellbreen Glacier in Svalbard due to accelerated glacier melting caused by climate change.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...