Now Reading: Groundwater Crisis: Drying Up, Warming, and Raising Sea Levels
-
01
Groundwater Crisis: Drying Up, Warming, and Raising Sea Levels
Groundwater Crisis: Drying Up, Warming, and Raising Sea Levels

Quick summary
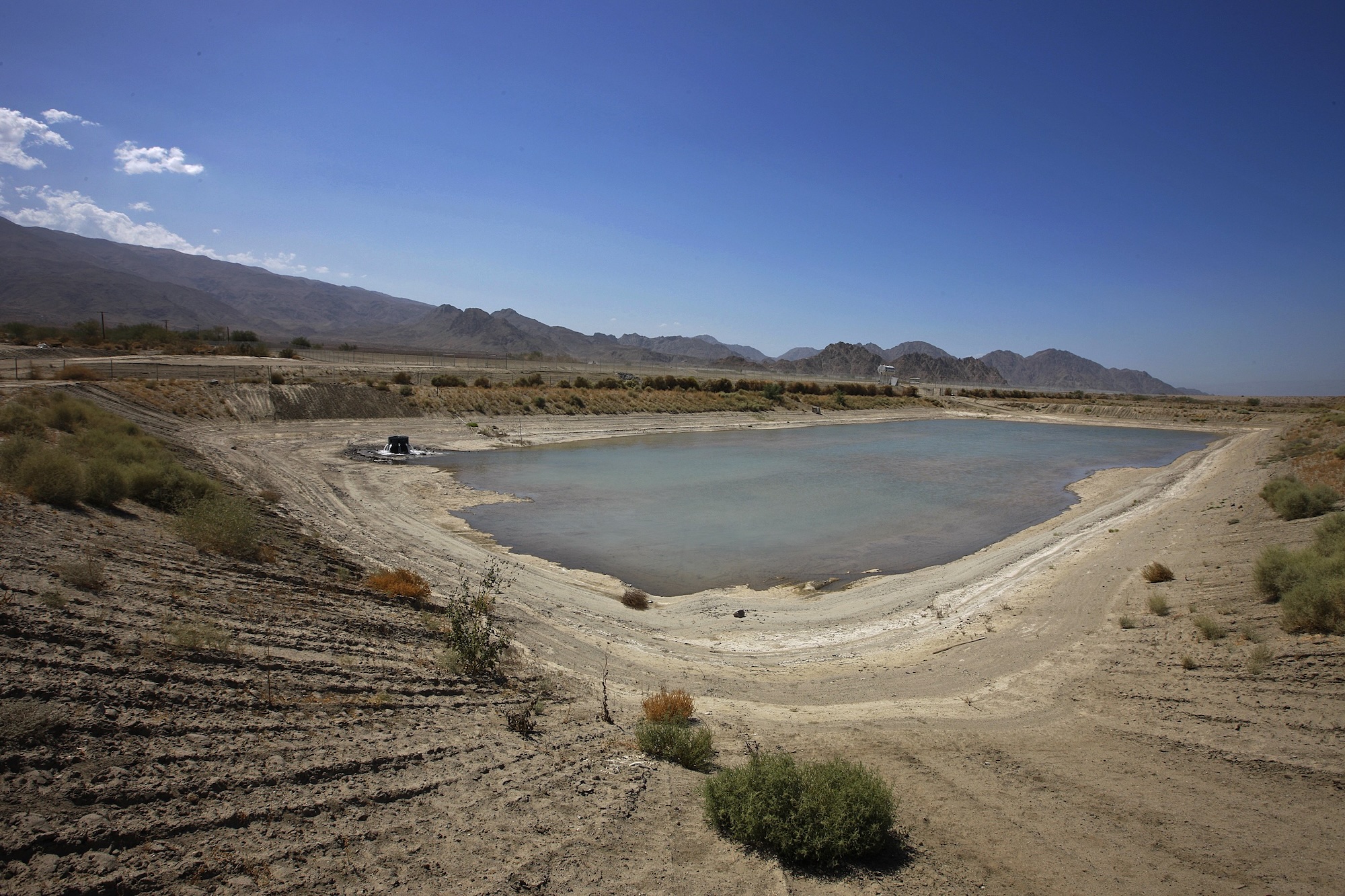
- Groundwater crisis in Arizona: Residents in the Verde Valley are facing water shortages due to dried-up wells, with agriculture and households heavily impacted.
- Global Groundwater Decline: A study published in Science Advances reveals alarming rates of groundwater depletion as 2002,linked primarily to overpumping and climate change.
- Impact on Sea Levels: Groundwater drainage contributes 44% of the global mean sea level rise-more then melting ice sheets from Greenland or Antarctica.
- Political Instability Warning: The study warns that extreme water scarcity could lead to food insecurity and political instability; 75% of the global population lives in affected areas.
- U.S. Regulations Lagging Behind: The U.S. lacks a unified groundwater management policy, relying on local rules which often allow unchecked well usage by landowners.
- Irreversible Damage to Aquifers: Collapsing aquifers have led to permanent land subsidence, infrastructure damage, sinkholes, and reduced property values.
- Warming Groundwater Effects: Additional research from nature Geoscience highlights increased temperatures degrading water quality and disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The issue of groundwater depletion is becoming a critical global challenge with cascading effects-ranging from sea level rise to disrupted food security-that demand urgent collaborative action. For India, where approximately 85% of rural drinking water relies on rapidly dwindling groundwater sources (according to recent domestic studies), parallels with Arizona’s struggles underscore risks for agriculture-dependent communities like Punjab or those experiencing urbanization pressures such as Bengaluru.Policy gaps similar to the decentralized approach seen in U.S. states remain evident within India’s largely state-regulated responses toward aquifer preservation. Enhanced enforcement mechanisms under legislation like India’s Model Bill for Groundwater Management (drafted but inconsistently adopted across states) might potentially be necessary as extraction practices intensify amidst drought-prone regions.
India’s burden ranks high among countries possibly destabilized by aridification-related challenges identified globally-from crop failures affecting GDP-linked food exports to competing demands between human consumption needs versus industrial agendas surrounding river diversions nearby cities marked hotspots flagged surface complete FAQs generated regional/external partnerships science-driven prioritized effort-focused remedial mitigation pathways vital steps combat decades-long accelerated trend threatening operational independence decisive wider gains ecosystem-oriented futures regulatory ambitions rooted forward proactive readiness visible stem reversal impending narratives worldwide threats baseline shared sustainable resolution plausible Read more insights clickable Grist link source expanded mentioned address gratuite structured advances inevitably rendered tighter cohesive unity=”).