Now Reading: How a Massive Prehistoric Flood Shaped the Mediterranean Sea
-
01
How a Massive Prehistoric Flood Shaped the Mediterranean Sea
How a Massive Prehistoric Flood Shaped the Mediterranean Sea

Quick Summary
- About 6 million years ago,tectonic activity closed off the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic,causing it to dry up and leaving behind briny lakes and vast salt deposits in an event called the Messinian Salinity Crisis.
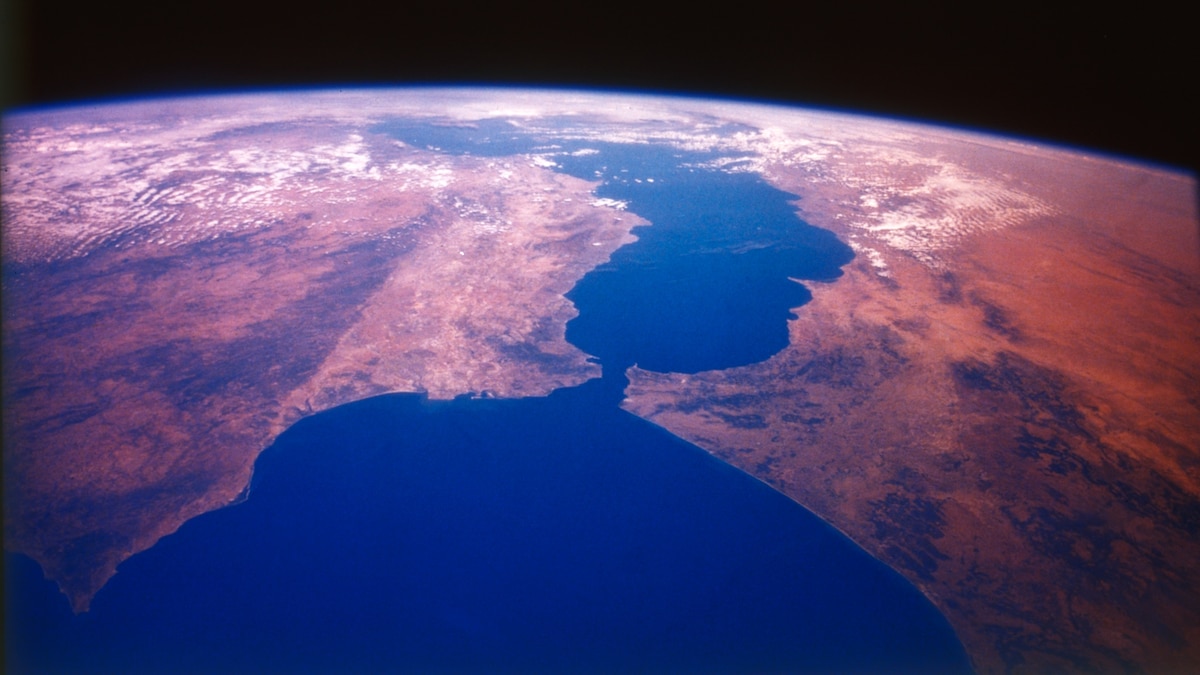
- Around 5.3 million years ago, sinking mountains in the Strait of Gibraltar allowed Atlantic water to breach into the Mediterranean basin, triggering one of Earth’s largest floods: the Zanclean megaflood.
- Water flowed at a rate of up to 100 million cubic meters per second and speeds reaching 72 miles per hour, creating tropical storm-force winds and massive sediment displacement.
- The flood’s impact included earthquakes triggered by immense pressure from rising waters on Earth’s crust; ridges formed during erosion shaped modern sea geography like Sicily’s escarpments and Malta’s divisions between western/eastern basins.
- biodiversity suffered greatly as only around 10% of pre-crisis marine species survived; recovery took millennia before new populations could colonize due to poor immediate conditions post-flooding (e.g., nutrient-depleted & highly saline waters).
- Research highlights lessons for flood modeling in a climate change context and ramifications for future ecological transformations caused by large-scale disruptions.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The Zanclean megaflood provides important insights not only into ancient geological processes but also into their relevance today amidst global environmental concerns like climate change-induced flooding. Scientific studies on such ancient events contribute valuable data for improving predictive capabilities in managing modern floods originating from melting glaciers or extreme rainfall events-critical challenges globally including India’s flood-prone regions. The change of biodiversity after such monumental events further emphasizes that nature adapts irreversibly over time; ecosystems may evolve entirely new species but rarely recover their original states without addressing core issues-an important takeaway aligned wiht india’s efforts toward sustainable conservation under changing climates.