Now Reading: Hubble and Chandra Uncover Rare Black Hole Devouring a Star
-
01
Hubble and Chandra Uncover Rare Black Hole Devouring a Star
Hubble and Chandra Uncover Rare Black Hole Devouring a Star
Fast Summary
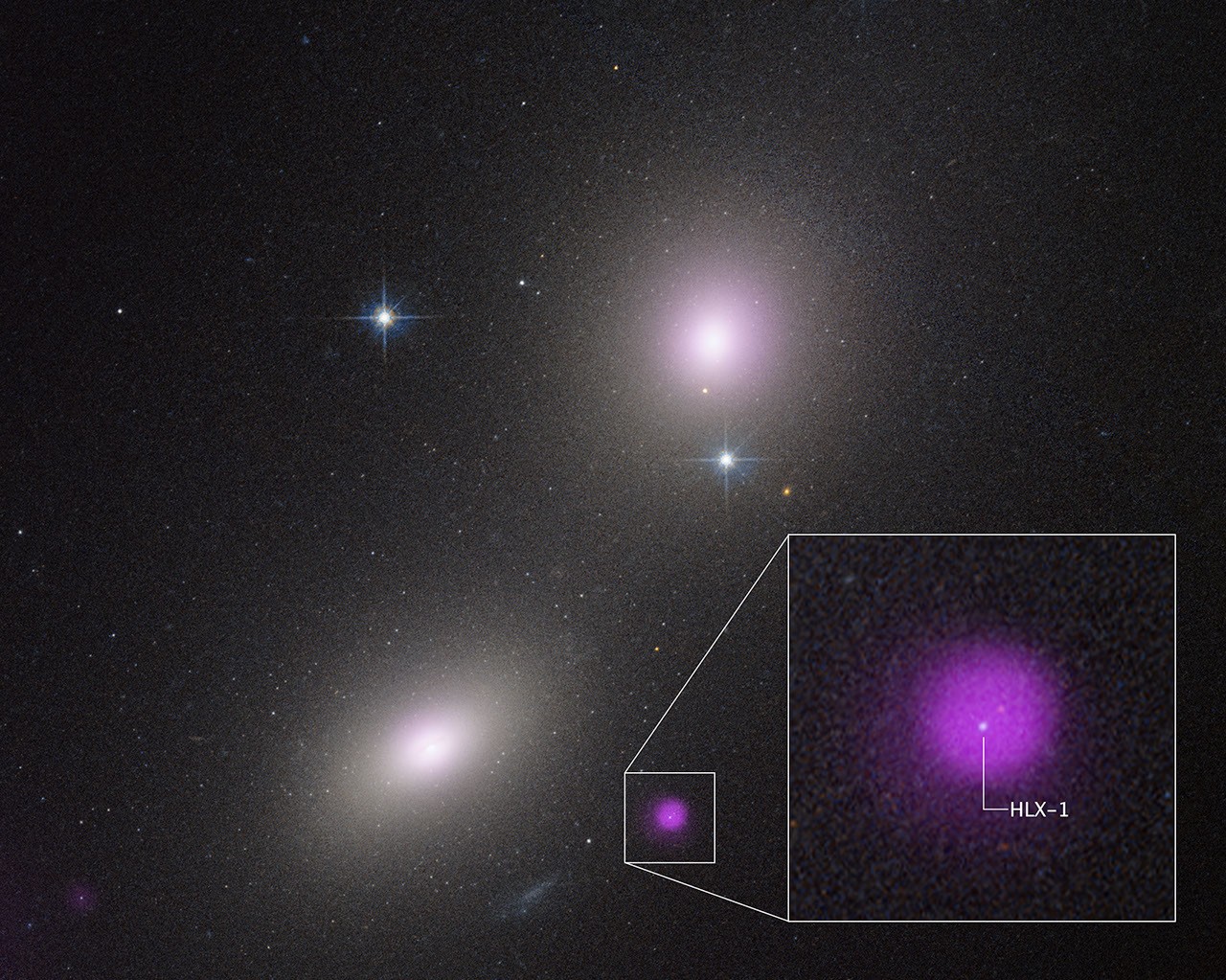
- NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and Chandra X-ray Observatory identified a potential intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH), named NGC 6099 HLX-1, in the outskirts of an elliptical galaxy about 450 million light-years away in the Hercules constellation.
- IMBHs are rare black holes weighing between hundreds to 100,000 times the mass of our Sun.Unlike supermassive or stellar-mass black holes, they are hard to detect due to limited radiation emission unless actively consuming stars.
- NGC 6099 HLX-1 displays X-ray emissions from a tidal disruption event, suggesting it is indeed tearing apart nearby stars in a dense star cluster with temperatures reaching 3 million degrees.
- This IMBH was first noted by Chandra in 2009, peaked in brightness around 2012, and has been steadily declining since then. Astronomers continue monitoring its activity for insights into black hole behavior.
- The study reveals two major theories about how supermassive black holes grow:
– via merging smaller galaxies and absorbing satellite IMBHs over cosmic time.
– Through direct collapse of gas clouds inside dark-matter halos without forming stars first-supported by discoveries indicating disproportionally massive distant supermassive black holes.
Read More: NASA’s Hubble & Chandra Spot Rare Type of Black hole Eating A Star
indian Opinion Analysis
The identification of NGC 6099 HLX-1 introduces significant advancements in understanding intermediate-mass black holes (IMBHs)-a missing link between stellar-sized and supermassive ones. For India’s space science ambitions under organizations like ISRO that already focus on astrophysical research, findings like these set critical benchmarks for future observational missions aimed at studying elusive celestial phenomena.
Moreover, this discovery reinforces international scientific cooperation exemplified by projects such as Hubble’s partnership between NASA and ESA. Such frameworks could serve as models for India’s collaborative ambitions with lunar and space telescopes planned globally. fostering regional expertise on phenomena such as IMBH evolution may help India contribute toward broader questions regarding cosmic history-particularly concerning how galaxies shape themselves through mergers & collapses-a topic often tied with advancing national research narratives.



























