Now Reading: Hubble Captures Stunning Image of Galaxy Messier 77
-
01
Hubble Captures Stunning Image of Galaxy Messier 77
Hubble Captures Stunning Image of Galaxy Messier 77

Rapid Summary
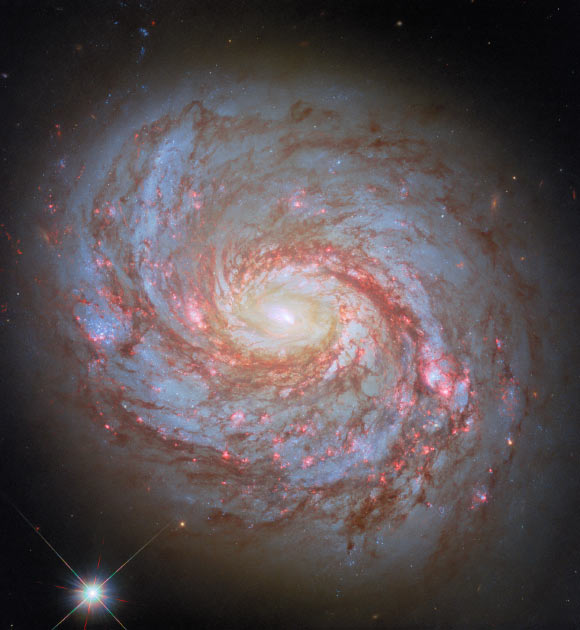
- NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a vivid image of the barred spiral galaxy Messier 77.
- Located 62 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus, it is also known as NGC 1068, LEDA 10266, and Cetus A (or “Squid Galaxy”).
- French astronomer Pierre Méchain discovered it in 1780 as a nebula; its true identity as a galaxy was recognized much later wiht advances in technology.
- The galaxy has an apparent magnitude of 9.6 and measures approximately 100,000 light-years across.
- Messier 77’s gravity influences nearby galaxies by warping them and features an active galactic nucleus (AGN), making it one of the brightest objects across multiple wavelengths.
- Its accretion disk is obscured by dust and gas clouds despite being popular with astronomers for observation purposes.
Image:
!Messier 77
The Squid galaxy name stems from filamentary structures resembling squid tentacles around its disk.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The detailed study of celestial bodies like Messier 77 represents meaningful progress for global astronomy which also has relevance for India’s ambitious space programs such as ISRO’s ongoing efforts to expand scientific inquiry within interstellar domains or satellite-based observational capacity advancements proposed under various missions.
For Indian scholars, Messier galaxies offer potential research opportunities aiding basic understanding about active galactic nuclei phenomena offering broader knowledge transferable learn crossfields..