Now Reading: Hubble Captures Stunning New View of Messier 96
-
01
Hubble Captures Stunning New View of Messier 96
Hubble Captures Stunning New View of Messier 96

Quick Summary
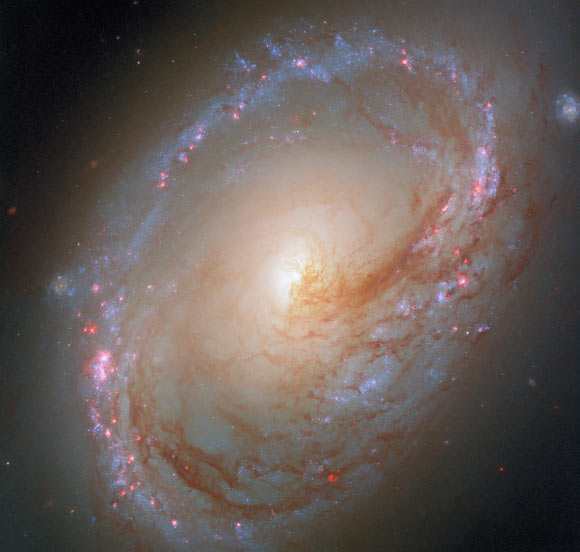
- Messier 96 (also known as NGC 3368,LEDA 32192,or M96) is a spiral galaxy located in the Leo constellation,approximately 34 million light-years away from Earth.
- Discovered by Pierre Méchain on March 20, 1781 and later cataloged by Charles Messier.
- Spanning roughly 100,000 light-years across with an estimated mass of 80 billion solar masses-similar in size to the Milky Way Galaxy.
- A dominant member of the Leo I galaxy group that includes Messier 95, Messier 105, and other fainter galaxies; it’s considered the nearest group containing both radiant spiral and elliptical galaxies.
- The galaxy is highly asymmetric: its dust and gas are unevenly distributed across weak spiral arms and an off-center core. This irregular shape may be influenced by gravitational interactions within its galactic group.
- The latest image from NASA/ESA’s hubble Space Telescope highlights star formation phenomena using ultraviolet and optical observations.
– Pink gas bubbles indicate regions surrounding young massive stars embedded in dusty clouds from which they were born. These highlight active star-forming zones at the edges of the galaxy.
– New observational data aids research on processes like dust filtration of starlight and environmental impacts caused by stars.
Indian opinion Analysis
India’s robust participation in space exploration has brought astronomical achievements to national attention thru missions such as Chandrayaan. Observations like those of Messier M96 facilitate crucial insights into universal phenomena including star formation processes-critical knowledge for future interstellar studies or projects such as building indigenous deep space observatories.
While discoveries about cosmic structures may seem distant from immediate Indian priorities, they underscore humanity’s collective progress toward understanding fundamental truths about our universe. Investments in domestic research capability could position India better for collaboration with leading agencies like NASA or ESA.
The asymmetrical features showcased in this study connect scientific curiosity with applied relevance in determining how celestial environments evolve under gravitational stresses-a topic ripe for deeper academic inquiry.