Now Reading: Hubble Explores Supernova Remnants in Milky Way’s Satellite Galaxy
-
01
Hubble Explores Supernova Remnants in Milky Way’s Satellite Galaxy
Hubble Explores Supernova Remnants in Milky Way’s Satellite Galaxy
Swift Summary
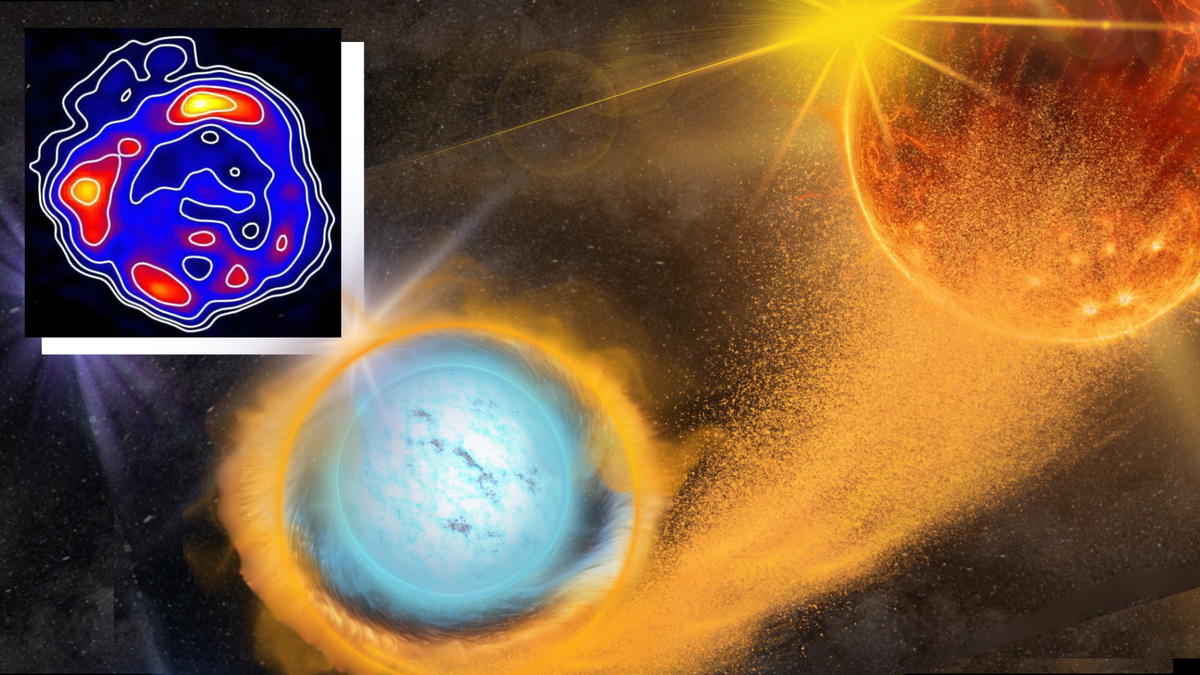
- Astronomers have utilized teh Hubble Space Telescope along with other observatories such as NASA’s Chandra X-ray space observatory, ATCA, and the Parkes telescope to study supernova remnant MC SNR J0519-6902 in the Large Magellanic cloud (LMC), a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.
- MC SNR J0519-6902 features a 26-light-year diameter ring-like structure, thought to be created by a Type Ia supernova-a thermonuclear explosion of a white dwarf star.
- Two potential mechanisms for Type Ia supernovas are identified:
– A “vampire” white dwarf pulling matter from its companion star until reaching the Chandrasekhar limit.
– two white dwarfs merging after spiraling together.
- Recent observations revealed faint northeast structures and an associated cloud of atomic hydrogen around the remnant.Magnetic field data indicates similarities with young supernova remnants in both LMC and Milky Way galaxies.
- Scientists estimate that MC SNR J0519-6902 is approximately 2,000 years old and entering its Sedov-Taylor phase-where expanding material interacts with surrounding interstellar medium.
- Further studies using ASKAP are planned to determine if nearby atomic hydrogen clouds are directly linked to this remnant.
Images featured in this study:
- Artistic renderings of type Ia supernovas caused by binary interactions (feeding or merging).
- High-resolution images showcasing magnetic field activity and motion dynamics within atomic hydrogen gas near MC SNR J0519-6902.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings surrounding MC SNR J0519-6902 contribute significantly to our understanding of stellar evolution and violent cosmic phenomena like Type Ia supernovas. While primarily advancing global astronomy research, these insights have broader scientific implications for India’s growing aspirations within space exploration. India’s active involvement in international collaborations like ASKAP or similar initiatives could further reinforce its role as an emerging player in deep-space observational science.
As India expands its capabilities thru projects such as ISRO’s Aditya-L1 solar mission or proposed deep-space telescopes under Gaganyaan-era initiatives, studying phenomena like white dwarf collisions can enrich domestic knowledge pools on stellar lifecycle processes critical for astrophysics research. Potential applications extend beyond academic interests into areas such as gravitational wave detection-an area attracting increasing global convergence.
educational advancements arising from studies like this may bolster India’s future astronomers while fostering international exchanges aligned toward human ingenuity navigating global mysteries.
























