Now Reading: Hubble Uncovers Ancient Galactic Relic
-
01
Hubble Uncovers Ancient Galactic Relic
Hubble Uncovers Ancient Galactic Relic

Rapid Summary
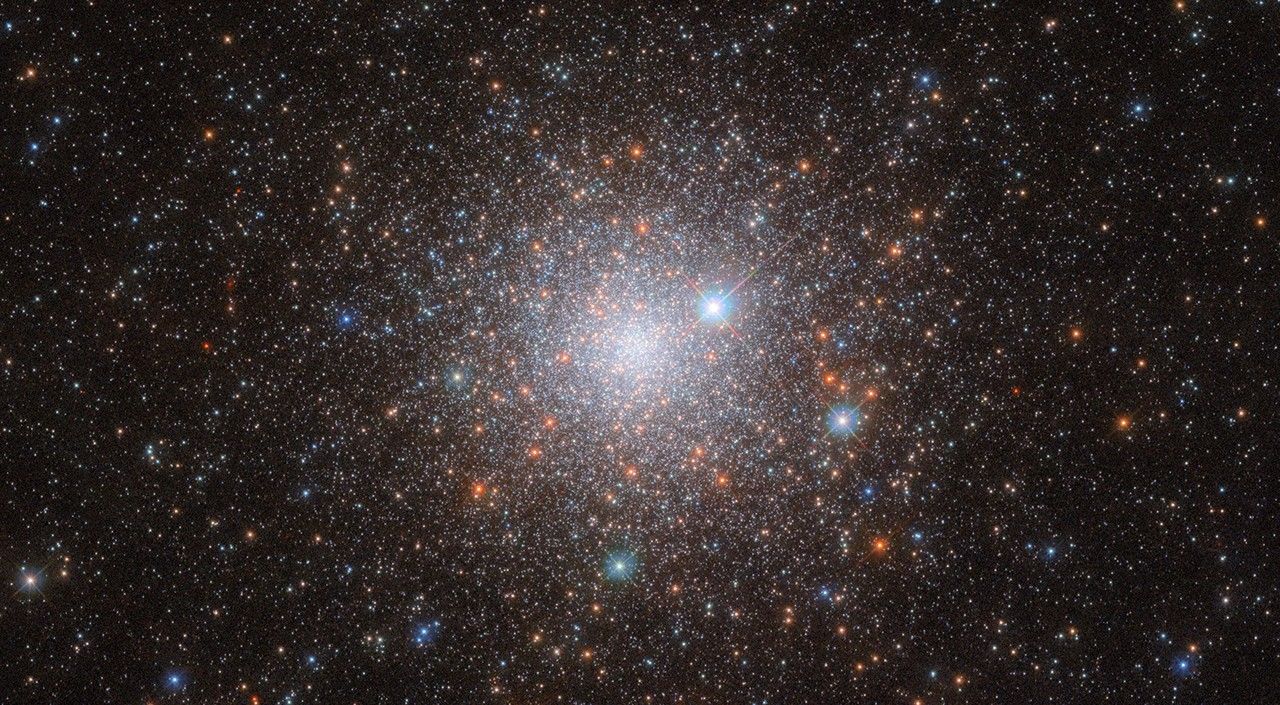
- The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captured an image of the globular cluster NGC 1786, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way about 160,000 light-years from Earth.
- NGC 1786 is situated in the constellation Dorado and was discovered in 1835 by Sir John Herschel.
- A scientific program compares globular clusters from dwarf galaxies like LMC to those found within the Milky Way to study their formation and evolution.
- Globular clusters, being stable and long-lived, act as “galactic time capsules” preserving stars from early galaxy formation phases.
- Research has revealed multiple populations of stars with different ages within globular clusters – previously believed to have formed simultaneously.
- Studies on external galaxies’ star clusters aim to provide insight into both their history and that of our own Milky Way.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The ongoing studies on globular clusters using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope not only advance astronomical research but also deepen our understanding of galactic histories. Insights into star populations from external galaxies such as LMC can improve models for galaxy formation – perhaps enriching global collaborations involving India’s astronomy initiatives like AstroSat or ISRO’s upcoming space observatories. The data could strengthen India’s contribution to international research discussions on cosmic evolution while encouraging further exploration projects aligned with these findings.