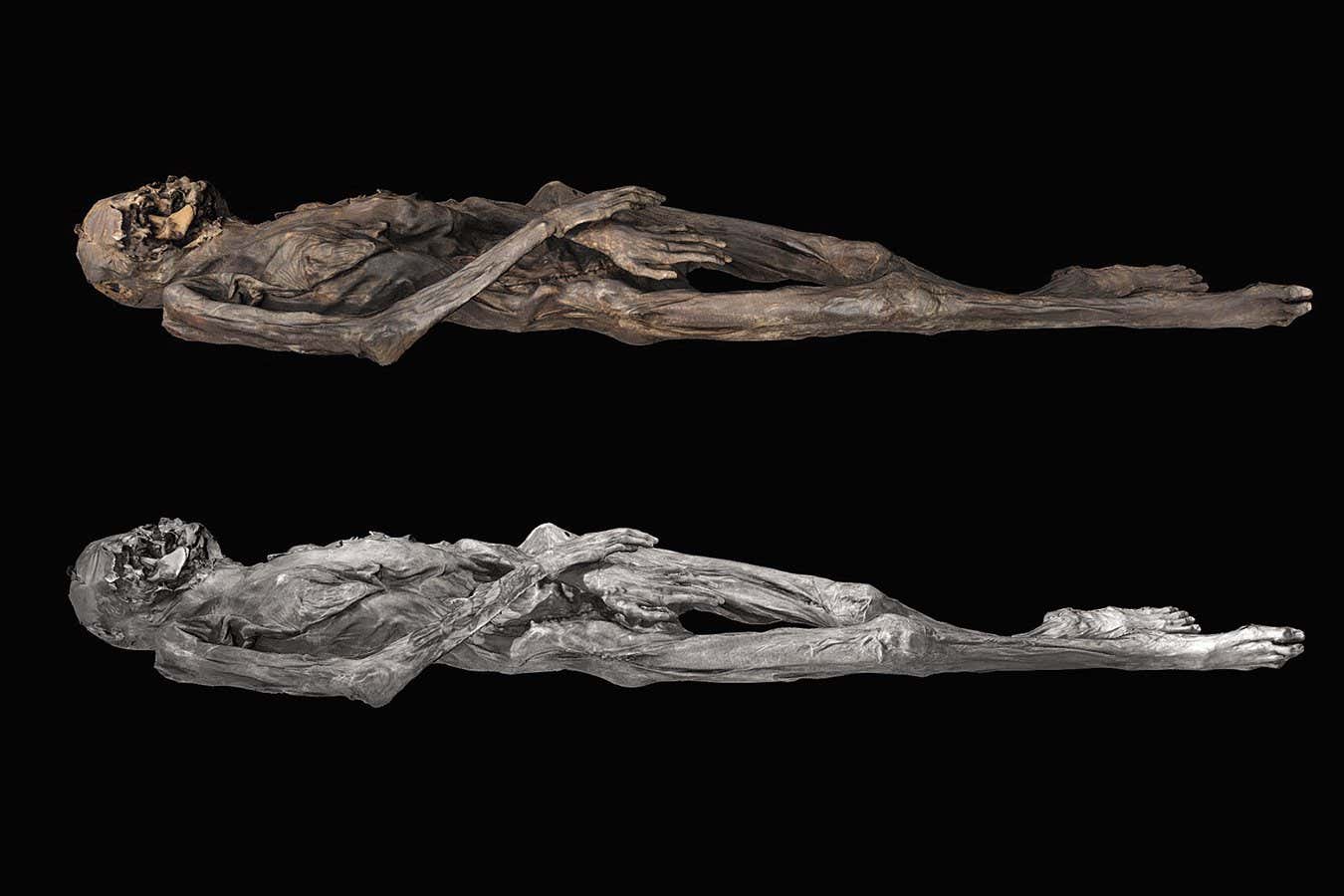
Now Reading: Human Milk May Hold Key to Combating Pregnancy-Threatening Infections
-
01
Human Milk May Hold Key to Combating Pregnancy-Threatening Infections
Human Milk May Hold Key to Combating Pregnancy-Threatening Infections
Quick Summary
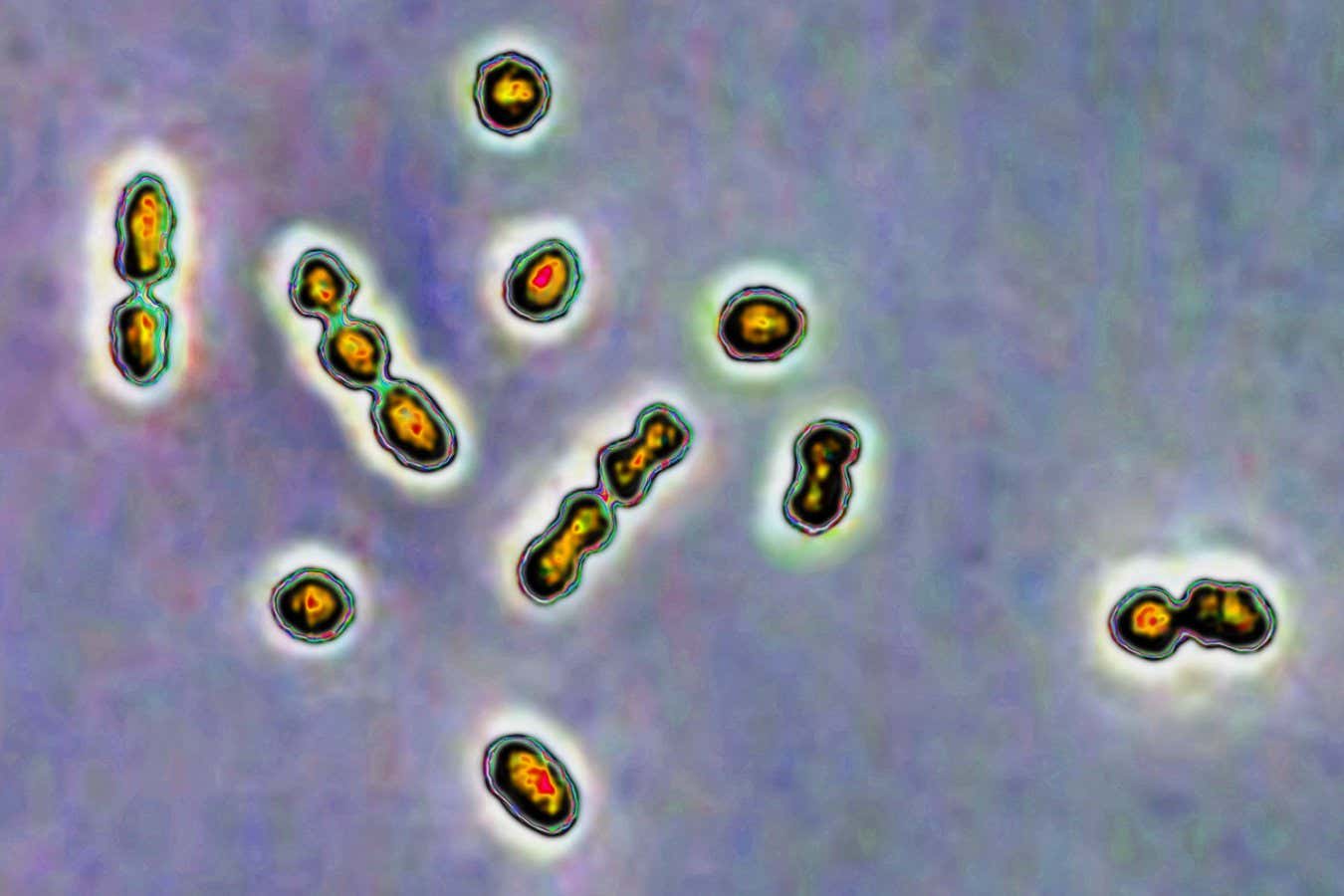
- Researchers at Vanderbilt University studied the potential therapeutic effects of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) against Group B Streptococcus (GBS), which can complicate pregnancies when present in the vagina.
- HMOs, found exclusively in human milk, are emerging as highly effective prebiotics that support healthy microbiome development.
- Experiments on lab-engineered vaginal tissue and mice showed that hmos promote the growth of healthy Lactobacillus bacteria, which outcompete GBS and create acidic conditions antagonistic to harmful bacteria.
- The research highlights potential avenues for regulating and restoring a healthy vaginal microbiome without over-relying on antibiotics, which can lead to antibacterial resistance.
- Experts caution that therapies using HMOs are still years away from practical request and warn against premature use due to risks like infectious disease transmission via untreated breast milk.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings surrounding human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) open new possibilities for addressing key health challenges related to maternal and newborn care globally – challenges particularly relevant for India due to its high population density and healthcare disparities.If future therapies leveraging HMOs prove viable,they could reduce dependency on antibiotics while mitigating risks of bacterial resistance-a critical issue given India’s widespread availability of antibiotics without regulated prescription protocols.
Further exploration into non-antibiotic treatments could align with India’s ongoing efforts toward affordable healthcare innovations. though, premature experimentation or commercialization could backfire in areas with limited public health education regarding infectious diseases transmitted through untreated substances like breast milk. Continued research backed by strict safety protocols will be essential as India studies such advancements under its own medical landscape needs.