Now Reading: India Launches World’s Most Accurate Space Clock with Limited Lifespan
-
01
India Launches World’s Most Accurate Space Clock with Limited Lifespan
India Launches World’s Most Accurate Space Clock with Limited Lifespan

Swift Summary
- The European Space Agency (ESA) is launching the Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES), the most accurate clock ever sent to space, on 21 April via a spacex Falcon 9 rocket.
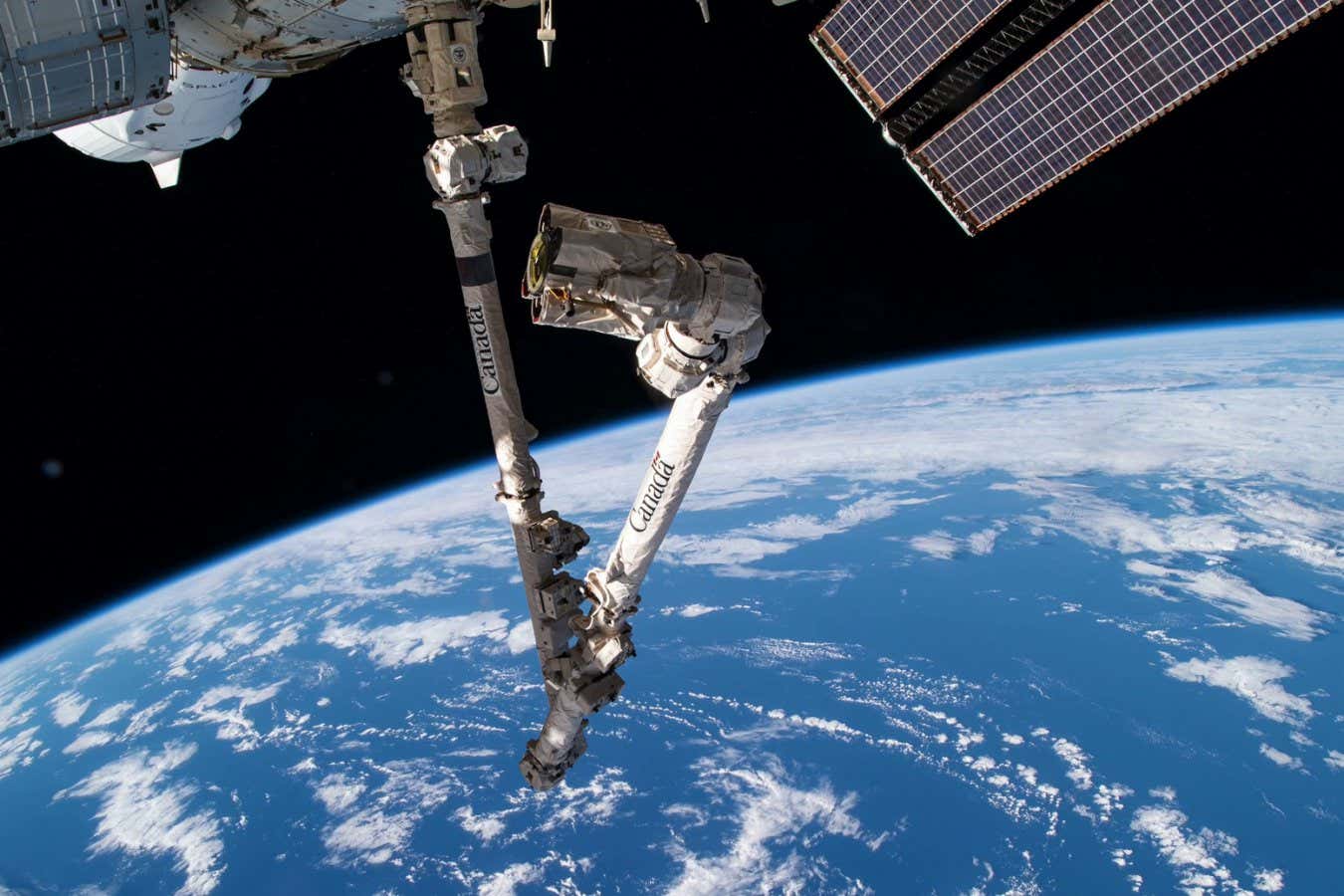
- ACES will be attached to ESA’s Columbus laboratory on the ISS using Canadarm2, the robotic arm built by the Canadian space Agency.
- The device consists of two clocks: SHM for short-term stability and PHARAO, which sprays cooled caesium atoms in microgravity for unprecedented precision. Together, they would lose less than one second over 300 million years-making them ten times more accurate than GPS satellite clocks.
- ACES will synchronize Earth’s best clocks via laser signals transmitted from nine ground stations and test Einstein’s theory of general relativity wiht high accuracy.
- it will assist research related to dark matter and string theory but only operate until 2030 as it burns up upon deorbiting alongside the ISS at decade’s end.
- Development began in the 1990s; commissioning takes six months after reaching orbit, followed by a year-long calibration process before operational signals begin.
[Image: Canadarm2 used on ISS] (Credit: ESA/NASA)
Indian Opinion Analysis
The ACES mission represents meaningful strides in scientific innovation that merge engineering excellence with foundational physics exploration. It’s potential impact includes improving global timekeeping precision and enabling groundbreaking insights into theories like general relativity-a cornerstone of modern physics. For India, which has burgeoning ambitions in space exploration through ISRO programmes such as Gaganyaan and its focus on innovative payload technologies (e.g.,NavIC satellites),this milestone underscores opportunities for collaboration or autonomous advances that could enhance national capabilities in atomic timekeeping systems.
India may find inspiration from ACES not only technologically but also procedurally-balancing project costs against achieving scientific breakthroughs over decades-long timelines amid evolving international partnerships. Areas such as telecommunications alignment or gravitational field studies may become emerging fronts for Indian research initiatives post-launch analysis results from ESA’s cutting-edge trials.