Now Reading: India Leads World in Flood-Prone Slum Clusters
-
01
India Leads World in Flood-Prone Slum Clusters
India Leads World in Flood-Prone Slum Clusters

Fast Summary
- Flooding affects over 2.3 billion people yearly, with over 600 million exposed too coastal or inland flooding in India.
- A study analyzed satellite imagery of slum settlements in 129 low- and middle-income countries, comparing them with maps of past floods.
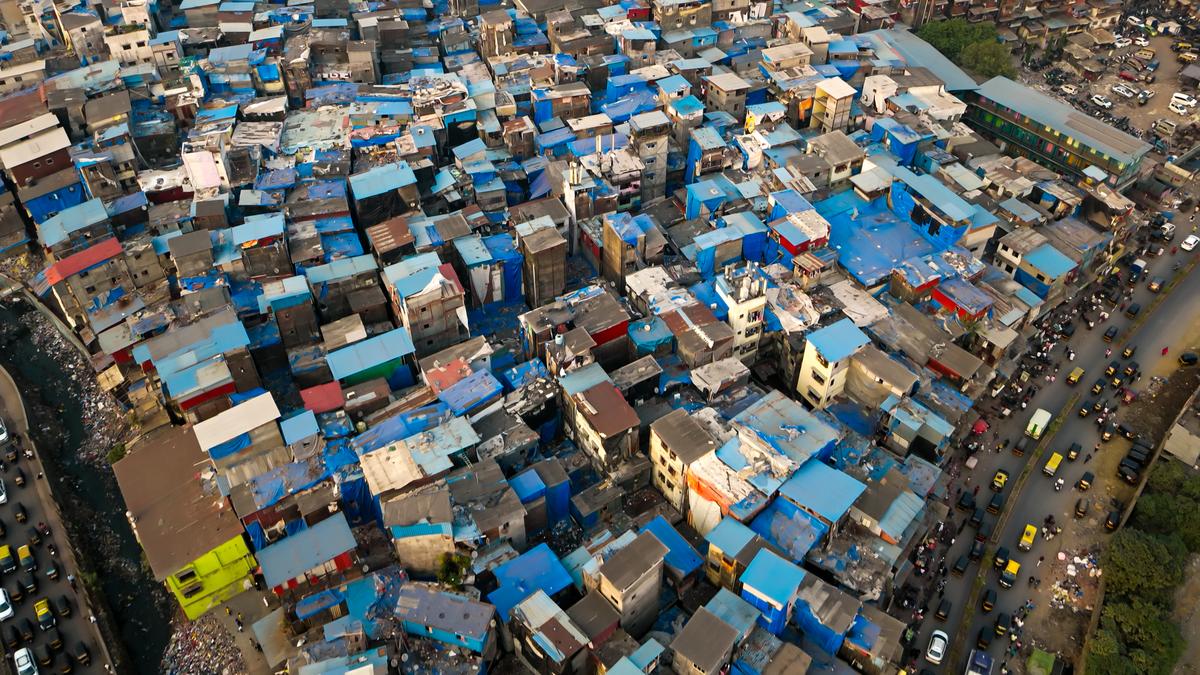
- India has the largest number of slum dwellers in flood-prone areas globally,approximately 158 million concentrated mostly in the Ganga delta.
- South Asia features high numbers; northern India leads globally, followed by Indonesia, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
- Vulnerable populations suffer indirect consequences like job loss and lack of access to services due to floods. Socioeconomic factors like income levels exacerbate vulnerability.
- Slum dwellers are more likely to settle in floodplains due to lower housing costs compared to non-slum populations. In urban areas like Bengaluru or Mumbai, cheaper land near flood-prone regions attracts informal settlement development.
- Global South lacks infrastructural protections (e.g., levies) seen elsewhere; governments often fail vulnerable communities while focusing on population-wide strategies.
- The study aligns its findings with Lasting Development Goals (SDGs), emphasizing a human-centric approach and community collaboration for climate resilience.
Indian Opinion analysis
The study highlights critical challenges for India regarding urban planning and climate adaptation strategies. With over 158 million slum dwellers residing in floodplains prone to extreme weather events-predominantly driven by socioeconomic pressures-it underscores the urgency of targeted interventions addressing both immediate disaster response needs and long-term resilience-building solutions.
This data-driven analysis points toward stark inequities: economic barriers push marginalized populations into high-risk zones while wealth-driven gentrification shifts risks further downstream physically and socially. As India’s urbanization accelerates alongside looming SDG deadlines for poverty alleviation and sustainable infrastructure development (2030), local stakeholders must prioritize inclusive tools such as better drainage systems, skill development for migrant workers, and collaboration between policymakers and at-risk communities.
Given India’s scale relative not just regionally but globally within this scenario-balancing affordable housing goals against rising climatic uncertainties may demand technology-propelled innovations like machine learning-based insights outlined within studies now gaining international visibility around predictive policymaking regarding socio-geographic vulnerability trends caused mutually intensifying crossover Feedback Loops Immediate action gaps require disaster-prepared ground-bold experimental-spaces safeguards-future-minimizing loss same!
Read more: [The Hindu](https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-surroundings/indian-cities-node Rationalize “Equitable Proposal”>