Now Reading: India Prepares for Stellarator Breakthrough in Fusion Technology
-
01
India Prepares for Stellarator Breakthrough in Fusion Technology
India Prepares for Stellarator Breakthrough in Fusion Technology
Swift Summary
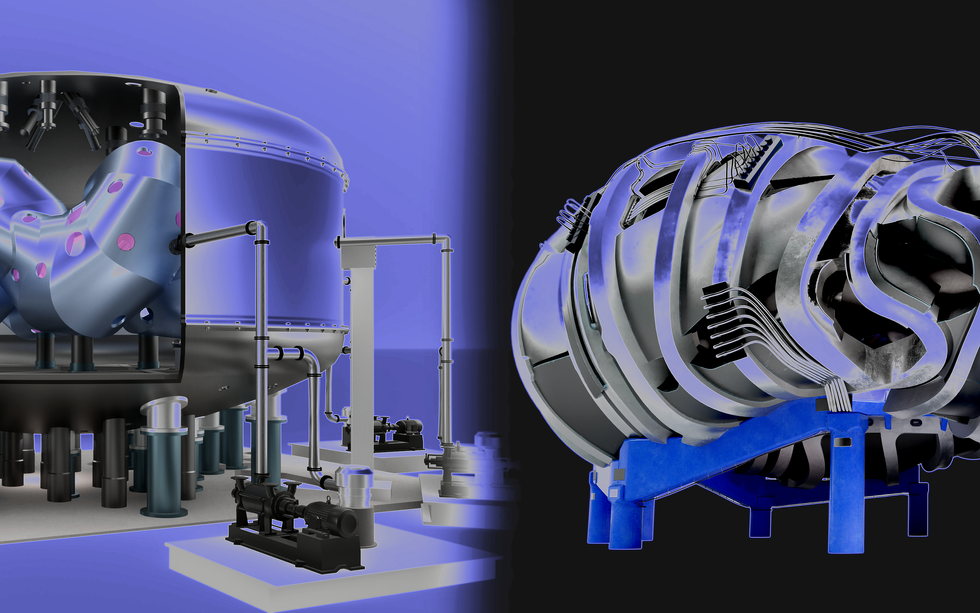
- nuclear Fusion and Stellarators: Stellarators, complex fusion reactors using twisted magnetic fields, are gaining renewed attention as they eliminate disruptions in plasma confinement. Unlike tokamaks, stellarators operate continuously without strong internal plasma currents.
- Key Players: germany’s Proxima Fusion and tennessee-based Type One Energy have published peer-reviewed papers showcasing their respective designs for commercial stellarator reactors.
– Proxima Fusion: Focuses on engineering integration for its Stellaris design, featuring high-temperature superconducting magnets (HTS), AI optimization, and a liquid-metal breeding blanket to produce tritium fuel. Targeted power output: 1 gigawatt.
– Type one Energy: Highlights advancements in plasma physics for its Infinity Two reactor with similar HTS magnets and optimized magnetic fields. Targeted power output: 350 megawatts.
- AI Contributions: AI-enhanced optimization tools were pivotal to advancing stellarator designs by simulating and creating more effective magnet geometries. Proxima favors quasi-isodynamic (QI) structures while Type One has shifted away from quasi-symmetry toward QI-based optimizations.
- Progress Plans:
– Proxima fusion: Alpha demo unit set for completion by the early 2030s; aims to first demonstrate net energy production in a steady-state system by around 2031.
– Type One Energy: Infinity One test platform planned for construction in 2026; full-scale Infinity Two reactor projected grid connection by mid-2030s via collaboration with Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA).
- Funding challenges: Type One has raised $82 million with plans to secure over $200 million further financing.Proxima has garnered $65 million in public/private capital.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancements made by Proxima Fusion and Type one Energy underscore nuclear fusion’s movement closer to practical application after decades of being an elusive technological goal. Both companies’ efforts signal crucial innovation within the transition toward cleaner energy systems that could substantially aid global climate objectives once commercially viable.
From India’s perspective, successful development of commercial stellarators holds critical potential implications:
- If deployed globally at scale, these reactors could provide carbon-free electricity generation capabilities that would complement India’s ambitious renewable energy goals under commitments such as COP26 or Mission net Zero initiatives aimed at curbing emissions reliance amidst growing demand curves rising because expanding massive urbanization /urban domains beforehand scaling market levels over rich Industry- However like any Scientific leadership Now remains well metricized infact needs carefully ensures expertise diligently towards future techabwa partnerships stakeholders investments nurturing!