Now Reading: Indian Snack Brand Aims to Redefine Chocolate
-
01
Indian Snack Brand Aims to Redefine Chocolate
Indian Snack Brand Aims to Redefine Chocolate

Speedy Summary
- Founder and Mission: Oded brenner, former co-founder of Max Brenner restaurants, launched Blue Stripes in 2018 to create food products from all parts of the cacao plant, addressing food waste and environmental impacts.
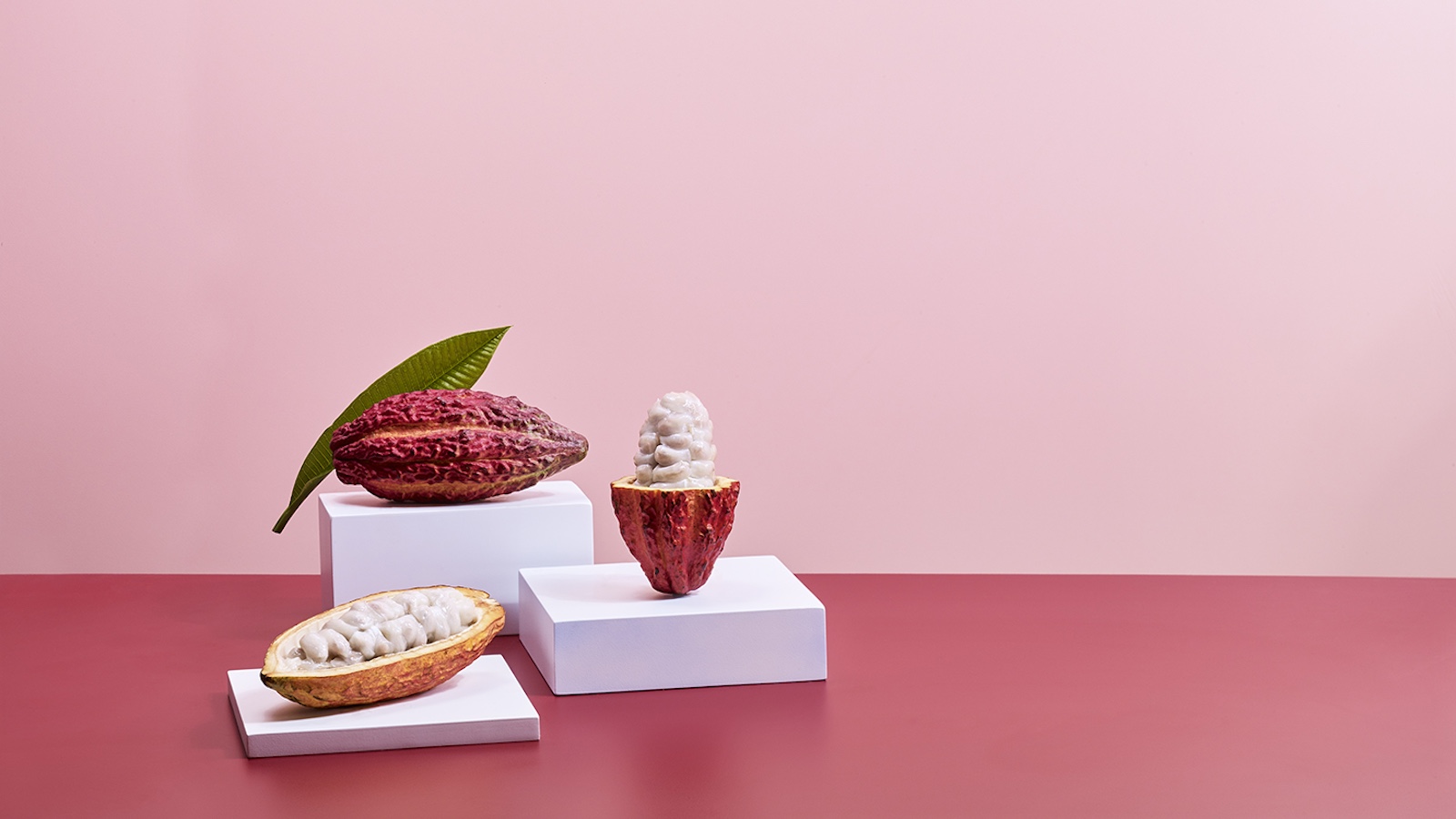
- Products: Blue Stripes offers cacao pulp-based drinks,dried fruit snacks,trail mixes,granola,and whole-cacao chocolate bars through platforms like Amazon and retail stores such as Whole Foods.
- Environmental Focus: The company aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from cacao waste (pulp and husks), which traditionally causes methane emissions due to decay or improper disposal.
- Economic Impact on Farmers: Sourcing cacao pods directly from two dozen Ecuadorian farms reportedly added $1.5 million revenue for farmers between mid-2022 and late 2024. Farmers are paid for beans at market rates but also earn additional income from pulp and husk flour.
- Global Industry Challenges: deforestation in some cocoa-producing regions remains the largest contributor to cacao’s carbon footprint globally despite efforts on waste reuse. blue Stripes’ Rainforest Alliance certification ensures products meet specific sustainability standards.
- Scaling Strategy: Success depends on popularizing the lesser-known parts of the cacao fruit among consumers with health-focused branding (
superfood) while localizing production near farms rather of conventional chocolate manufacturing hubs.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Blue Stripes’ innovative approach could reshape parts of global agriculture by demonstrating that sustainable practices can together benefit smallholder farmers economically while reducing environmental impacts caused by agricultural byproducts. For india’s agrarian economy-with its challenges tied to sustainability-this model showcases how direct sourcing combined with upcycling can boost farmer incomes without expanding plantations or compromising ecological balance.
overreliance on consumer interest in health-focused food markets may pose scaling risks if public adoption lags behind expectations. Though, localization strategies such as regional manufacturing rather of export-dependent intermediary processes highlight a potential pathway India might explore for other cash crops like sugarcane or coconut-both notorious for generating significant agricultural waste.
India’s burgeoning interest in organic farming coupled with ongoing conversations around farmer welfare could find inspiration here; integrating innovative crops into broader value chains might improve livelihoods without threatening natural resources already under stress.