Now Reading: James Webb Telescope Discovers ‘Sleeping Beauty’ Galaxies from the Early Universe
-
01
James Webb Telescope Discovers ‘Sleeping Beauty’ Galaxies from the Early Universe
James Webb Telescope Discovers ‘Sleeping Beauty’ Galaxies from the Early Universe

Quick Summary
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has revealed 14 “dormant” galaxies in the early universe that unexpectedly paused star formation within 10 too 25 million years before observation.
- These galaxies span a wide range of masses, from about 40 million to 30 billion solar masses.
- Star formation may halt due to stellar feedback (supernovas or stellar winds), supermassive black holes, or interactions with neighboring galaxies.
- Dormancy is often temporary; gas expelled or heated during feedback processes eventually cools and falls back into the galaxy, allowing star formation to resume.
- Researchers anticipated active star formation in early galaxies but discovered some had stopped temporarily-a phenomenon described as “stop-and-go” cycles rather than steady activity.
- Alba Covelo Paz, lead researcher from the University of Geneva, notes uncertainty around how long these dormant phases last and whether some galaxies stay inactive indefinitely.
- A future JWST program titled “Sleeping beauties” aims to further explore dormant galaxies in the early universe.
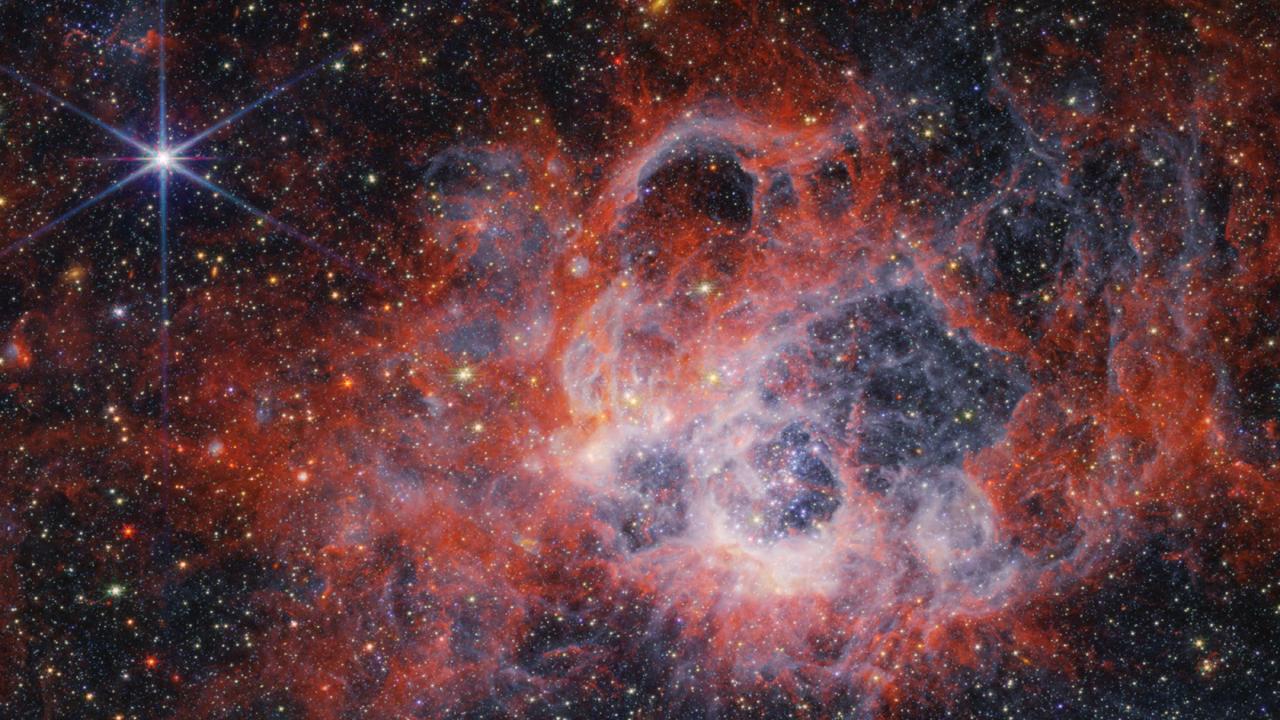
!Star-forming region NGC 604 captured by NASA’s JWST
Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI.
!NASA’s nircam image showing cavities carved by stellar winds
Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The revelation of dormant galaxies through data provided by JWST adds crucial understanding to cosmic evolution during the first billion years after the Big Bang. With implications for astrophysics research worldwide-including India-this milestone underscores our growing ability to unravel complex phenomena related to galaxy formation.India’s astrophysics community may notably gain insights by leveraging similar high-resolution instruments such as AstroSat.
The surprising observation of “stop-and-go” star formation cycles challenges standard assumptions that all early-universe galaxies exhibited relentless growth. For India’s space science ambitions-which aim at enhanced participation within global astronomical collaborations-the results are encouraging as it highlights gaps in current models that developing nations like India can address through theoretical contributions and precision studies.
While immediate applications for this knowledge in areas like technological progress are limited domestically today concerning scientific utility perspectives such reactors propulsion physics policymakers possibly integrate examining national restructuring planets binnenclature planetary effort expansion scenarios