Now Reading: James Webb Telescope Unveils ‘Cosmic Tornado’ with Surprising Discovery
-
01
James Webb Telescope Unveils ‘Cosmic Tornado’ with Surprising Discovery
James Webb Telescope Unveils ‘Cosmic Tornado’ with Surprising Discovery

Quick Summary
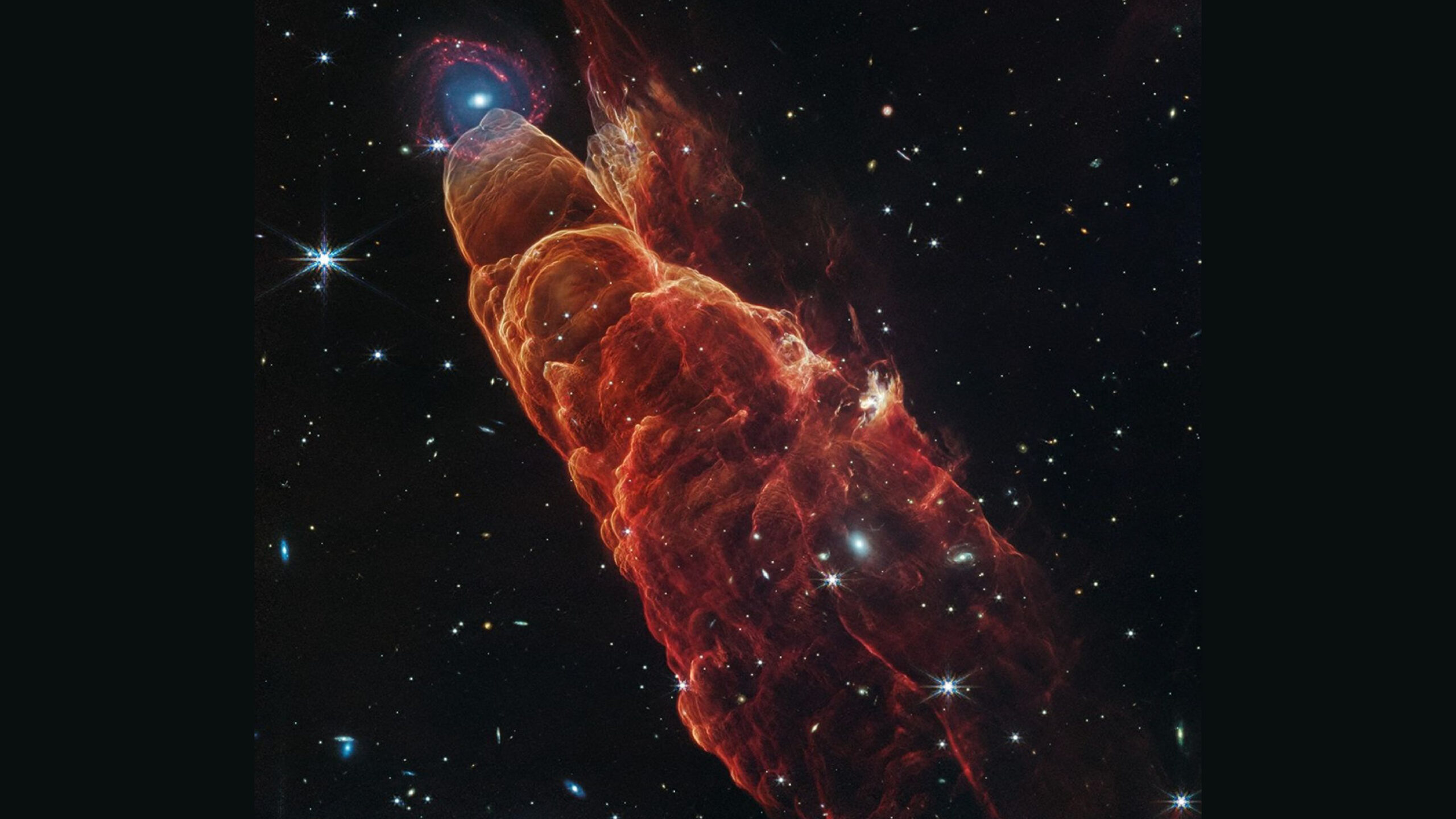
- NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) captured a detailed image of Herbig-Haro 49/50, nicknamed the “cosmic tornado,” showing bright plumes of gas emitted from a newborn star.
- Located about 625 light-years away in the Chamaeleon I Cloud complex, HH 49/50 is formed by jets of ionized gas colliding with surrounding material at hundreds of miles per second.
- The JWST composite image uses infrared wavelengths to reveal intricate features invisible to the human eye, previously captured by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope in less detail.
- Astronomers identified cederblad 110 IRS4, a Class I protostar about 100,000 years old and embedded in surrounding gas and dust, as responsible for HH 49/50’s outflow.
- A distant background spiral galaxy was mistaken as part of HH 49/50 in earlier observations but clarified by JWST imaging.
- The study provides insights into how young stars like our sun form and interact with their environments during early phases of stellar evolution.
Image Highlights:
!Cosmic Tornado
Caption: Image of Herbig-Haro 49/50 captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
!Comparison Image
Caption: Side-by-side comparison: Spitzer Space Telescope (left) vs Webb (right).
indian Opinion Analysis
NASA’s continued exploration using advanced telescopes like JWST builds on the global effort to better understand star formation processes-topic areas relevant not only scientifically but also philosophically for human advancement including nations such as India prioritising STEM where boost future also related indirectly Science severally modernly equals nations.Middle quest Explorations temp disciplines indeed Particle on Basic tags .On Ending Seen , skill