Now Reading: Lightning: Key Facts and Insights
-
01
Lightning: Key Facts and Insights
Lightning: Key Facts and Insights

Quick Summary
- Definition & Causes: Lightning is an electrical discharge stemming from imbalance between storm clouds and the ground or within clouds. Collisions of rain, ice, or snow particles during storms frequently enough fuel these imbalances.
- Heat: Lightning heats surrounding air to 50,000°F-five times hotter than the sun’s surface-causing thunder due to rapid air expansion.
- Types of Lightning:
– Common types include cloud-to-ground bolts (up to one billion volts) and internal cloud lightning.
– Rare forms: Positive lightning strikes far distances; ball lightning is unexplained but floats and glows; volcanic eruptions or snowstorms can trigger other varieties like rocket and ribbon lightning.
- Impact: Causes about 24,000 yearly global fatalities and injuries ranging from burns to neurological effects like memory loss. Despite severity,nine out of ten struck individuals survive.
- Safety Tips: Avoid water bodies, metal objects, tall trees during storms; grounded buildings provide safety but avoid running water or using landlines indoors during electrified conditions.
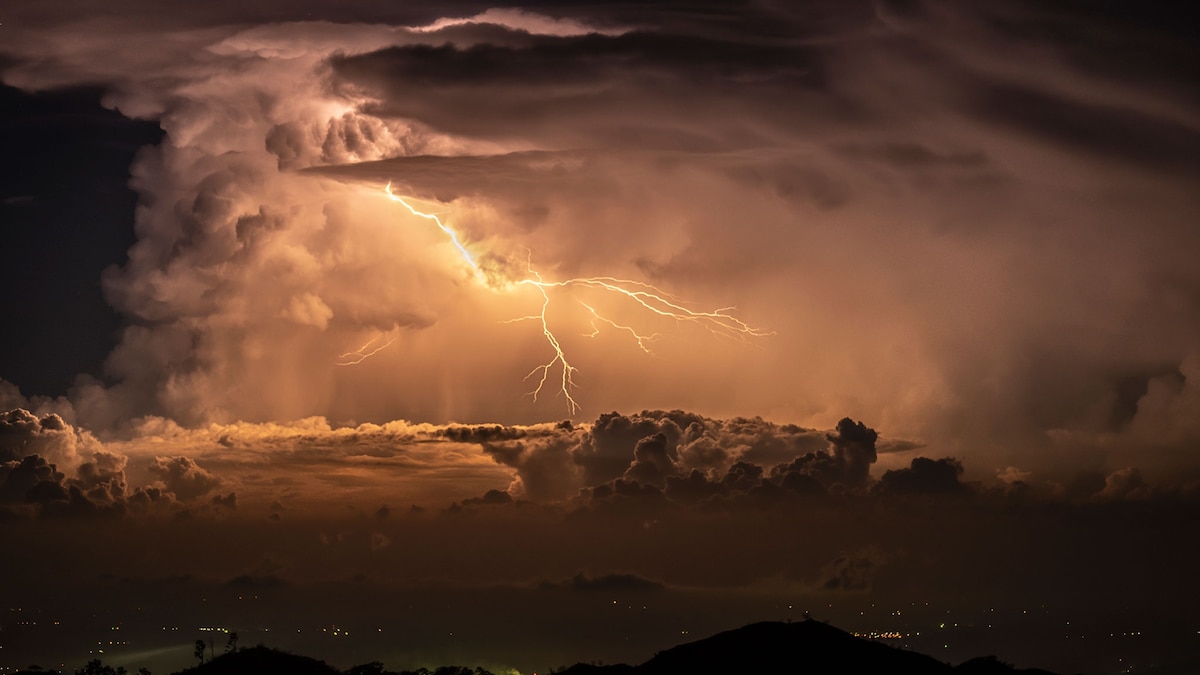
Image Description:
!A dark sky with lighting
Lightning strikes off the coast of Portland, Maine. Photograph by robbie George (Nat Geo Image Collection).
Indian Opinion Analysis
Lightning’s scientific explanation illuminates its immense power yet unpredictability-a pressing issue for India’s rural regions were thunderstorms substantially impact communities reliant on open spaces for agriculture and housing. Fatalities linked with natural disasters such as severe weather events disproportionately affect those underserved by infrastructure like safe shelters or grounded homes.
India has seen increased efforts in disaster preparedness initiatives through awareness programs on common myths (e.g., multiple strikes in one spot) alongside equipping regions prone to thunderstorms with warning systems. However, further emphasis on integrating localized solutions-like ensuring rural homes are equipped with grounding mechanisms or storm-proofing-is critical due to varied regional needs across such a diverse nation.
Addressing climate-driven intensifying patterns affecting tropical monsoon zones could ensure harmony between India’s developmental trajectory even amidst heightened vulnerabilities faced under erratic systems globally shifting including heat-led variability inevitably affected developing precipitation lightning storm anchoring ad-hoc formulating public solutions!