Now Reading: Lviv Pysanka: Unveiling the World’s Oldest Easter Egg
-
01
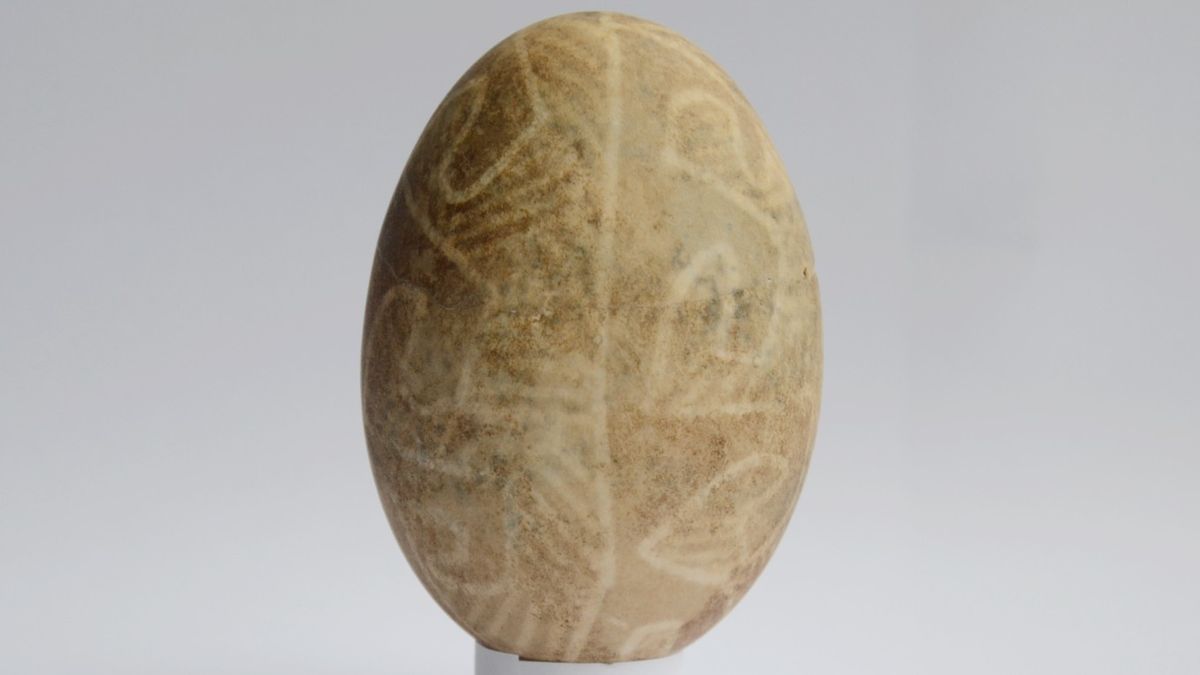
Lviv Pysanka: Unveiling the World’s Oldest Easter Egg
Lviv Pysanka: Unveiling the World’s Oldest Easter Egg

Quick Summary
- Artifact Name: lviv pysanka (Ukrainian for “written egg”).
- Origin: Lviv, Ukraine.
- Past Context: Made in the early 16th century; oldest known decorated Easter egg in the world.
- Revelation:
– Found in a medieval well during construction work in 2013.
– Preserved alongside various objects like charcoal, dishes, and utensils after cleanup post-Great Fire of Lviv (1527).
- Crafting Technique:
– Created using wax-resist method on a duck eggshell.
– Only minor damage to its structure over time (~2 square centimeters lost).
- Cultural Significance:
– Decorating Easter eggs is an ancient tradition with archaeological evidence tracing back centuries or even millennia (e.g., Stone Age Cucuteni-Trypillia culture).- Originally pagan symbol absorbed into Christian traditions tied to the resurrection of Jesus Christ.
– Recognized by UNESCO as Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity as 2024.
- current Display Location: Housed at the Pysanka Museum in Kolomyia.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery and preservation of historically significant artifacts, such as the Lviv pysanka, highlight humanity’s enduring cultural practices that transcend specific regions or religions. While this Ukrainian artifact does not directly relate to India,its multidisciplinary context-combining archaeology,history,craftsmanship,and heritage-offers valuable parallels for India’s efforts to protect its rich traditions.
India boasts many art forms rooted in antiquity that also bridge pre-Christian or pre-Islamic rituals with modernity (e.g., rangoli designs and intricate textiles). Global recognition like UNESCO’s designation shows the importance of safeguarding intangible cultural practices amidst changing societal landscapes. India’s focus on promoting crafts through initiatives such as GI tagging could similarly contribute toward preserving artisan legacies while fostering international appreciation.
The story reinforces how community identity and resilience are closely tied to preserving traditional arts linked to nature’s symbolism-a universal concept relevant for Indian creators looking toward heritage-inspired global influence.