Now Reading: Measuring the Mass of a Black Hole
-
01
Measuring the Mass of a Black Hole
Measuring the Mass of a Black Hole
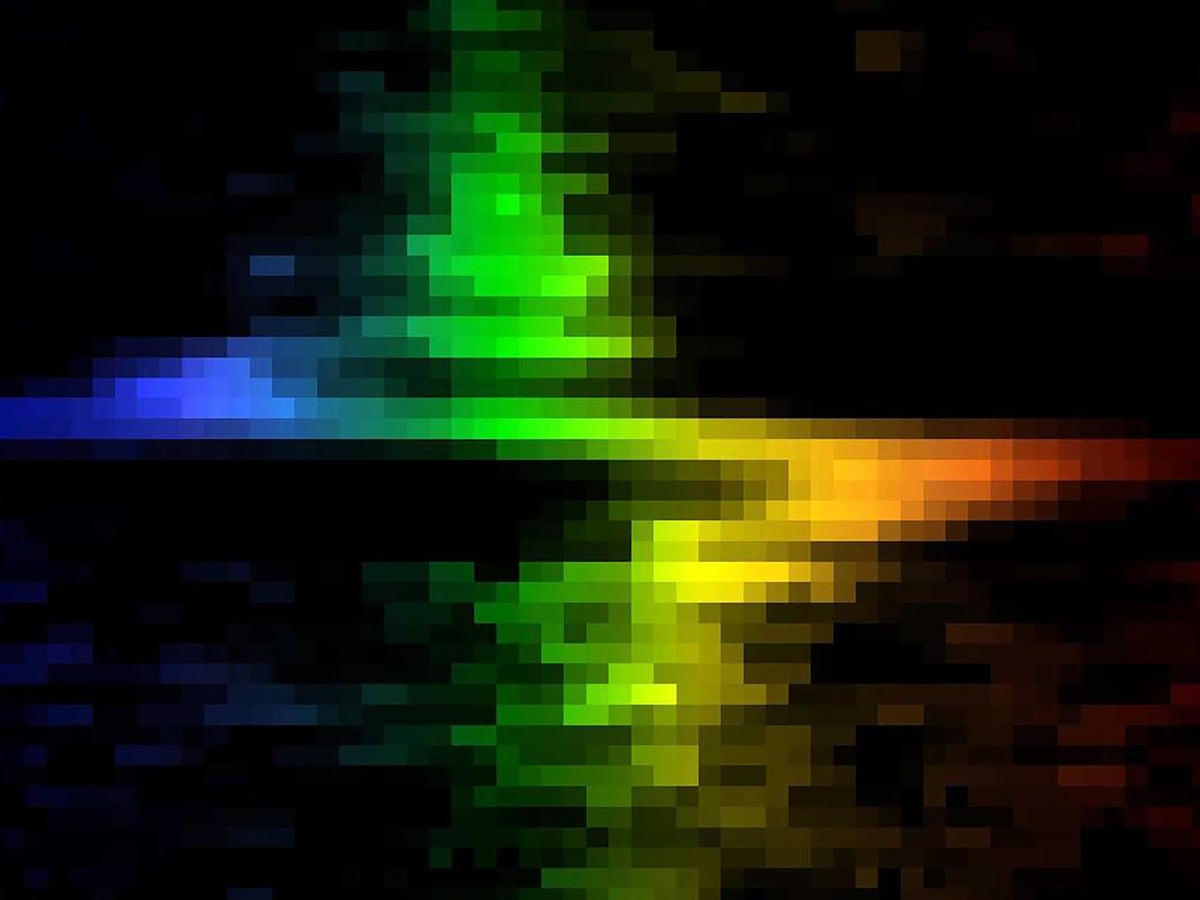
Swift Summary:
- Black holes are challenging to study due to their “black” nature, which prevents light from escaping them.
- Measuring black hole mass relies on indirect methods such as observing gravitational interactions with nearby objects.
- Stellar-mass black holes (3-100 times teh Sun’s mass) often form when massive stars end their life cycles in supernovae.
- Key measurement technique includes studying binary systems where a visible star orbits an unseen object,applying Doppler shifts and Kepler’s laws to estimate the black hole’s mass.
- Supermassive black holes (millions or billions of solar masses) found in galaxy cores are gauged by the orbital motion of surrounding stars or gas emitting dual blueshift/redshift spectra.
- X-ray emissions, tidal disruption events (stars shredded near black holes), and gravitational waves from merging black holes also provide data on masses for both stellar-mass and supermassive types.
- Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope’s STIS have successfully detected Doppler shifts pointing to massive central black holes, e.g., 300 million solar mass estimation for M84’s centre.
- Current technology measures stellar-mass mergers via gravitational waves; proposed future tools like LISA aim to capture supermassive collisions.
Image Included: Depicts spectral shifts captured by Hubble around galaxy M84’s core showing motions indicating a central supermassive black hole.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancements in measuring techniques for determining the properties of elusive phenomena like black holes highlight humankind’s ingenuity and scientific progress. For India, which is increasingly investing in its space missions via ISRO and collaborations with global observatories, these discoveries emphasize opportunities for technological innovation. Black hole research offers deep insights into areas like gravitational physics-a domain that could benefit Indian students and researchers under international science exchanges or indigenous projects.
Additionally, India’s growing astrophysics research community may engage with emerging technologies such as new generation space-based telescopes (e.g., LISA). Such collaboration can bolster India’s positioning within scientific forums while inspiring more young minds toward space sciences-a critical aspect of long-term knowledge economy enhancement. however, fostering an ecosystem supportive of such high-level research may require policy focus on funding advanced instrumentation alongside academic-industry synergy.
























