Now Reading: Meet the Dinosaur with 500 Teeth: A Prehistoric Marvel
-
01
Meet the Dinosaur with 500 Teeth: A Prehistoric Marvel
Meet the Dinosaur with 500 Teeth: A Prehistoric Marvel
Quick Summary
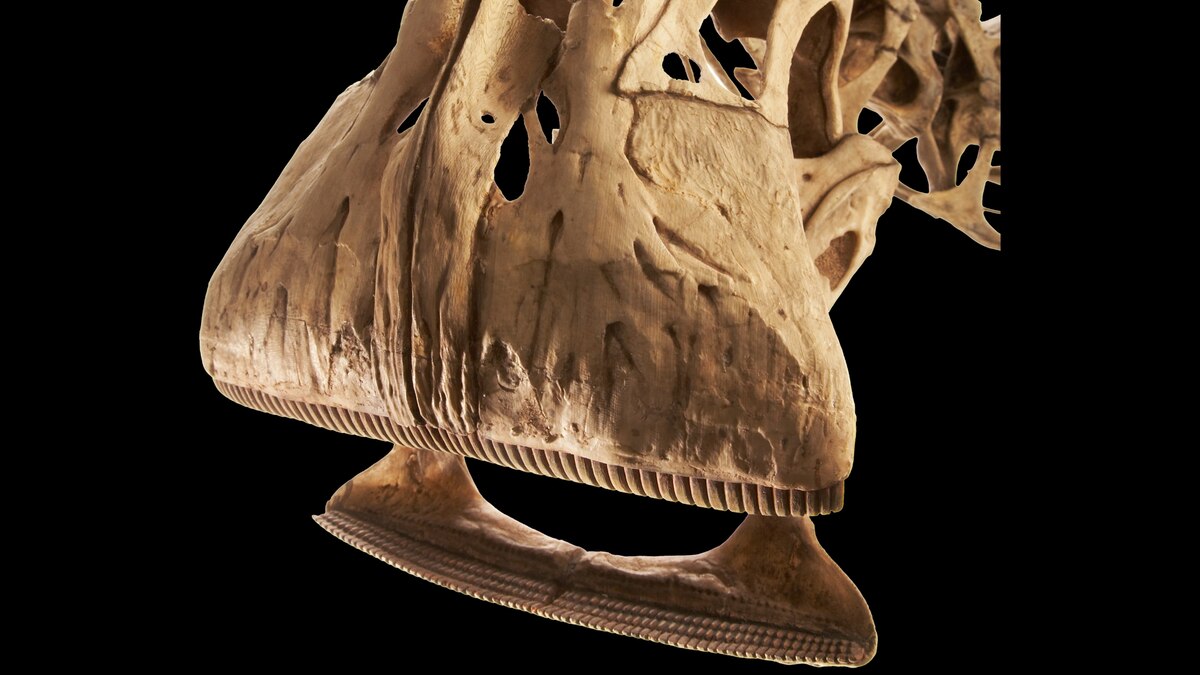
- dinosaur Identification: Nigersaurus taqueti lived 105 million years ago in present-day Niger, africa.It was a unique herbivore with 500 teeth that replaced every 14 days.
- Physical Description: Weighed two tons, stretched 30 feet long, had hollow bones supported by air sacs, and its eyes were positioned high on the skull for better vision against predators.
- Discovery and Naming:
– First identified between 1965-1972 by French paleontologist Philippe Taquet at the Gadofaoua site.- Rediscovered in 1997 by Paul Sereno’s team; named Nigersaurus taqueti in honor of Taquet and Niger in 1999.- Digital CT scans reconstructed details such as anatomy, skull shape, inner ear positioning for posture analysis, and brain cavity functions.
- Plant Consumption Efficiency: Square-shaped muzzle designed for grazing low-grow vegetation containing sand or silica. Teeth slid together like shears to manage tough plants efficiently but wore down quickly due to gritty diets.
- Research Importance: Highlights evolutionary adaptations like rapid tooth replacement (every two weeks) to thrive in challenging environments.
!Scientists unveil reconstructed skeleton of Nigersaurus
Photograph by Bill O’Leary/The Washington Post/Getty Images
!Illustration of Nigersaurus grazing near other dinosaurs
Illustration by Arthur Dorety/Stocktrek Images/Getty Images
Indian Opinion Analysis
Nigersaurus taqueti’s discovery demonstrates how cutting-edge technology is revolutionizing paleontology. The use of digital CT scans allowed researchers not only to reconstruct its delicate bones but also analyze evolutionary traits like efficient plant consumption mechanisms through rapid tooth replacement.
For India as a country with archaeological aspirations akin to uncovering historical human civilizations within its borders-such innovations provide insight into how collaboration with global entities can aid discoveries. Moreover, it fosters interdisciplinary research opportunities combining engineering (CT scan technology), biology (bone structure studies), and environmental science.
Studying prehistoric organisms like Nigersaurus expands understanding about survival strategies that shaped Earth’s biodiversity over millions of years. Lessons from evolutionary resilience could indirectly inform conservation efforts worldwide-including safeguarding flora/fauna ecosystems closer home.

























