Now Reading: Microwaving Rocks: A New Tool to Capture CO2 in Mining
-
01
Microwaving Rocks: A New Tool to Capture CO2 in Mining
Microwaving Rocks: A New Tool to Capture CO2 in Mining

Quick Summary
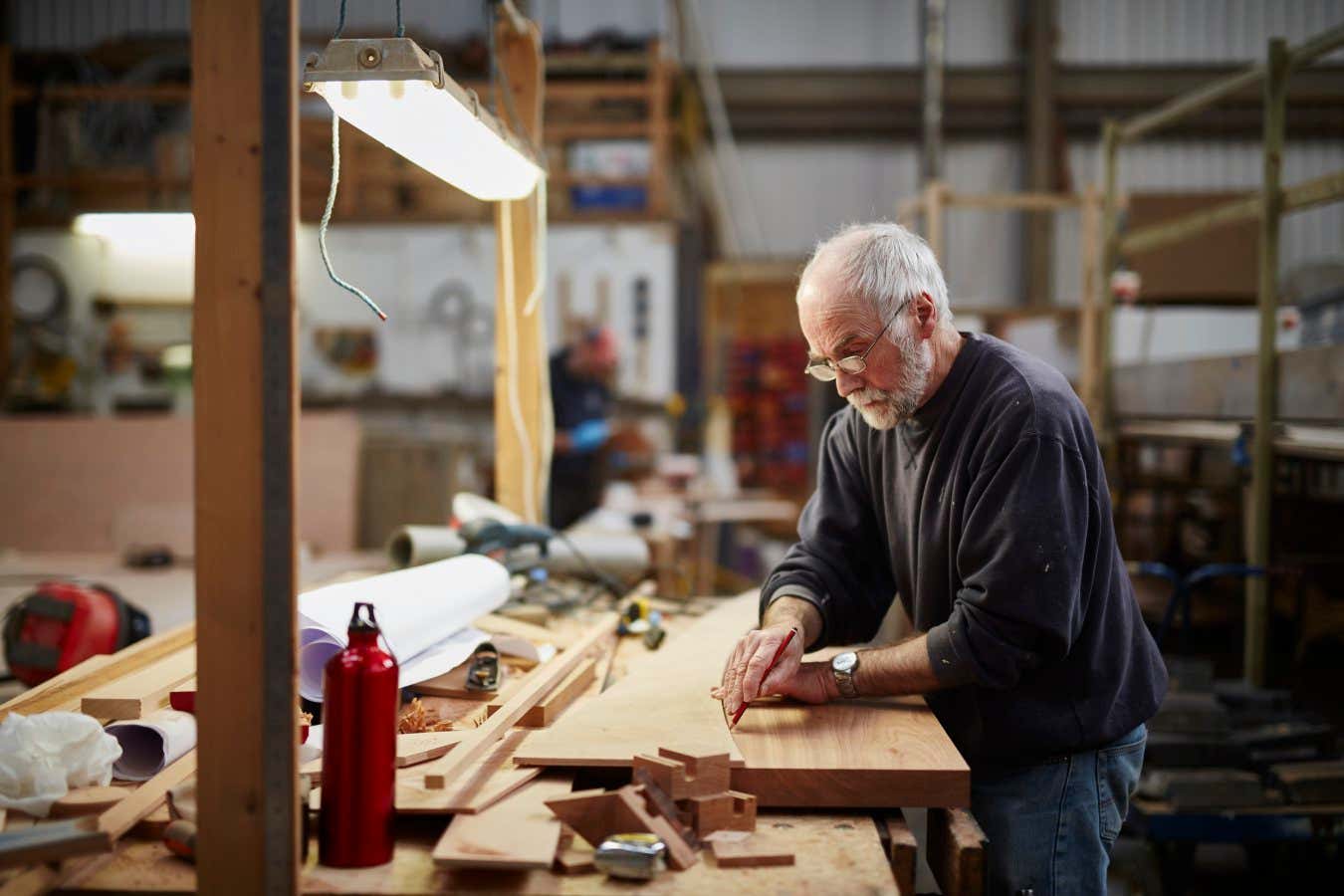
- A Canadian carbon dioxide removal company, Arca, is exploring the use of microwaves to make mining waste rocks react with CO2, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Current methods for enhancing rock reactivity require burning fossil fuels at high temperatures; microwaving could provide a cleaner and more energy-efficient alternative.
- Microwaves heat specific molecules in the rock structure rather than heating the entire rock mass, perhaps accelerating chemical reactivity and reducing energy consumption.
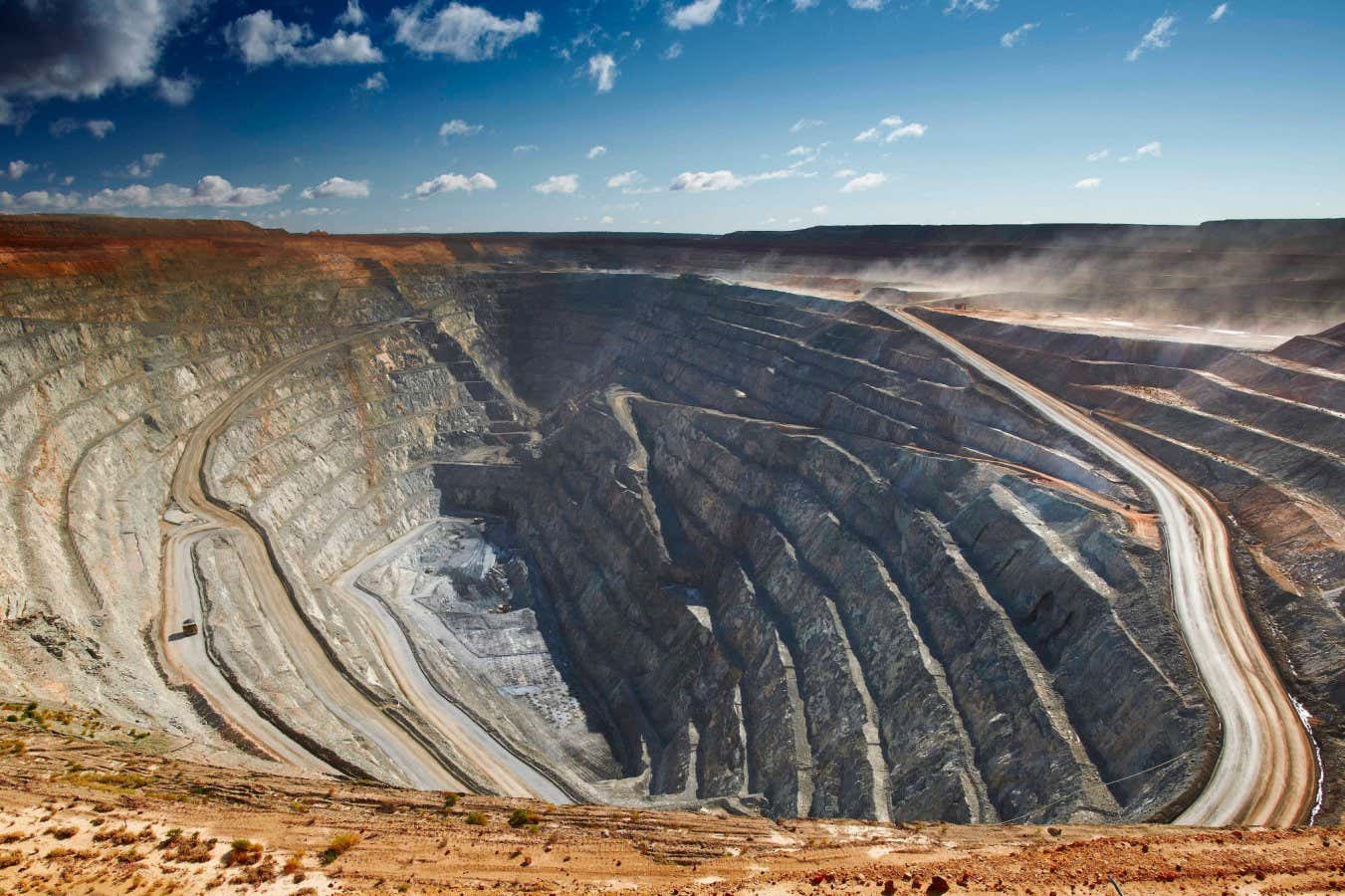
- serpentine minerals in certain tailings (mining waste) are rich in magnesium and can store CO2 when treated effectively. About 28 billion tonnes of tailings worldwide could store up to 8.7 billion tonnes of CO2-equivalent to two years’ worth of US emissions.
- The approach has only been tested in laboratories thus far but shows an “order of magnitude boost” in both rate and capacity for CO2 capture compared to untreated rocks, according to claims by Arca researchers.
- Future scaling plans include conveyor systems paired with microwave fields or autonomous equipment like rovers designed for efficient tailing churning and exposure during storage operations.
- Some experts view these innovations as promising but caution that scaling challenges remain unclear from initial lab results.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The innovation being pursued by Arca highlights a growing trend toward leveraging industrial processes for carbon capture-a critical focus as nations tackle climate change goals globally. For India notably-a leading force in mining production-the technology points toward two potential benefits: improving environmental sustainability within its mining sector and bolstering commitments under climate accords such as COP26.
If adopted widely, such advancements could address India’s notable reliance on coal-based energy-intensive industries while enabling better utilization of its ample nickel resources essential for electric vehicle batteries-an expanding market aligned with India’s renewable push under initiatives like ‘National Electric Mobility Mission Plan.’
However, practical implementation hurdles must be noted-the scalability gap between lab-based findings versus real-life applications underscores critical uncertainties about feasibility at mine sites across geographically diverse terrains like those found domestically (e.g., Jharkhand or Odisha). Developing countries may also face additional financial pressures around investing heavily into retrofit systems without established success models internationally.
While promising conceptually due largely neutral tone insight scientific preview awaits large-scale field deployments track credible long-term impacts!