Now Reading: How Diamonds Are Safeguarding the Okavango River Basin
-
01
How Diamonds Are Safeguarding the Okavango River Basin
How Diamonds Are Safeguarding the Okavango River Basin

Rapid Summary
- Geological forces over millions of years have created unique phenomena, such as diamonds and southern africa’s Okavango Delta, shaped by tectonic pressure and time.
- Diamonds form under extreme pressures (45,000-60,000 atmospheres) and temperatures (~1200°C) in Earth’s mantle beneath ancient continental crust but require volcanic eruptions to transport them to the surface.
- Kimberlite pipes are rare formations that carry diamonds to the surface; only 15% of these pipes globally contain diamonds viable for mining.
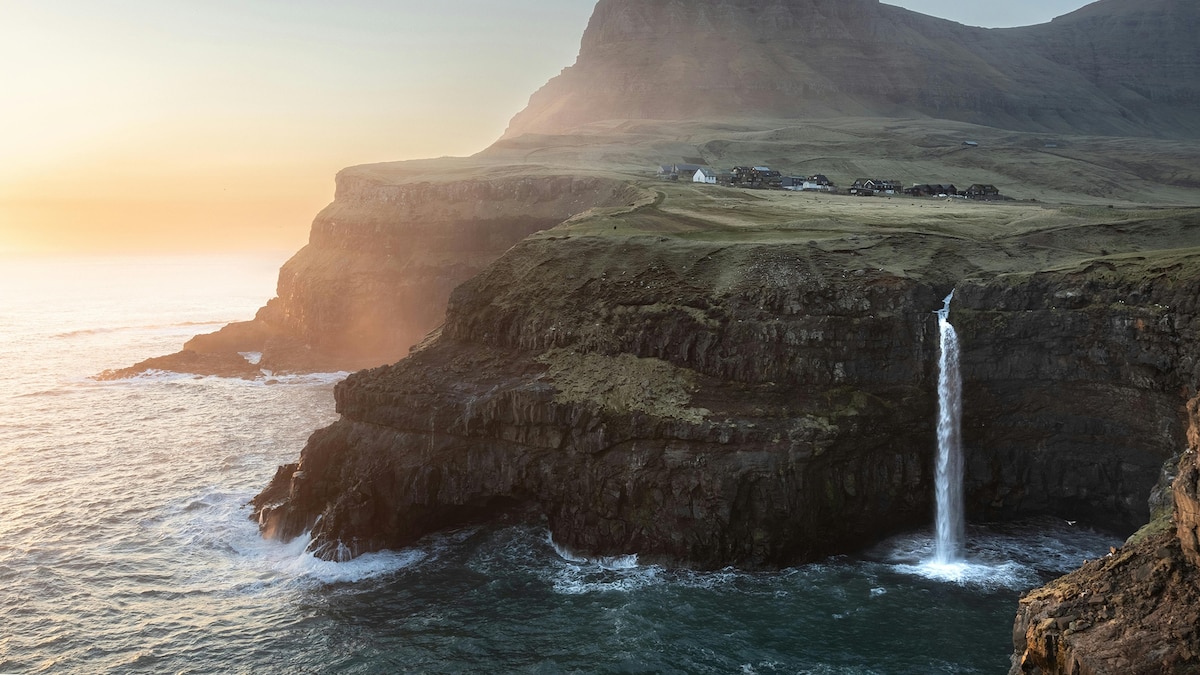
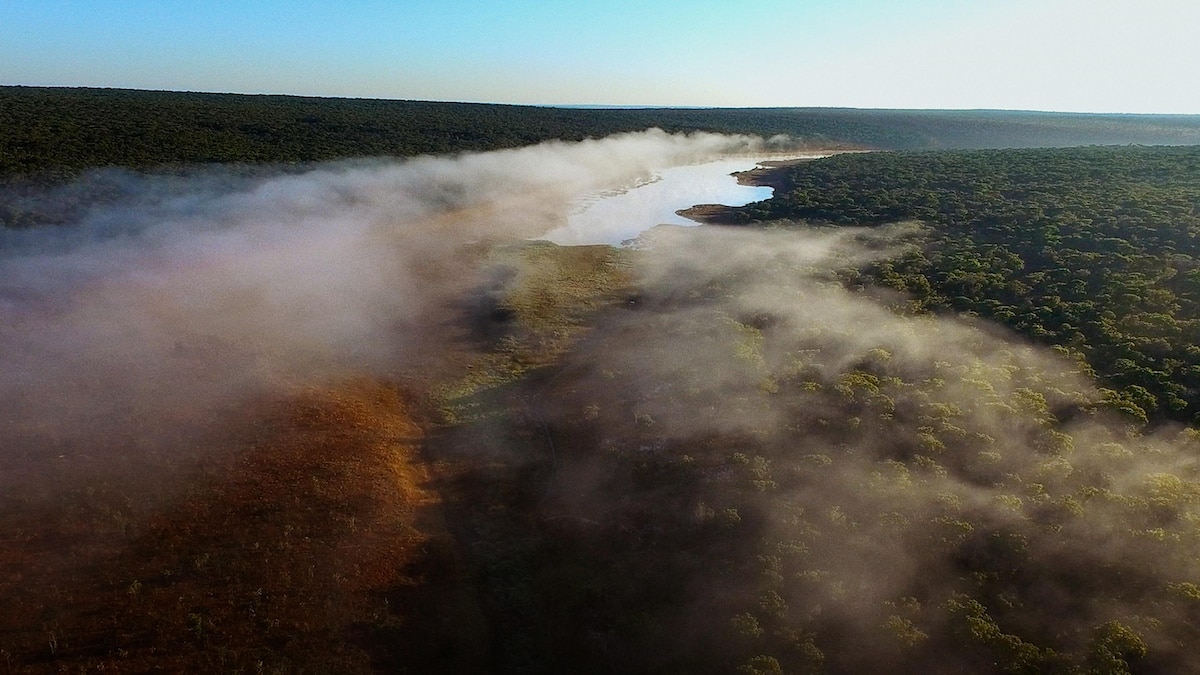
- Northern Botswana hosts fault lines stemming from the east African Rift that formed a unique geomorphological feature: the freshwater inland Okavango Delta.
- The Okavango Delta is sustained by waters flowing from Angola’s Highlands into Botswana’s kalahari Desert.
- The delta supports remarkable biodiversity-including endangered cheetahs, rhinos, lions-and serves as a crucial habitat for Africa’s largest elephant population.
- Population growth, commercial agriculture, climate change, and growth threaten water sources funneling into the Delta from Angola’s Highlands.
- “Okavango Eternal,” a partnership between De Beers and National Geographic seeks to preserve biodiversity while creating enduring livelihoods in local communities.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India can draw valuable lessons about ecological preservation from efforts like “Okavango Eternal.” Southern Africa’s success in merging conservation goals with community involvement demonstrates an approach sensitive to environmental priorities while bolstering livelihoods-an increasingly relevant topic given India’s own biodiversity challenges such as drying rivers and forest depletion.Additionally,India should note how geological phenomena can be leveraged sustainably without jeopardizing natural ecosystems or habitats.The commitment of private enterprises like De Beers offers insights into public-private partnerships focused on long-term sustainability goals-a model implementable within India’s rich but fragile environmental heritage areas like Sundarbans or Western Ghats.
Understanding international conservation frameworks also highlights opportunities for India to enhance protection efforts for its endemic species through cooperative programs involving indigenous populations alongside government initiatives.