Now Reading: Millipedes Could Hold the Key to Pain Relief, Study Finds
-
01
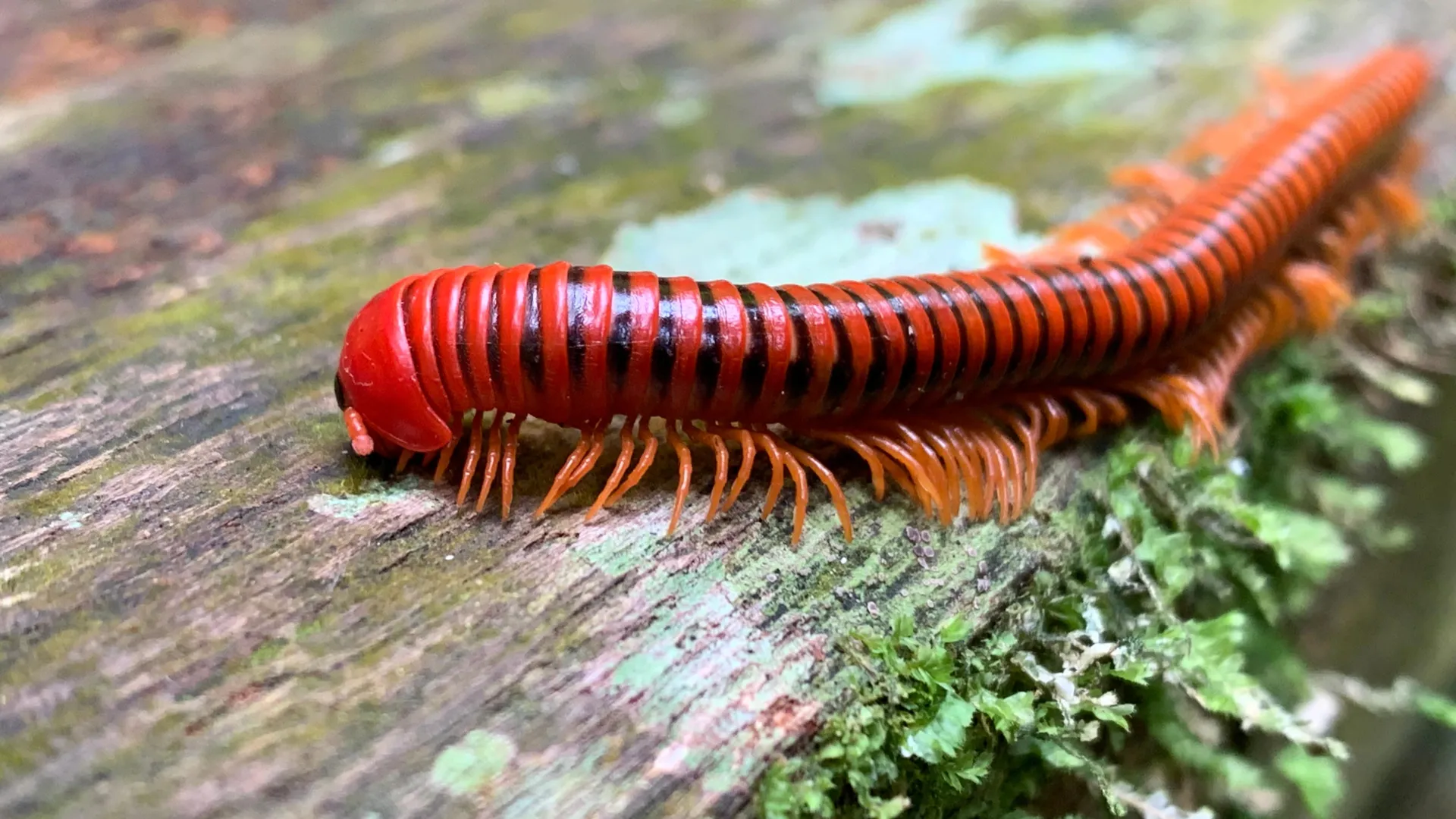
Millipedes Could Hold the Key to Pain Relief, Study Finds
Millipedes Could Hold the Key to Pain Relief, Study Finds

Rapid Summary
- Millipedes secrete compounds called alkaloids,discovered to modulate neuroreceptors in ant brains,perhaps aiding neurological drug advancement.
- Chemist Emily Mevers and her team identified these compounds, named “andrognathanols” and “andrognathines,” from millipedes found at Virginia Tech’s Blacksburg campus.
- Previous studies demonstrated related millipede alkaloids interact with Sigma-1 neuroreceptors linked to pain and neurological treatments.
- The newly discovered substances disorient ants (a natural predator) when millipedes release secretions after physical disturbance.
- These findings aim at synthesizing larger quantities of complex molecules for probing broader biomedical applications.
Indian Opinion analysis
The finding underscores the potential of lesser-explored organisms like millipedes in contributing to medical advancements-especially in pain management and treating neurological disorders. For India, with its wealth of biodiversity spanning unique ecological niches, this research emphasizes the importance of conserving native species while investing in biochemistry exploration for therapeutic innovation. Additionally, such studies could strengthen India’s position as a knowledge hub for indigenous drug discovery utilizing untapped natural resources responsibly.