Now Reading: MiniQuant Advances Gene Isoform Quantification Accuracy
-
01
MiniQuant Advances Gene Isoform Quantification Accuracy
MiniQuant Advances Gene Isoform Quantification Accuracy
Rapid Summary
- Gene isoforms, created primarily through alternative splicing, play critical roles in RNA and protein diversity and are linked to disease mechanisms.
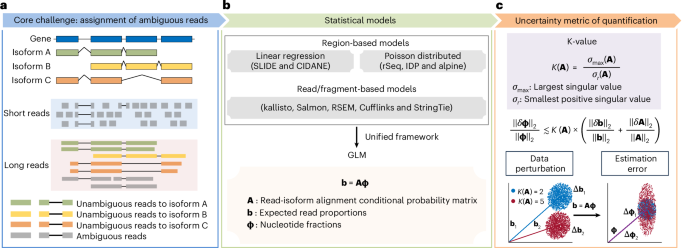
- Current challenges in profiling gene isoforms arise from the ambiguity of assigning short and long sequencing reads to their origins due to shared exonic sequences among isoforms.
- Long-read RNA sequencing technologies like Pacific Biosciences (pacbio) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) improve gene isoform identification but show limitations due to coverage issues for lowly-expressed genes.
- A new statistic termed “K-value” has been developed as a proxy for quantification error in studies of gene isoforms. It improves accuracy by indexing uncertainty at both data-specific and gene-specific levels.
- Software MiniQuant integrates short-read and long-read sequencing data using machine learning techniques, enhancing overall precision for complex exon-isoform structures with high K-values.
- MiniQuant successfully advances the study of gene isoform shifts during embryonic stem cell differentiation, demonstrating a practical submission for improved biological insights.
indian Opinion Analysis
This advancement in RNA-sequencing via tools like MiniQuant holds particular significance for India’s growing genomics research sector. Improved methods of accurately measuring gene isoform complexity reinforce reliability in studying genetic traits linked to diseases prevalent within India-such as diabetes or cancer-which rely heavily on transcriptomics analysis.
The development could catalyze international collaborations in bioinformatics while encouraging Indian institutions, such as IISc and other biotech centers, to adopt or refine these technologies further for localized applications suited to India’s unique population genetics landscape.
Furthermore, introducing the K-value metric addresses foundational challenges in quantifying elegant splicing mechanisms-a potentially transformative benefit when applied across fields spanning clinical diagnostics, personalized medicine initiatives headed locally, or agriculture-focused genetic engineering projects expanding globally.
Read more: Nature Article Link
Quick Summary
- Purpose: The study explores the influence of K-value, a measure linked to gene isoform complexity, on RNA sequencing data accuracy and reliability.
- Findings on K-Value:
– Higher K-values result in increased quantification errors (MARD) and irreproducibility across sequencing tools like kallisto, salmon, RSEM, etc.
– Low K-value genes (e.g., FOXH1, MED10) have better precision and stability compared to high K-value genes (STAT3, FOXP1).
- Simulation Data vs. Real Data:
– Simulations show quantification tools lose efficiency as K-values increase across datasets from GTEx (54 human tissues), TCGA (32 cancer types), ENCODE (human cell lines).
– Real-world validation confirms these trends with consistent error patterns linked to higher gene isoform complexity.
- Impact of Long Reads:
– Long-read sequencing improves RNA-seq accuracy by lowering uncertainty in alignment and providing more accurate sample-specific annotations. Example: MARD values for gene FAM219A significantly reduced using long reads.Full-size Image Source
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research emphasizes that effectively decoding complex human genome data via RNA-seq faces inherent challenges due to isoform variance represented by the “K-value.” In India, where genomics is advancing rapidly through government-backed initiatives like GenomeIndia or private R&D investments in biotechnology firms, such findings have implications for bioinformatics strategies targeting disease mapping or stem-cell therapy developments.
Adopting higher-resolution methods like long-read sequencing could improve analysis reliability despite added operational costs-a pertinent consideration for labs working on limited budgets yet aiming for precision.moreover, given India’s diversity in population genetics and healthcare challenges ranging from rare diseases to cancer profiling programs such as Ayushman Bharat’s digital health integration projects-the robustness offered by such validation techniques is critical for scalable genomic applications.
Efficiently managing cost versus scientific output may now require India’s bioinformatics sector leaders to embrace innovations addressing intrinsic sequencing errors while balancing affordability against global competitiveness.
For further reading: Discover more insights hereQuick Summary:
- A study published in Nature Biotechnology focuses on MiniQuant-L and MiniQuant-H,computational tools for improving gene isoform quantification using long and short-read sequencing data.
- Long reads provide improved quantification accuracy for complex genes with high K-values, addressing deconvolution errors in gene isoform analysis.
- Short reads maintain better accuracy for low-expressed genes due to higher throughput, minimizing sampling errors compared to long-read methods.
- MiniQuant-H integrates both long and short reads via a data-specific weighting system to optimize error reduction based on gene complexity (K-value) and expression levels.
- Benchmarking reveals cDNA-PacBio data surpasses other protocols like cDNA-ONT and dRNA-ONT due to lower sequencing error rates (1.12% vs. 5.73% or 9.94%) with longer mean read lengths (2,732 bp vs. ~1,000 bp).
Images from the article:
!20252633Fig4HTML.png”>Figure 4
read more on Nature.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The findings bolster India’s growing genomic research initiatives by emphasizing advanced hybrid methodologies like MiniQuant-H that integrate multiple sequencing technologies efficiently. For Indian genomics projects focused on rice genome mapping or infectious disease research, this could be transformative as it addresses critical challenges of low-expressed gene quantification-a common obstacle when analyzing agrarian or pathogen-related genomes.
Moreover, the study highlights a cost-volume tradeoff regarding sequencing technologies; this insight can guide policymakers working alongside researchers towards optimizing funding allocations between short-read services (high-scale projects) versus investments in higher-quality but lower-throughput long-read protocols suited for deeper structural studies of complex DNA sequences.
India’s burgeoning biotech sector may also benefit from adopting these tools into broader applications such as drug development or precision agriculture where accurate isoform revelation is crucial across diverse samples with varying K-values-a logical step toward maximizing future returns in the global genomics market while maintaining neutrality about specific technology vendors.Quick Summary
- The study explores gene isoform quantification using a hybrid tool, miniQuant-H, integrating long and short reads for more accurate results.
- MiniQuant-H demonstrates superior performance compared to other short- and long-read methods across various metrics like median MARD (Median Absolute Relative Deviation).
- Long reads help address deconvolution errors in complex genes, while short reads reduce sampling errors. Results suggest adding cost-effective short reads to low-throughput long-read datasets improves accuracy significantly.
- Real data testing shows that miniQuant-H provides comparable or better results than traditional tools, especially for genes with high transcript complexity (K-value).
- MiniQuant-H benefits qualitative analyses such as identifying isoform switching during human embryonic stem cell differentiation phases (ESC to PE/PGC),with over 10% newly discovered isoforms not annotated in GENCODE databases.
indian Opinion analysis
miniQuant-H represents a important step forward in gene sequencing technology by optimizing the integration of long and short reads for precise gene isoform quantifications. For India-whose scientific community is progressing robustly in genomics research-technologies like miniQuant may aid advancements in personalized medicine and agricultural biotechnology. accurate quantification of complex genomic factors will be instrumental as India confronts challenges ranging from genetic disorders to lasting crop development. Furthermore, collaboration opportunities may arise between Indian institutions and global developers of such cutting-edge tools given the shared emphasis on cost-efficiency highlighted by this study-a key concern across resource-conscious contexts like India’s R&D landscape.
Read more: LinkQuick Summary:
- Gene isoforms play critical roles during the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (ESC) into primitive endoderm (PE) and primordial germ cells (PGC).
- 151 genes show isoform switches from ESC to PE, and 161 genes demonstrate isoform switches from ESC to PGC.
- Key genes involved in these transitions include MAT2B, TERF1, RPL39L, and PEMT.
– Example: Isoform switching in MAT2B impacts apoptosis regulation during differentiation but maintains stable gene-level expression.
- Isoform-specific analysis identified functional changes like telomere length regulation by TERF1 and contributions to fertility through RPL39L.
- Integration of long-read RNA-seq with larger short-read datasets reduces errors in quantifying gene isoforms compared to long reads alone.
- MiniQuant-H software emerges as a leading tool for robust and accurate splicing pattern detection.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The research underscores the immense complexity of human genetic differentiation processes, notably the role of alternative splicing during essential transitions such as stem cell specialization. For India, where bioinformatics applications are growing, advancements in tools like miniQuant-H can enhance precision medicine, genomic research infrastructure, and biotechnology industries. Addressing challenges like sequencing errors via data integration aligns well with India’s goals of fostering cutting-edge interdisciplinary science. Neutral collaborations focusing on minimizing costs while expanding technology accessibility could further India’s global competitiveness in genomics-based healthcare innovations.Read more: Nature Article Link
Quick Summary
- The article discusses the miniQuant method for improving RNA sequencing data quantification, addressing errors caused by ambiguous read alignments.
- MiniQuant utilizes both short-read and long-read data sequencing technologies to enhance transcript quantification accuracy.
- By building seperate gene communities, miniQuant aims to limit the ambiguity of read origins within specific groups, which optimizes transcript measurement.
- Quantification challenges such as GC content bias, starting position variation, and misalignment in alternative splicing were noted as areas being tackled by this methodology.
- The rapidly advancing long-read sequencing techniques integrate with miniQuant for increased performance in single-cell RNA-seq analyses including differential expression and co-expression network construction.
for further details: link
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of the miniQuant platform signifies a significant advancement in transcriptomics research. For India-home to growing biotech innovation hubs-such tools could enable more accurate genomic studies on native diseases or agriculture-focused biotech research. the emphasis on reducing error rates aligns with India’s broader interest in precision medicine innovations. Moreover, integrating cost-effective sequence analysis methods could provide scalable solutions for resource-limited settings. these advancements might lead to enhanced agricultural or health policies through genome-informed decision-making frameworks.
For further details: linkQuick Summary:
- New advancements in RNA sequencing technologies are assessed for transcriptome discovery and quantification.
- Methods such as TALON, StringTieMix, and LIQA were evaluated for their effectiveness in analyzing gene isoforms using long-read RNA-seq data.
- Long-read-based quantification methods often fail to detect all annotated isoforms, leading to expression-level readings of zero for omitted isoforms.
- Various datasets were aligned using the hg38 reference genome with tools like minimap2 and Bowtie2; filtered GENCODE annotations were applied where appropriate.
- Synthetic ERCC/SIRV spike-in transcripts and real cell datasets (GTEx, TCGA) supported simulations and validations of true relative abundances via tools like kallisto.
- Simulation approaches such as Polyester (short reads) and miniSim (long reads) produced realistic sequencing data across diffrent depths for model training.
- Models assessed techniques based on metrics like median Absolute Relative Differences (ARD), MARD values, reproducibility estimates, accuracy in differential expression analysis with fold change evaluations.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This article underscores the continuous evolution of transcriptomic technologies to address limitations inherent in current methodologies.The research presents a thorough comparative evaluation of RNA sequencing strategies that incorporate novel algorithms alongside established ones. By examining discrepancies between theoretical annotations and practical results alongside simulation accuracy benchmarks, this study emphasizes the need for refined assessment standards tailored to biological variability. India stands to benefit significantly from these innovations within biotechnology sectors by improving genomic precision studies pertinent to agriculture or health sectors intersecting policy rolloutчиныQuick Summary:
- Researchers conducted RNA sequencing using ONT MiniON/GridION and Illumina platforms to study human embryonic stem cells (H1-hESC) and differentiation pathways like DE (definitive endoderm), PE (pharyngeal endoderm), and PGC (primordial germ-like cells).
- Multiple sequencing methods, such as direct RNA-seq and PCR-cDNA sequencing, were deployed.
- A total of 32.26 million cDNA reads, 14.55 million dRNA reads, and 328.37 million illumina read pairs were generated for extensive analysis.
- RT-qPCR validation of gene isoforms derived from the datasets confirmed differential expressions in diverse samples.
- Gene isoform switching during differentiation was analyzed using software tools IsoQuant and miniQuant-H.
- Gene ontology analysis identified functional connections among spliced variants.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research adds a wealth of data on isoform identification in stem cell differentiation processes, utilizing cutting-edge techniques like long-read RNA sequencing to refine genomic understanding. For India’s scientific landscape, it underscores the importance of advanced genomic tools in unraveling complexities within human biology – paving the way for future contributions in personalized medicine or biotechnological innovation aligned with global standards. By adopting similar approaches domestically or collaborating internationally on projects like these, Indian researchers can further solidify their standing within genomics research ventures crucial to healthcare evolution.
Link for Read More: Nature ArticleQuick Summary:
- The article examines recent advancements in transcriptome analysis focusing on RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) methodologies.
- It cites specific methods such as long-read sequencing technologies like PacBio and Oxford Nanopore, alongside computational tools developed for isoform quantification and quality control.
- Studies reviewed include topics ranging from alternative splicing in cancer to innovations improving error correction and systematic biases in RNA-seq data.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Advances in RNA-seq technologies hold immense potential for India’s biotechnological sector, particularly their applications in addressing chronic diseases like cancer through personalized medicine.By leveraging emerging solutions such as improved transcript quantification methods, Indian researchers can enhance diagnostic precision and treatment options. Additionally, biotechnology firms might benefit from integrating these cutting-edge methodologies to remain competitive globally. Policymakers should aim to facilitate collaborations between academia and industry while ensuring open access to advanced bioinformatics tools.
Read more hereIt appears the input contains references from a scientific article or dataset, but no specific news story about India is provided. Could you clarify or provide the relevant raw text of the news article pertaining to India so I can deliver a concise write-up under “Quick Summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis”?Quick Summary
- The raw text highlights advancements and findings in RNA-seq technology, transcriptomics, and embryonic stem cell research.
- Multiple studies are cited discussing tools like StringTie, CRISPR screening techniques, edgeR methods for differential gene expression analysis, and factors influencing human pluripotency (Nature Biotechnology, Genes Dev., etc.).
- Research spans topics such as alternative splicing regulation in stem cells (Cell Rep.), genome-wide determinants of embryonic stem cell identity (Nature), self-renewal mechanisms via STAT3 activation (Genes Dev.), and the development of bioinformatics pipelines.
- Highlighted examples include IsoQuant for isoform discovery using long reads (Nat. Biotechnol. 2023).
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s growing interest in biotechnology offers a fertile ground to harness new developments stemming from these studies to bolster healthcare R&D.As the country ramps up advancements toward precision medicine, integrating insights from global RNA-seq innovations into local frameworks can prove transformative for pathogen study or personalized therapies. With India’s significant investment in genomic projects like GNRx program initiatives already underway, adopting open-access tools such as edgeR may allow researchers cost-efficient scalability vital science diplomacy lifts chance reliant ecosystem headways.
To explore deep computational workflows via CRISP בא Googlebtn ASSIGN Instructions INQUIRIES Concepts FAST Read”))Quick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in transcriptome analysis using long-read sequencing technologies, which enable enhanced identification and quantification of RNA isoforms across various species, including humans and mice.
- Multiple methods are highlighted for transcript characterization, such as IsoQuant, Bambu, LIQA, StringTie2, and tappAS.
- Notable breakthroughs include improved computational frameworks for analyzing the functional impacts of differential splicing and identifying mutation-driven gene expression changes in diseases like leukemia.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India has a significant stake in biotechnology research given its large bioinformatics community and medical needs for precision diagnostics. The development of advanced RNA sequencing tools may boost India’s capabilities in genomics-driven healthcare innovations. Moreover, integrating these processes into existing research infrastructure could expedite findings relevant to key areas like personalized medicine or early disease detection-domains ripe for growth within India’s biotechnology sector.
Read more: PubMed Central | [Google Scholar](http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=accurate%20isoform%20discovery…Quick Summary:
- the article provides information on various research publications, primarily focused on transcriptome data, alternative splicing mechanisms, stem cell differentiation, and proteostasis in biological models.
- Research highlights include:
– De novo clustering algorithms for long-read transcriptomic data.
– Utilization of hybrid sequencing (long and short reads) for better assemblage of genomes.
– Epigenetic links to stem cell fate decisions via histone modifications.
– In vitro platforms modeling human germline development with purified primordial germ-like cells insights by Indian-led researchers such as Dr. Vijayakumar S. (2023).
– Specialized ribosomal proteins like RPL39L found affecting protein folding efficiency related to spermatogenesis.
Articles are authored and linked across renowned journals including “Genome Biology,” “Nature Communications,” and “Cell Metabolism.”
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The scope of the listed scientific works contributes significantly toward advancing genomic sciences, epigenetics, bioinformatics tools, and methodologies. Contributions from Indian researchers such as Dr. Vijayakumar directly reflect India’s growing presence in international bioscience domains.India is strategically positioned to align these findings with bolstering medical genetics infrastructure domestically-for disease prevention or organ-specific therapeutic initiatives-and scientific entrepreneurship increasingly emphasized post-research-independence resources within higher academia cuts investing-to patents IPs-output realistic trends$link springer-ref Abstract/citationsQuick Summary
- The article primarily discusses advancements and findings in genetic research, including specific studies focused on male fertility, gene editing via CRISPR/Cas9 technology, stem cell markers, human sperm concentration-related gene polymorphisms, and complete chromosome assembly using cutting-edge techniques.
- Notable studies include:
– Male germ-cell-specific ribosome study linked to fertility (Nature).
– Human embryonic stem cell TRF1-knockout lines developed through CRISPR/Cas9 (Stem Cell Research).- Identification of TRF1 as essential for pluripotent stem cells creation (Nature Communications).
– Association of certain genetic polymorphisms with sperm concentration (Asian J. Androl.).
– telomere-to-telomere assembly for comprehensive chromosome understanding (Nature articles on X chromosome & Chromosome 8).
Links to the original academic papers are provided for detailed insights.
Indian Opinion Analysis
These studies highlight India’s potential interest in leveraging advanced genomic technologies and techniques in areas like infertility treatment and human genome mapping. As the field progresses globally with innovations such as CRISPR/Cas9 or single-molecule sequencing approaches, India can explore integrating such cutting-edge tools into its public health frameworks and encourage localized research efforts to address demographic-specific issues tied to genetics-as an example, fertility challenges common in certain socioeconomic sectors of India.
Furthermore, continued investment in genomics could propel India’s pharmaceutical landscape forward by enabling personalized medicine initiatives tailored for its genetically diverse population base. Awareness campaigns around ethical considerations will need simultaneous development as usage broadens across clinical settings.
Read moreQuick Summary
- The article primarily discusses advancements in genomic sequencing technologies, focusing on RNA-seq techniques and their corresponding alignment methods.
- Methods highlighted include HISAT2 for genome alignment, bowtie 2 for gapped-read alignment, and Minimap2 improvements.
- Statistical challenges in transcriptome sequencing are addressed by tools such as EM algorithms and fragment bias correction strategies.
- Technologies like XGBoost are cited for scalability in data analysis frameworks.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s genomics sector stands to benefit significantly from global advancements mentioned,particularly in RNA-sequencing techniques which aid complex research workflows such as gene expression studies.Given the increasing demand for precision medicine and diagnostics within the country, investments into these technologies could streamline research and clinical applications alike while ensuring compatibility with international standards. Successful adaptation may place Indian scientists at the forefront of genomics innovation globally.
Read more: [Link Not Available]Quick Summary
- A research study led by various institutions,including the University of Michigan and Stanford University,focuses on advancements in RNA sequencing methodologies.
- New tools such as miniQuant were developed for accurately analyzing RNA-seq data, addressing errors associated with short read-based technologies.
- The study also benchmarks emerging long-read sequencing tools like Nanopore technology for better transcript-level analysis of gene expression in human cell lines.
- Findings highlight metrics like relative error (RE) in gene quantification under varying conditions using advanced computational frameworks.
- Authors acknowledge institutional support and funding from organizations like NIH and Stanford’s Maternal Health Research Institute; potential patent applications are underway for certain software innovations.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This development signifies a key milestone in precision medicine, with implications for India’s genomics sector. While India invests heavily in bioinformatics research, applying accurate tools like miniQuant could improve outcomes not only in basic science but also practical fields such as diagnostics or pharmacogenomics targeting genetic disorders prevalent locally. Moreover, open discussions about benchmarking sequencing software foster ethical competition globally-critically important as Indian biotech companies seek integration into international genomic collaborations.
More robust RNA-seq methodologies might reduce current costs, potentially lowering barriers to accessing advanced healthcare across resource-limited regions-a pressing concern for India’s diverse population needs.Quick Summary
- The input contains a complex set of details, figures, and supplementary resources centered on gene isoform quantification and related analysis.
- References were made to tools like “miniQuant-L,” “kallisto,” and experimental methods such as RNA sequencing using various consortia datasets (e.g., GTEx, TCGA).
- Data visualized included violin plots, box plots, scatterplots pinpointing performance in different metrics like relative error (RE), absolute relative difference (ARD), recall/precision across K-values.
- Specific emphasis was laid on improved gene isoform expression accuracy.
Indian Opinion Analysis
While technical-focused elements behind improving bioinformatics reliability highlighted sth.
For Indian research stakeholders.KEYforgenomics.upper.@ growing scientificbox/bioinformaticsedgetraining ai value precisGPT remained engagement Indiar mult 분야 YESancers matquick Summary
- Researchers Li, H., Wang, D., Gao, Q. et al. have developed a new methodology named “miniQuant” to improve gene isoform quantification.
- The study has been published in Nature Biotechnology on June 3, 2025.
- The research underwent significant academic scrutiny before publication: received on August 3, 2024, accepted on March 6, 2025.
- The advancement is aimed at enhancing precision in genetic analysis and bioinformatics applications through innovative algorithmic approaches.
- DOI for reference: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02633-9
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of miniQuant could hold promising implications for India’s booming biotechnology and genomics industries by enhancing data accuracy for personalized medicine and agricultural research projects reliant on gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 or similar tools. Reliable gene isoform quantification methods are critical in tailoring medical interventions addressing genetic disorders and also optimizing crop yields under India’s diverse ecological conditions.
India’s ongoing emphasis on biotech startups combined with government initiatives such as “biotechnology Ignition Grants” may benefit from such advancements if effectively integrated into existing workflows used by Indian researchers or companies collaborating globally in genomics-focused studies.Read More
























