Now Reading: NASA Begins Testing StarBurst to Decode Cosmic Explosions
-
01
NASA Begins Testing StarBurst to Decode Cosmic Explosions
NASA Begins Testing StarBurst to Decode Cosmic Explosions

Fast Summary
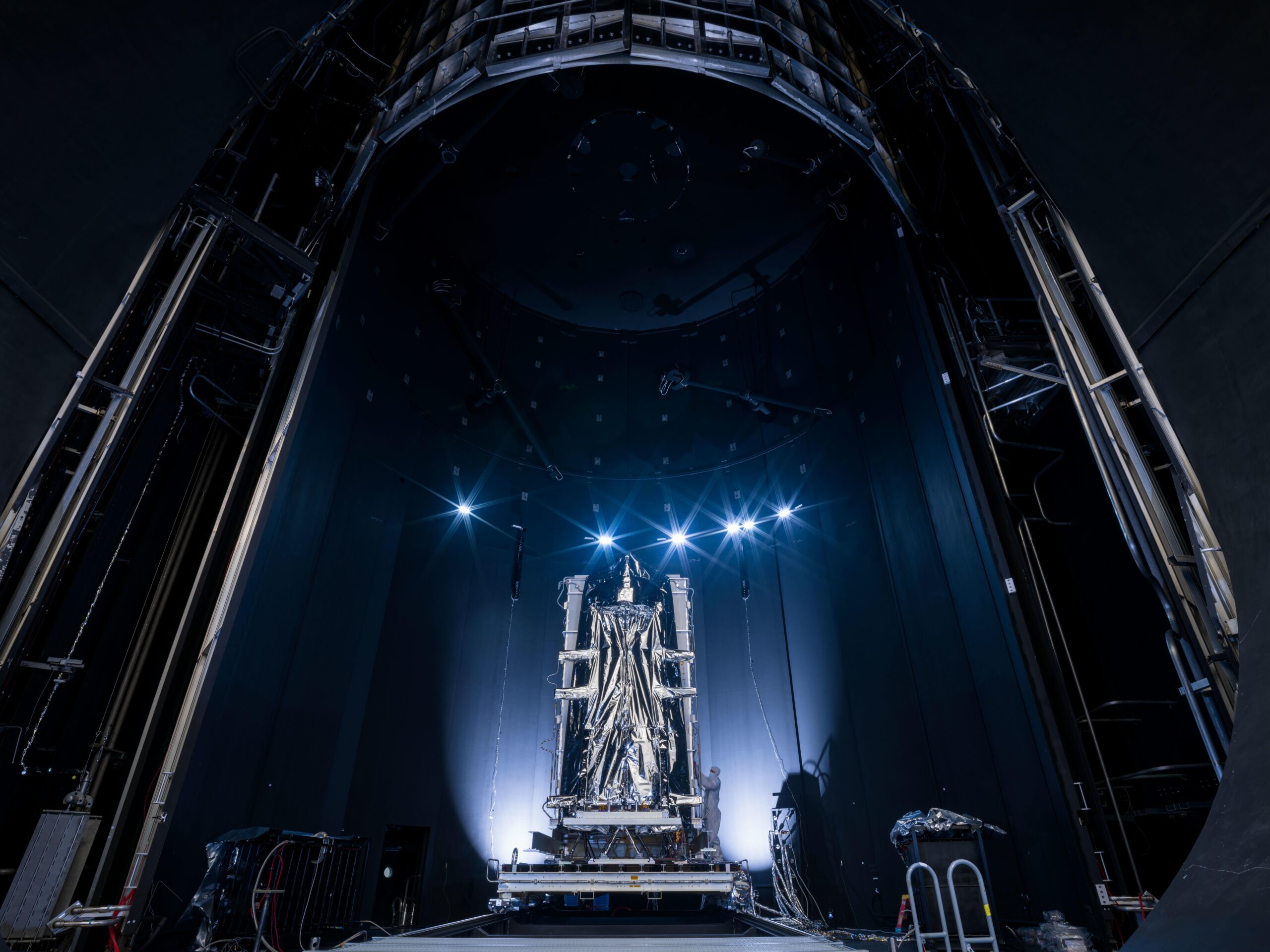
- StarBurst,a gamma-ray observatory,has arrived at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville,Alabama for environmental testing and final instrument integration.
- The observatory is designed to detect short gamma-ray bursts from neutron star mergers, which provide insights into black hole formation, gravitational waves, and extreme physics.
- Gamma-ray bursts from neutron star mergers enable scientists to study both electromagnetic signals (light) and ripples in space-time (gravitational waves).
- Neutron star mergers forge heavy elements like gold and platinum and help scientists understand the origins of Earth’s building blocks.
- The instrument will undergo rigorous flight vibration testing at the Sunspot Thermal Vacuum Testing Facility to ensure resilience in space conditions.
- Final optical system adjustments will be made at the Stray light Facility to reduce interference from unwanted light sources.
- StarBurst involves collaboration among NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; U.S. Naval Research Laboratory; University of Alabama Huntsville; Universities Space Research Association; and UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory.
- It belongs to NASA’s Astrophysics Pioneers program aimed at developing lower-cost missions for breakthrough astrophysical science.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of StarBurst marks a significant advancement in astrophysical research through cost-efficient means under NASA’s Astrophysics pioneers program. By detecting short gamma-ray bursts linked with neutron star mergers, it can deepen our understanding of cosmic phenomena such as black hole formation and element creation-a topic relevant globally as nations collaborate on large-scale astrophysics missions.
For India, such developments underscore potential opportunities for scientific partnerships with international space research organizations like NASA while serving as benchmarks for enhancing its own capabilities under initiatives by ISRO. Specifically given India’s interest in advancing its space telescopes (like AstroSat), deeper collaboration may open new vistas for joint scientific exploration into cosmic events crucial not just scientifically but also technologically.read More